< Summary (English) >
Recent years have seen the successful application of machine learning algorithms in astronomy for data analysis and interpretation.
The growing complexity and size of astronomical datasets necessitates new efficient tools for data analysis.
Machine learning methodologies can revolutionize our ability to interpret observations and provide new means of discovery.
A study by Ho et al.
showed that ML algorithms outperform conventional statistical methods in predicting the dynamical mass of galaxy clusters.
Both supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms are used in astronomy, with CNNs being popular for studying strong and weak gravitational lensing maps.
Developing robust data analysis tools for next-generation astronomy is an ongoing interdisciplinary effort.
The growing complexity and size of astronomical datasets necessitates new efficient tools for data analysis.
Machine learning methodologies can revolutionize our ability to interpret observations and provide new means of discovery.
A study by Ho et al.
showed that ML algorithms outperform conventional statistical methods in predicting the dynamical mass of galaxy clusters.
Both supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms are used in astronomy, with CNNs being popular for studying strong and weak gravitational lensing maps.
Developing robust data analysis tools for next-generation astronomy is an ongoing interdisciplinary effort.
< 요약 (Korean) >
최근 머신러닝 알고리즘이 천문학에서 데이터 분석 및 해석에 성공적으로 사용되었습니다.
천문학 데이터의 복잡성과 크기가 증가하고 있어서 새로운 효율적인 데이터 분석 도구가 필요합니다.
머신러닝 방법ologies는 관찰 해석을 변화시키고 새로운 발견 방법을 제공할 수 있습니다.
호 등의 연구에서는 ML 알고리즘이 우주 모임 클러스터의 동적 질량을 예측하는데 대표적인 통계 방법보다 더 잘 작동합니다.
천문학에서는 슈퍼바이저드와 언사퍼바이저드 머신러닝 알고리즘을 모두 사용하며, CNNs가 강력한 그라비테이션 LENSING 및 약한 그라비티 LENSING 맵에 대해 인기 있습니다.
다음 세대 천문학의 강력한 데이터 분석 도구를 개발하는 것은 여전히 진행 중인 광범위한 연구입니다.
Technical terms explanation: * Machine learning: 기계학습 * Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): 卷积神经网络(CNN) * Support Vector Machine (SVM): 지원벡터기계(SVM) * Random Forest (RF): 랜덤포레스트(RF) * Hierarchical Clustering: 계층적 클러스터링.
Title, Source, URL
* [2] Title, Author/Source, URL
천문학 데이터의 복잡성과 크기가 증가하고 있어서 새로운 효율적인 데이터 분석 도구가 필요합니다.
머신러닝 방법ologies는 관찰 해석을 변화시키고 새로운 발견 방법을 제공할 수 있습니다.
호 등의 연구에서는 ML 알고리즘이 우주 모임 클러스터의 동적 질량을 예측하는데 대표적인 통계 방법보다 더 잘 작동합니다.
천문학에서는 슈퍼바이저드와 언사퍼바이저드 머신러닝 알고리즘을 모두 사용하며, CNNs가 강력한 그라비테이션 LENSING 및 약한 그라비티 LENSING 맵에 대해 인기 있습니다.
다음 세대 천문학의 강력한 데이터 분석 도구를 개발하는 것은 여전히 진행 중인 광범위한 연구입니다.
Technical terms explanation: * Machine learning: 기계학습 * Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): 卷积神经网络(CNN) * Support Vector Machine (SVM): 지원벡터기계(SVM) * Random Forest (RF): 랜덤포레스트(RF) * Hierarchical Clustering: 계층적 클러스터링.
