This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “The Role of the Random Magnetic Fields in the ISM: HVCs Numerical Simulations”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
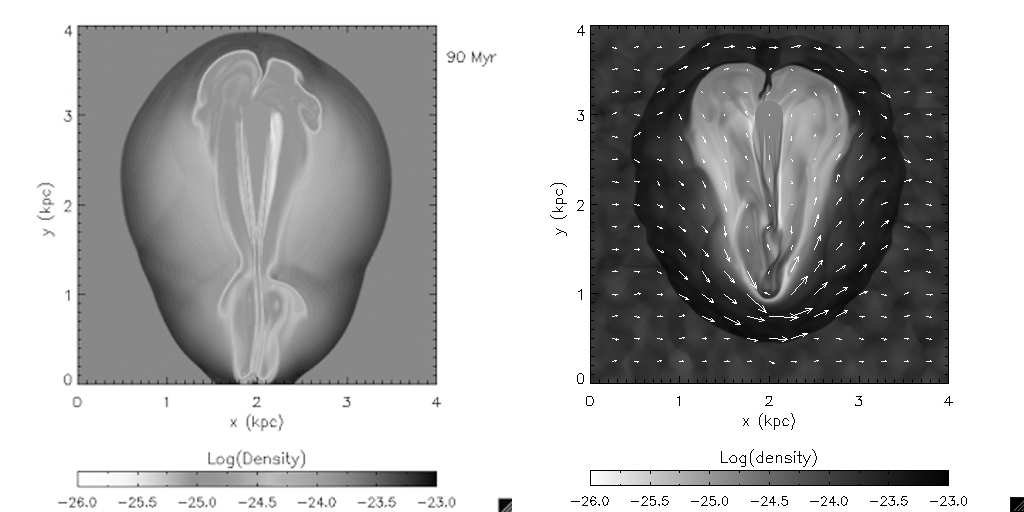
This paper explores numerical simulations associated with the interaction of supersonic flows located in high latitudes, studying the effect of random magnetic fields on magnetized objects. The researchers present simulations without and with magnetic field using ZEUS–3D code (Stone & Norman 1992a,b). Both models display similar characteristics such as galactic shock directed downwards along with reverse shock penetrating into the cloud. However, in the horizontal component of random magnetic fields case, HVC distorts and compresses B-field lines during evolution, increasing both field pressure and tension due to magnetic tension forming a barrier for moving gas. In figure 1, simulations without and with magnetic field show density as logarithmic gray scale plots and magnetic field indicated by arrows at 90 Myr. The numerical calculations were performed using UNAM’s supercomputers.
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
- High Velocity Clouds (HVC) [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Galactic structures moving with high velocities, interacting with interstellar medium. - Random Magnetic Fields [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Variable magnetic fields possessing random components in addition to mean uniform component within galaxies. - ISM–1 and ISM–2 [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Interaction models without and with magnetic field respectively, used for numerical simulations of HVCs interacting with the interstellar medium.
View Original Excerpt (English)
Cosmic Magnetic Fields: From Planets, to Stars and Galaxies Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 259, 2009 c⃝2009 International Astronomical Union K.G. Strassmeier, A.G. Kosovichev & J. Beckmann, eds. DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X The Role of the Random Magnetic Fields in the ISM: HVCs Numerical Simulations A. Santill´an1†, J. Kim2, F.J. S´anchez–Salcedo3 J. Franco3 and L. Hern´andez–Cervantes3 1Direcci´on General de Servicios de C´omputo Acad´emico, UNAM, 04510, Mexico City, Mexico email: alfredo@astrosu.unam.mx 2Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute, 61–1, Hwaam–dong, Yuseong–gu, Daejeon, Republic of Korea 305-348 3Instituto de Astronom´ıa , UNAM, 04510, Mexico City, Mexico Abstract.2008 We know that the galactic magnetic field possesses a random component in addition to the mean uniform component, with comparable strength of the two components. This random com- ponent is considered to play important roles in the evolution of the interstellar medium (ISM).Dec In this work we present numerical simulations associated with the interaction of the supersonic 23 flowsgalacticlocatedISM inat orderhigh latitudeto studyintheoureffectGalaxythat(HighproducesVelocitya randomClouds,magneticHVC) fieldwith inthethemagnetizedevolution of this objects. Keywords. Random Magnetic Fields, High Velocity Clouds, ISM 1. Introduction Numerical simulations of the evolution of