< Summary (English) >
English Summary:
This paper presents the photometric and astrometric calibration of the Pan-STARRS1 3π Survey.
The survey was conducted using the 1.
8m Pan-STARRS1 telescope from May 2010 to March 2014, covering a wide field of view with gP1, rP1, iP1, zP1, and yP1 filters.
The calibration aims to reduce systematic effects introduced by the camera and detectors and place all observations onto a consistent photometric system.
The Pan-STARRS Data Release 2 (DR2) astrometry is tied to Gaia DR1 release.
codegen<|im_start|> assistant
This paper presents the photometric and astrometric calibration of the Pan-STARRS1 3π Survey.
The survey was conducted using the 1.
8m Pan-STARRS1 telescope from May 2010 to March 2014, covering a wide field of view with gP1, rP1, iP1, zP1, and yP1 filters.
The calibration aims to reduce systematic effects introduced by the camera and detectors and place all observations onto a consistent photometric system.
The Pan-STARRS Data Release 2 (DR2) astrometry is tied to Gaia DR1 release.
codegen<|im_start|> assistant
< 요약 (Korean) >
이 논문은 Pan-STARRS1 3π Survey의 광량과 위치 계산 조정을 설명합니다.
2010년 5월부터 2014년 3월까지 1.
8m Pan-STARRS1 텔레스코프를 사용하여 광량 gP1, rP1, iP1, zP1, yP1 필터를 사용하여 넓은 시야 영역을 커버했습니다.
조정의 목표는 카메라와 감지기에서 도입된 시스템적 효과를 줄이고 모든 관측을 일관된 광량 시스템으로 배치하는 것입니다.
Pan-STARRS Data Release 2 (DR2)의 위치 계산은 Gaia DR1 출처에 연결됩니다.
2010년 5월부터 2014년 3월까지 1.
8m Pan-STARRS1 텔레스코프를 사용하여 광량 gP1, rP1, iP1, zP1, yP1 필터를 사용하여 넓은 시야 영역을 커버했습니다.
조정의 목표는 카메라와 감지기에서 도입된 시스템적 효과를 줄이고 모든 관측을 일관된 광량 시스템으로 배치하는 것입니다.
Pan-STARRS Data Release 2 (DR2)의 위치 계산은 Gaia DR1 출처에 연결됩니다.
< 기술적 용어 설명 >
* 광량 조정: 광량 및 위치 데이터를 일관성 있는 시스템으로 조정하여 시스템적 오류를 줄이는 과정입니다. * 위치 계산 조정: 광량 및 위치 데이터에서 시스템적 효과를 제거하고 신뢰할 수 있는 위치를 얻기 위한 조정 과정입니다.
< 참고 논문 또는 관련 자료 >
* [1] “Pan-STARRS System and Surveys Overview” by Chambers et al. (2017)
* [2] “Astrometric Calibration of the Pan-STARRS1 First Data Release” by Magnier et al. (2016a)
* [2] “Astrometric Calibration of the Pan-STARRS1 First Data Release” by Magnier et al. (2016a)
< Excerpt (English) >
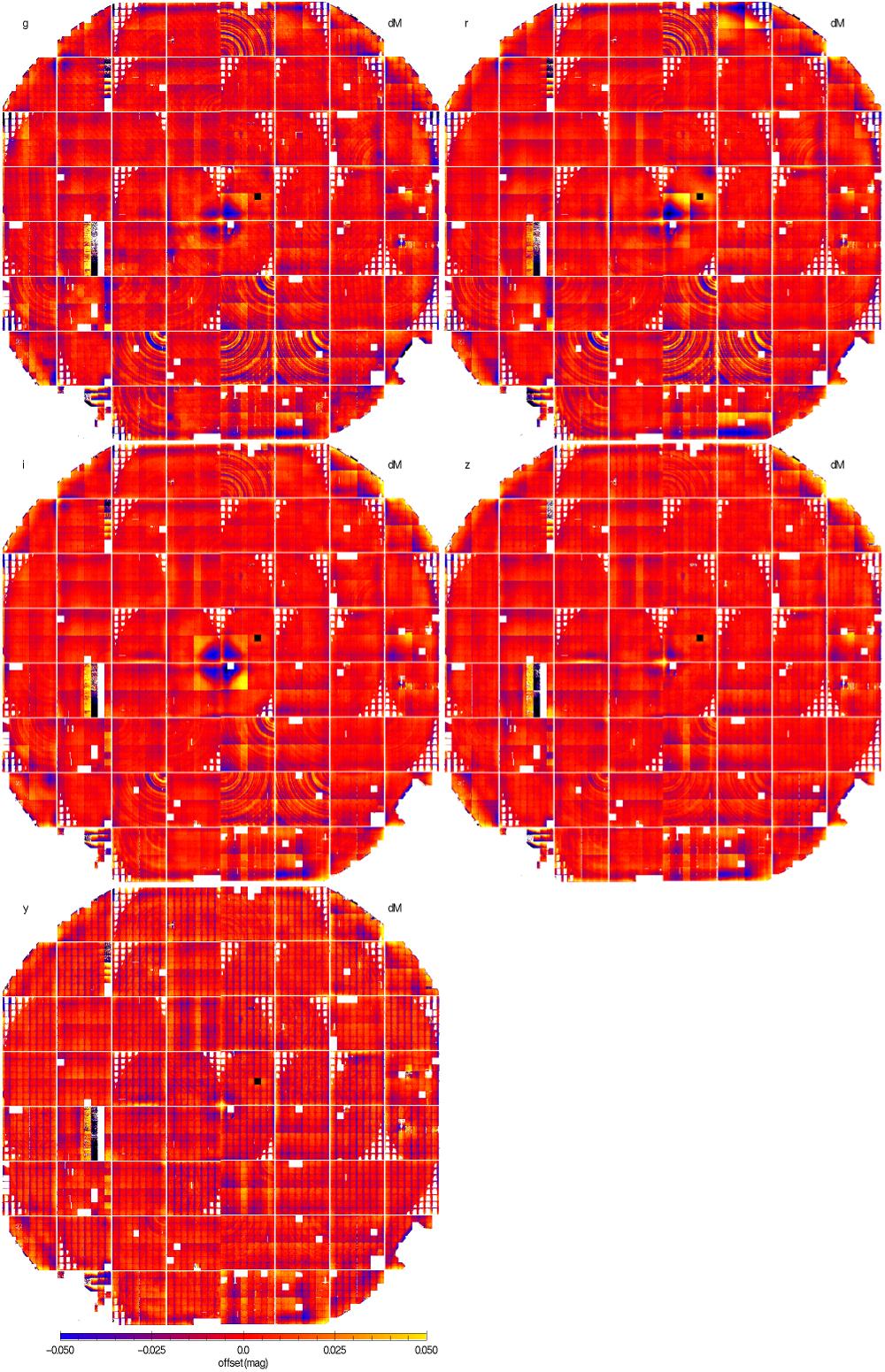
