This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “Density of electronic states, resistivity and superconducting transition temperature in density-wave compounds with imperfect nesting”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
—
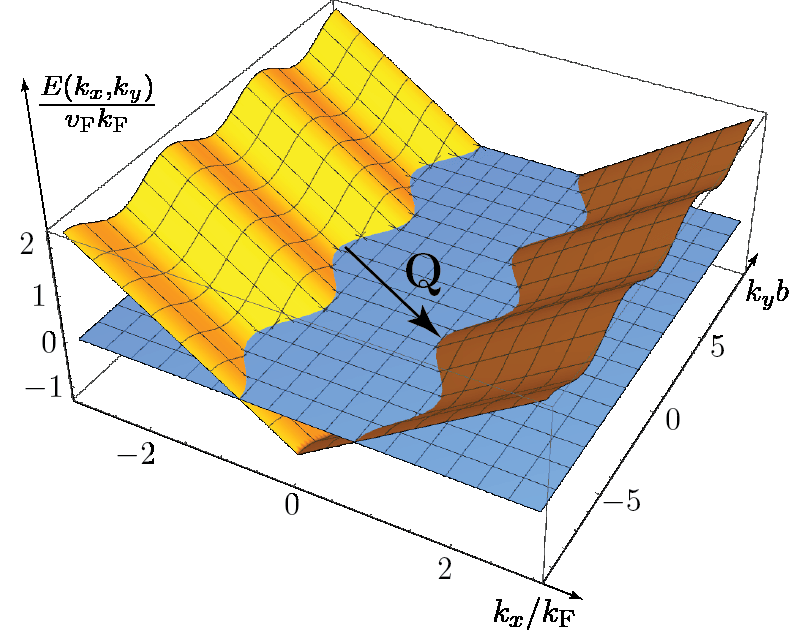
This paper explores the effects of imperfect nesting in density wave (DW) state electronic properties within a simple 2D tight-binding model. It focuses on materials where DW emerges and shows that imperfect nesting leads to unusual singularities in quasiparticle density of states, affecting superconducting transition temperature Tc. Results derived at arbitrary antinesting may help understand phase diagrams for various density wave compounds.
—
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
- Density-wave state with imperfect nesting [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Refers to materials where electronic properties exhibit spatial modulation due to imperfect FS nesting, leading to reduced electron DoS at the Fermi level and impacted SC transition temperature Tc in weak-coupling regime. - Electron dispersion [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Describes electron movement across wave vector Q in materials with imperfect nesting. It is crucial for understanding electronic properties affected by DW background, even without superconductivity. - Antinesting amplitude t′y [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Violates perfect nesting condition (4) and competes with energy one-dimensionality, although its electronic transport may be hidden in materials like rare-earth tritellurides or tetratellurides. It impacts Fermi surface instability and DW formation.
View Original Excerpt (English)
Density of electronic states, resistivity and superconducting transition temperature in density-wave compounds with imperfect nesting A. V. Tsvetkova,1 Ya. I. Rodionov,2, 3 and P. D. Grigoriev4, 1 1National University of Science and Technology MISIS, Moscow, 119049 Russia 2Institute for Theoretical and Applied Electrodynamics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, 125412 Russia 3National Research University Higher School of Economics, Moscow 101000, Russia 4L.D. Landau Institute of Theoretical Physics, RAS, Chernogolovka, 143423, Russia (Dated: January 23, 2025) We study the effects of imperfect nesting in the density wave (DW) state on various electronic properties within a simple 2D tight-binding model. The discussed model reflects the main features of quasi-1D metals where the DW emerges. We show that a DW with imperfect nesting leads to2025 unusual singularities in the quasiparticle density of states and to a power-law renormalization of the superconducting critical temperature. Our results are derived at arbitrary large antinesting and may help to understand the phase diagram of the wide class of density-wave superconductors. WeJan also compute the conductivity tensor in a wide temperature range, including the DW transition, 22 andmanyobtainother aDWsatisfactorymaterials.agreement with the experimental data on rare-earth trichalcogenides and PACS numbers: 72.10.-d, 72.15.Gd, 71.55.Ak, 72.80.-r I. INTRODUCTION ∆0 for some k at the FS. In this case the metallic conductivity survives in a DW state till T →0, be- ing anisotropically reduced, e.g., as in various rare-earth The interplay between superconductivity (SC) and three-chalcogenides [60] and many other materials [32– charge or spin density wave (DW) attracts a vast re- 34, 36]. One could expect an exponential decrease of the search activity. The SC-DW competition and coex- superconducting transition temperature Tc in the pres- istence appears in various strongly-correlated electron ence of the DW background even in the imperfect-nesting systems, including the high-temperature cuprate [1–9] case, because according to the BCS…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
—
이 논문은 단순한 2D 타이트 바인딩 모델 내에서 밀도 웨이브 (DW) 상태 전자 특성에서 불완전한 둥지의 영향을 탐구합니다. 그것은 DW가 나오는 재료에 초점을 맞추고 불완전한 둥지가 정지 입자 밀도의 비정상적인 특이성으로 이어져 초전도 전이 온도 TC에 영향을 미친다는 것을 보여줍니다. 임의의 반 인류에서 파생 된 결과는 다양한 밀도 웨이브 화합물에 대한 위상 다이어그램을 이해하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
—
주요 기술 용어 (한글 설명)
- Density-wave state with imperfect nesting
설명 (Korean): 전자 특성이 불완전한 FS 중첩으로 인한 공간적 조절을 나타내는 재료를 말해, 페르미 수준에서 전자 DOS가 감소하고 약한 커플 링 체제에서 SC 전이 온도 TC에 영향을 미쳤다.