HVC collisions with the Milky Way have[astro-ph] been performed for more than two decades by different authors. The details of resulting supersonic flows depend of on the model assumptions, and the intensity and initial con- figuration of the magnetic field. Santill´an et al. (1999) made models that illustrate the effects of magnetic pressure, and differentiate them from those due to magnetic tension. The evolution of the interaction of a HVC with a magnetized interstellar medium, is studied by setting a random magnetic field that satisfies the divergence–free constraint (∇• B =0) at all times. To mimic the average galactic magnetic field, that is oriented parallel to the disk, the horizontal component dominates over the vertical component. 2. Results We perform simulations of HVCs interacting…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
이 논문은 높은 위도에 위치한 초음속 흐름의 상호 작용과 관련된 수치 시뮬레이션을 탐구하여 자화 된 물체에 대한 임의의 자기장의 영향을 연구합니다. 연구원들은 Zeus -3D 코드를 사용하여 자기장없이 또는 자기장을 사용하지 않고 시뮬레이션을 제시합니다 (Stone & Norman 1992a, b). 두 모델 모두 클라우드에 대한 역 충격과 함께 아래쪽으로 향한 은하 충격과 같은 유사한 특성을 나타냅니다. 그러나, 랜덤 자기장의 수평 구성 요소에서, HVC는 진화 동안 B- 필드 라인을 왜곡하고 압축하여 가스 이동에 대한 장벽을 형성하는 자기 장력으로 인해 전계 압력과 장력을 증가시킨다. 도 1에서, 자기장이없는 시뮬레이션은 90 MYR에서 화살표로 표시된 로그 회색 스케일 플롯 및 자기장으로 밀도를 나타낸다. 수치 계산은 Unam의 슈퍼 컴퓨터를 사용하여 수행되었습니다.
주요 기술 용어 (한글 설명)
- High Velocity Clouds (HVC)
설명 (Korean): 고속 매체와 상호 작용하는 고속으로 이동하는 은하 구조.
(Original English: Galactic structures moving with high velocities, interacting with interstellar medium.) - Random Magnetic Fields
설명 (Korean): 가변 자기장은 은하 내에서 평균 균일 성분뿐만 아니라 임의의 성분을 갖는다.
(Original English: Variable magnetic fields possessing random components in addition to mean uniform component within galaxies.) - ISM–1 and ISM–2
설명 (Korean): 자극 매체와 상호 작용하는 HVC의 수치 시뮬레이션에 사용되는 자기장이 없거나있는 상호 작용 모델.
(Original English: Interaction models without and with magnetic field respectively, used for numerical simulations of HVCs interacting with the interstellar medium.)
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
우주 자기 분야 : 행성에서 별과 은하 절차에 이르기까지 IAU 심포지엄 No. 259, 2009 C⃝2009 International Astronomical Union K.G. Strassmeier, A.G. Kosovichev & J. Beckmann, eds. doi : 00.0000/x0000000000000000x ISM에서 랜덤 자기장의 역할 : HVCS 수치 시뮬레이션 A. Santill´an1 †, J. Kim2, F.J. S´anchez – Salcedo3 J. Franco3 및 L. Hernandez – Cervantes3 1Direcci, General Servicios Decicios de alfututo, deal servicios devirecci. UNAM, 04510, 멕시코 시티, 멕시코 이메일 : alfredo@astrosu.unam.mx 2korea 천문학 및 우주 과학 연구소, 61–1, Hwaam-Dong, Yuseong – Gu, Daejeon, 공화국 305-348 3instito de Astronom’ato, Unam, 04510, 멕시코 시티, 멕시코 시티, 멕시코 시티. 필드는 두 성분의 비슷한 강도를 갖는 평균 균일 성분 외에 랜덤 성분을 보유합니다. 이 무작위 조합은 성간 매체 (ISM)의 진화에서 중요한 역할을하는 것으로 간주됩니다 .DEC이 작업에서 우리는 수치식 23 유동 율산화 분류주의의 상호 작용과 관련된 수치 시뮬레이션을 제시합니다. 이 객체의 thethemangiedevolution. 키워드. 임의의 자기장, 고속 구름, ISM 1. 소개 은하수와의 HVC 충돌의 진화에 대한 수치 시뮬레이션은 [Astro-PH]가 20 년 이상 다른 저자들에 의해 수행되었습니다. 결과 초음속 흐름의 세부 사항은 모델 가정과 자기장의 강도 및 초기 구성에 따라 다릅니다. Santill´an et al. (1999)는 자기 압력의 효과를 보여주는 모델을 만들고 자기 장력으로 인한 것과는 다른 모델을 만들었다. HVC와 자화 성간 중간 매체의 상호 작용의 진화는 항상 분기가없는 제약 (∇ • b = 0)을 만족시키는 임의의 자기장을 설정함으로써 연구된다. 디스크와 평행 한 평균 은하 자기장을 모방하기 위해 수평 성분은 수직 성분보다 우세합니다. 2. 결과 HVCS 상호 작용의 시뮬레이션을 수행합니다 …
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기