Title, Source, URL
* [2] Title, Author/Source, URL
< 기술적 용어 설명 >
< 참고 논문 또는 관련 자료 >
< Excerpt (English) >
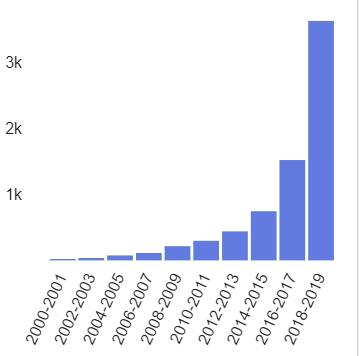
Success of machine learning algorithms in dynamical mass measurements of galaxy clusters Muhammad Haider Abbas December 12, 2019 Abstract In recent years, machine learning (ML) algorithms have been successfully employed in As- tronomy for analyzing and interpreting the data collected from various surveys. The need for new robust and efficient data analysis tools in Astronomy is imminently growing as we enter the new decade. Astronomical data sets are growing both in size and complexity at an exponential rate and ML methodologies can revolutionize our ability to interpret observations and provide new means of discovery. In this essay we focus on recent success of ML algorithms in predicting the dynamical mass of galaxy clusters. We discuss the results of the study performed by Ho et al. [1] and their implications, where it was found that ML algorithms outperform conventional statistical methods and can offer a robust and accurate tool for dynamical mass estimation. 1 Introduction The fields of Astronomy and observational Cosmology are entering an era of unprecedented data production and traffic as data sets continuously grow both in size and complexity. Although the ever-growing size in astronomical data sets faces challenges not directly addressable by advances in data science, e.g. with regard to data storage and transfer, it is more often than not the complexity of said data sets that makes them a rich reservoir for the application of ML algorithms. In recent years astronomers have used various ML tools to harvest novel information from astronomical data sets, and have done so with an unmatched level of efficiency in comparison to conventional paradigms. Figure 1 shows the number of Astrophysics Data System (ADS) [2] peer reviewed papers containing “machine learning” in their abstracts between the years 2000 and 2019 with more than 3000 papers between 2018 and 2019. Both supervised and unsupervised ML algorithms are used in Astronomy depending on the task at hand, and arguably unsupervised algorithms are more crucial in science as they can yield new discoveries unknown to us previously. To name a few, supervised ML algorithms such as Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Random Forest (RF) are widely used in Astronomy in classification and regression tasks, see for example [3]. Unsupervised algorithms such as Hierarchical Clustering and K-means are used to identify different clusters in the data set, see for example [4] and [5]. Furthermore, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are very popular in studying strong and weak gravitational lensing maps, for example [6,7]. 1 arXiv:1912.05316v1 [astro-ph.GA] 11 Dec 2019 Figure 1: ADS papers that include “machine learning” in their abstracts. The figure shows an exponential growth with more than 3000 peer reviewed arti- cles between 2018 and 2019 [2]. Developing a robust data analysis tool kit for next gen- eration Astronomy appropriate to the exponentially growing data sets is an ongoing interdisciplinary endeavor. Although ML techniques inarguably accelerated discovery in Astronomy, criticism is unavoidable and in this case, it is usually the lack on interpretability of ML algorithms which makes part of the community sceptical. This…
< 번역 (Korean) >
Galaxy Clusters의 동적 질량 측정에서 기계 학습 알고리즘의 성공 Muhammad Haider Abbas 2019 년 12 월 12 일 초록 최근 몇 년간 MACHING LEARNIGE (MARY LEARNME) 알고리즘은 다양한 조사에서 수집 한 데이터를 분석하고 해석하기 위해 AS- Tronomy에서 성공적으로 사용되었습니다.
천문학에서 새로운 강력하고 효율적인 데이터 분석 도구의 필요성은 새로운 10 년에 들어서면서 임박하게 성장하고 있습니다.
천문 데이터 세트는 지수 비율로 규모와 복잡성이 모두 증가하고 있으며 ML 방법론은 관찰을 해석하고 새로운 발견 수단을 제공하는 능력을 혁신 할 수 있습니다.
이 에세이에서 우리는 갤럭시 클러스터의 동적 질량을 예측하는 데 ML 알고리즘의 최근 성공에 중점을 둡니다.
우리는 Ho et al.
[1] ML 알고리즘이 기존의 통계적 방법을 능가하고 동적 질량 추정을위한 강력하고 정확한 도구가 될 수 있음을 발견했습니다.
1 소개 천문학 및 관찰 우주론의 분야는 데이터 세트가 크기와 복잡성 모두에서 지속적으로 성장함에 따라 전례없는 데이터 생산 시대에 들어가고 있습니다.
천문학적 데이터 세트에서 끊임없이 성장하는 규모는 데이터 과학의 발전으로 직접 해결할 수없는 문제에 직면 해 있습니다.
데이터 저장 및 전송과 관련하여, 상기 데이터 세트의 복잡성은 ML 알고리즘의 적용을위한 풍부한 저수지가됩니다.
최근 몇 년 동안 천문학 자들은 다양한 ML 도구를 사용하여 천문학적 데이터 세트에서 새로운 정보를 수확했으며 기존의 패러다임과 비교할 때 비교할 수없는 수준의 효율성으로 그렇게했습니다.
그림 1은 2018 년에서 2019 년 사이에 2000 년에서 2019 년 사이에 초록에“기계 학습”을 포함하는“ADS (Astrophysics Data System) [2] 동료 검토 논문의 수를 보여줍니다.
2018 년과 2019 년 사이에 3000 개가 넘는 논문이 포함되어 있습니다.
감독 및 감독 된 ML 알고리즘은 모두 천문학에서 사용되지 않으며, 신생이없는 알기리스는 무의미한 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
우리 이전에 우리.
지지 벡터 머신 (SVM) 및 임의의 포레스트 (RF)와 같은 감독 된 ML 알고리즘은 분류 및 회귀 작업에서 천문학에 널리 사용됩니다.