(Original English: Refers to materials where electronic properties exhibit spatial modulation due to imperfect FS nesting, leading to reduced electron DoS at the Fermi level and impacted SC transition temperature Tc in weak-coupling regime.) - Electron dispersion
설명 (Korean): 불완전한 둥지가있는 재료에서 파동 벡터 Q를 통한 전자 이동을 설명합니다. 초전도성 없이도 DW 배경의 영향을받는 전자 특성을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다.
(Original English: Describes electron movement across wave vector Q in materials with imperfect nesting. It is crucial for understanding electronic properties affected by DW background, even without superconductivity.) - Antinesting amplitude t′y
설명 (Korean): 전자 수송은 희귀 지구 삼중주 또는 테트라 텔루 라이드와 같은 재료에 숨겨 질 수 있지만 에너지 1 차원과의 완벽한 중첩 조건 (4)을 위반하고 에너지 1 차원과 경쟁합니다. 그것은 페르미 표면 불안정성과 DW 형성에 영향을 미칩니다.
(Original English: Violates perfect nesting condition (4) and competes with energy one-dimensionality, although its electronic transport may be hidden in materials like rare-earth tritellurides or tetratellurides. It impacts Fermi surface instability and DW formation.)
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
전자 상태의 밀도, 불완전한 중첩을 갖는 밀도 파 화합물의 전자 상태, 저항 및 초전도 전이 온도 A. V. Tsvetkova, 1 YA. I. Rodionov, 2, 3 및 P. D. Grigoriev4, 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11100 러시아, 러시아 응용 전기 역학, 러시아 과학 아카데미, 모스크바, 125412 러시아 3National Research University, 경제학 학교, 모스크바 101000, 러시아 4L.D. Landau Institute of Theoretical Physics, Ras, Chernogolovka, 143423, 러시아 (2025 년 1 월 23 일) 우리는 단순한 2D 타이트 바인딩 모델 내의 다양한 전자 특성에 대한 밀도 웨이브 (DW) 상태에서 불완전한 둥지의 영향을 연구합니다. 논의 된 모델은 DW가 나타나는 준 금속의 주요 특징을 반영합니다. 우리는 불완전한 둥지가있는 DW가 2025의 쿼션 입자 밀도에서 비정상적인 특이 단수와 초전도 임계 온도의 전력 법적 재조정으로 이어진다는 것을 보여준다. 우리의 결과는 임의의 큰 대립 방지에서 파생되며 넓은 종류의 밀도 파 초전도체의 위상 다이어그램을 이해하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. Wejan은 또한 DW 전이, 22 andmanyobtainother adwsatisfactory-materials를 포함하여 넓은 온도 범위에서 전도도 텐서를 계산합니다. 희귀 원유 트리칼 코게 나이드 및 PACS 수에 대한 실험 데이터에 대한 조상 : 72.15.gd, 71.55.ak, 72.80.-r I. 이 경우 금속 전도도는 T → 0까지 DW 상태에서 생존하여 이방성 적으로 감소 될 때, 예를 들어, 다양한 희박한 지구에서와 같이, 초전도성 (SC)과 360]과 다른 많은 재료 [32- 전하 또는 스핀 밀도 웨이브 (DW) 사이의 상호 작용은 광대 한 34, 36]을 끌어냅니다. 검색 활동의 지수 감소를 기대할 수 있습니다. PRESTENCE의 SC-DW 경쟁 및 공동 초전도 전이 온도 TC는 BCS에 따르면, 고온 조항 [1-9] 케이스를 포함하여 불완전한 네 베스트 시스템에서도 DW 배경의 다양한 상관 관계가있는 전자에서 나타납니다.
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기