This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “Electric Field Effect Tuning of Electron-Phonon Coupling in Graphene”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
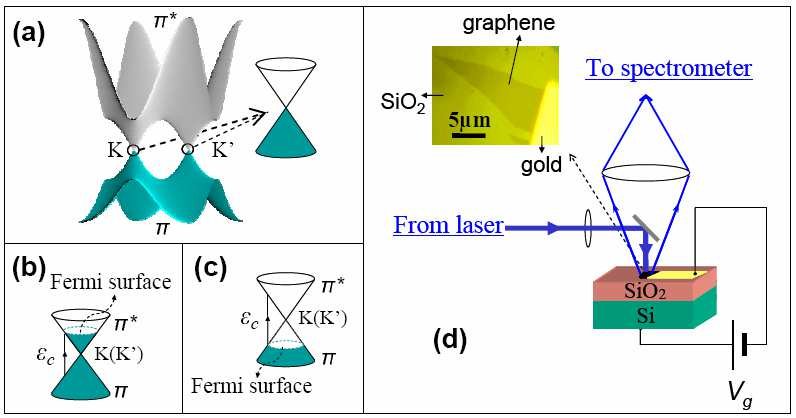
The study focuses on the electric field effect (EFE) tuning of electron-phonon coupling in graphene. Raman spectra reveal that EFE has marked impacts on long wavelength optical phonons, creating large density modulations of carriers with linear dispersion known as Dirac fermions. The changes of phonon frequency and line-width demonstrate particle-hole symmetry about charge neutral Dirac points.
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
- G band [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Optical phonon at long wavelengths markedly sensitive to electron-phonon coupling in graphene due to gate voltage and induced charge density, revealing physics linked to the electronic band structure near Dirac points; - D* band [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Second order Raman scattering prominent feature in graphite and carbon nanotubes associated with phonons that satisfy particle-hole symmetry; - Electron Phonon coupling [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Interaction between electrons and quantized lattice vibrations, responsible for optical phonon frequency dependence on gate voltage changes.
View Original Excerpt (English)
Electric Field Effect Tuning of Electron-Phonon Coupling in Graphene Jun Yan,1 Yuanbo Zhang,1 Philip Kim,1 and Aron Pinczuk1,2 1 Department of Physics, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA 2 Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA (Dated: October 29, 2018) Gate-modulated low-temperature Raman spectra reveal that the electric field effect (EFE), per-2006 vasive in contemporary electronics, has marked impacts on long wavelength optical phonons of graphene. The EFE in this two dimensional honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms creates large density modulations of carriers with linear dispersion (known as Dirac fermions). Our EFE Raman spectraDec display the interactions of lattice vibrations with these unusual carriers. The changes of phonon frequency and line-width demonstrate optically the particle-hole symmetry about the charge-neutral Dirac-point. The linear dependence of the phonon frequency on the EFE-modulated Fermi energy28 is explained as the electron-phonon coupling of mass-less Dirac fermions. The interaction between electrons and quantized lat- EFE in a single atomic layer and the phonon dynamics tice vibrations in a solid is one of the most fundamental that are associated with the two dimensional (2D) Dirac realms of study in condensed matter physics. In par- fermions. ticular, the electron-phonon interaction in graphene and We focus on the doubly degenerate optical phonon of its derivatives plays an important role in understanding E2g symmetry at ∼1580 cm−1, known as the G band. anomalies of photoemission spectra observed in graphite We also report on the smaller impact of the EFE on [1] and graphene [2], the non-linear high energy electron the second-order band at ∼2700 cm−1, known as the D* transport in carbon nanotubes [3, 4, 5, 6, 7], as well band. These two bands are prominent Raman features as phonon structures in graphite [8, 9] and carbon nan- in graphene [17,…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
이 연구는 그래 핀에서 전자-포논 커플 링의 전기장 효과 (EFE) 튜닝에 중점을 둡니다. Raman Spectra는 EFE가 긴 파장 광학 포논에 영향을 미쳤으며 Dirac fermions로 알려진 선형 분산을 갖는 캐리어의 큰 밀도 변조를 생성한다는 것을 보여준다. 포논 주파수 및 라인 폭의 변화는 전하 중성 디락 포인트에 대한 입자 구멍 대칭을 보여줍니다.
주요 기술 용어 (한글 설명)
- G band
설명 (Korean): 긴 파장에서의 광학 포논은 게이트 전압 및 유도 된 전하 밀도로 인해 그래 핀에서 전자-포논 커플 링에 현저히 민감하여 Dirac 지점 근처의 전자 밴드 구조에 연결된 물리학을 나타냅니다.
(Original English: Optical phonon at long wavelengths markedly sensitive to electron-phonon coupling in graphene due to gate voltage and induced charge density, revealing physics linked to the electronic band structure near Dirac points;) - D* band
설명 (Korean): 입자 구멍 대칭을 만족시키는 포논과 관련된 흑연 및 탄소 나노 튜브에서 2 차 라만 산란의 두드러진 특징;
(Original English: Second order Raman scattering prominent feature in graphite and carbon nanotubes associated with phonons that satisfy particle-hole symmetry;) - Electron Phonon coupling
설명 (Korean): 게이트 전압 변화에 대한 광학 포논 주파수 의존성을 담당하는 전자와 양자 격자 진동 사이의 상호 작용.
(Original English: Interaction between electrons and quantized lattice vibrations, responsible for optical phonon frequency dependence on gate voltage changes.)
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
전기장 e-exctron-phonon 커플 링 jun yan, 1 Yuanbo Zhang, 1 Philip Kim, 1 및 Aron Pinczuk1,2 1 컬럼비아 대학교, 뉴욕, 뉴욕, 뉴욕, Appried Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia University, New York, 2018, NY 10027, NY 10027, NY 10027, NY 10027, NY 10027, 미국. 저온 라만 스펙트럼은 현대 전자 장치에서 2006 년 당시 전기장 효과 (EFE)가 그래 핀의 긴 파장 광학 포논에 영향을 미쳤다는 것을 보여준다. 탄소 원자 의이 2 차원 벌집 격자의 EFE는 선형 분산 (Dirac fermions)을 갖는 캐리어의 큰 밀도 변조를 생성합니다. 우리의 EFE Raman Spectradec은 격자 진동과 이러한 특이한 캐리어의 상호 작용을 표시합니다. 포논 주파수와 라인 폭의 변화는 전하 중립 디라크 포인트에 대한 입자 구멍 대칭을 광학적으로 보여줍니다. EFE- 변조 된 Fermi Energy28에서 포논 주파수의 선형 의존성은 질량이없는 Dirac fermions의 전자-포논 커플 링으로 설명된다. 단일 원자 층에서 전자와 양자화 된 Lat-efe와 고체의 Phonon Dynamics tice 진동 사이의 상호 작용은 응축 된 물질 물리학에서 연구의 2 차원 (2D) Dirac 영역과 관련된 가장 근본적인 것 중 하나입니다. 참으로. Ticular, 그래 핀에서의 전자-포논 상호 작용 및 우리는 그 유도체의 이중 변성 광학 포논에 중점을 둔다. G 밴드로 알려진 ~ 1580 cm-1에서 E2G 대칭을 이해하는 데 중요한 역할을한다. 흑연에서 관찰 된 광 방출 스펙트럼의 이상은 또한 EFE가 [1] 및 그래 핀 [2]에 대한 작은 영향에 대해보고한다. 이 두 밴드는 흑연 [8, 9]의 포논 구조와 그래 핀 [17, …
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기