예를 들어 [3] 참조하십시오.
계층 적 클러스터링 및 K- 평균과 같은 감독되지 않은 알고리즘은 데이터 세트에서 다른 클러스터를 식별하는 데 사용됩니다 (예 : [4] 및 [5]를 참조하십시오.
또한 CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks)은 강력하고 약한 중력 렌즈 맵을 연구하는 데 매우 인기가 있습니다 [6,7].
1 ARXIV : 1912.05316V1 [Astro-PH.GA] 2019 년 12 월 11 일 그림 1 : 초록에 “기계 학습”을 포함하는 광고 논문.
이 그림은 2018 년과 2019 년 사이에 3000 개가 넘는 동료 검토 인공물로 기하 급수적 인 성장을 보여줍니다 [2].
기하 급수적으로 성장하는 데이터 세트에 적합한 차세대 천문학을위한 강력한 데이터 분석 도구 키트를 개발하는 것은 진행중인 학제 간 노력입니다.
ML 기술은 천문학에서 발견을 가속화 시켰지만, 비판은 피할 수 없으며,이 경우 일반적으로 커뮤니티의 일부를 회의적으로 만드는 ML 알고리즘의 해석 가능성이 부족하다.
이것…
천문학에서 새로운 강력하고 효율적인 데이터 분석 도구의 필요성은 새로운 10 년에 들어서면서 임박하게 성장하고 있습니다.
천문 데이터 세트는 지수 비율로 규모와 복잡성이 모두 증가하고 있으며 ML 방법론은 관찰을 해석하고 새로운 발견 수단을 제공하는 능력을 혁신 할 수 있습니다.
이 에세이에서 우리는 갤럭시 클러스터의 동적 질량을 예측하는 데 ML 알고리즘의 최근 성공에 중점을 둡니다.
우리는 Ho et al.
[1] ML 알고리즘이 기존의 통계적 방법을 능가하고 동적 질량 추정을위한 강력하고 정확한 도구가 될 수 있음을 발견했습니다.
1 소개 천문학 및 관찰 우주론의 분야는 데이터 세트가 크기와 복잡성 모두에서 지속적으로 성장함에 따라 전례없는 데이터 생산 시대에 들어가고 있습니다.
천문학적 데이터 세트에서 끊임없이 성장하는 규모는 데이터 과학의 발전으로 직접 해결할 수없는 문제에 직면 해 있습니다.
데이터 저장 및 전송과 관련하여, 상기 데이터 세트의 복잡성은 ML 알고리즘의 적용을위한 풍부한 저수지가됩니다.
최근 몇 년 동안 천문학 자들은 다양한 ML 도구를 사용하여 천문학적 데이터 세트에서 새로운 정보를 수확했으며 기존의 패러다임과 비교할 때 비교할 수없는 수준의 효율성으로 그렇게했습니다.
그림 1은 2018 년에서 2019 년 사이에 2000 년에서 2019 년 사이에 초록에“기계 학습”을 포함하는“ADS (Astrophysics Data System) [2] 동료 검토 논문의 수를 보여줍니다.
2018 년과 2019 년 사이에 3000 개가 넘는 논문이 포함되어 있습니다.
감독 및 감독 된 ML 알고리즘은 모두 천문학에서 사용되지 않으며, 신생이없는 알기리스는 무의미한 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
우리 이전에 우리.
지지 벡터 머신 (SVM) 및 임의의 포레스트 (RF)와 같은 감독 된 ML 알고리즘은 분류 및 회귀 작업에서 천문학에 널리 사용됩니다.
예를 들어 [3] 참조하십시오.
계층 적 클러스터링 및 K- 평균과 같은 감독되지 않은 알고리즘은 데이터 세트에서 다른 클러스터를 식별하는 데 사용됩니다 (예 : [4] 및 [5]를 참조하십시오.
또한 CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks)은 강력하고 약한 중력 렌즈 맵을 연구하는 데 매우 인기가 있습니다 [6,7].
1 ARXIV : 1912.05316V1 [Astro-PH.GA] 2019 년 12 월 11 일 그림 1 : 초록에 “기계 학습”을 포함하는 광고 논문.
이 그림은 2018 년과 2019 년 사이에 3000 개가 넘는 동료 검토 인공물로 기하 급수적 인 성장을 보여줍니다 [2].
기하 급수적으로 성장하는 데이터 세트에 적합한 차세대 천문학을위한 강력한 데이터 분석 도구 키트를 개발하는 것은 진행중인 학제 간 노력입니다.
ML 기술은 천문학에서 발견을 가속화 시켰지만, 비판은 피할 수 없으며,이 경우 일반적으로 커뮤니티의 일부를 회의적으로 만드는 ML 알고리즘의 해석 가능성이 부족하다.
이것…
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기