Draft version January 29, 2019 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 PAN-STARRS PHOTOMETRIC AND ASTROMETRIC CALIBRATION Eugene. A. Magnier,1 Edward. F. Schlafly,2,3 Douglas P. Finkbeiner,4,5 J. L. Tonry,1 B. Goldman,6 S. R¨oser,7 E. Schilbach,7 K. C. Chambers,1 H. A. Flewelling,1 M. E. Huber,1 P. A. Price,8 W. E. Sweeney,1 C. Z. Waters,1 L. Denneau,1 P. Draper,9 K. W. Hodapp,1 R. Jedicke,1 N. Kaiser,1 R.-P. Kudritzki,1 N. Metcalfe,9 C. W. Stubbs,10 R. J. Wainscoat1 Draft version January 29, 2019 ABSTRACT We present the details of the photometric and astrometric calibration of the Pan-STARRS 1 3π Survey. The photometric goals were to reduce the systematic effects introduced by the camera and detectors, and to place all of the observations onto a photometric system with consistent zero points over the entire area surveyed, the ∼30,000 square degrees north of δ = −30◦. The astrometric calibration compensates for similar systematic effects so that positions, proper motions, and parallaxes are reliable as well. The Pan-STARRS Data Release 2 (DR2) astrometry is tied to the Gaia DR1 release. Keywords: Surveys:Pan-STARRS 1 1. INTRODUCTION From May 2010 through March 2014, the Pan- STARRS Science Consortium used the 1.8m Pan- STARRS 1 telescope to perform a set of wide-field sci- ence surveys. These surveys are designed to address a range of science goals included the search for hazardous asteroids, the study of the formation and architecture of the Milky Way galaxy, and the search for Type Ia supernovae to measure the history of the expansion of the universe. The majority of the time (56%) was spent on surveying the 3 4 of the sky north of −30 Declination with gP1,rP1,iP1,zP1,yP1 filters in the so-called 3π Sur- vey. Another ∼25% of the time was concentrated on repeated deep observations of 10 specific fields in the Medium-Deep Survey. The rest of the time was used for several other surveys, including a search for potentially hazardous asteroids in our solar system. The details of the telescope, surveys, and resulting science publications are described by Chambers et al. (2017). The wide-field Pan-STARRS 1 telescope consists of a 1.8 meter diameter f/4.4 primary mirror with an 0.9 m secondary, producing a 3.3 degree field of view (Hodapp et al. 2004). The optical design yields low distortion and minimal vignetting even at the edges of the illuminated 1 Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, 2680 Wood- lawn Drive, Honolulu HI 96822 2 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, One Cyclotron Road, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA 3 Hubble Fellow 4 Institute for Theory and Computation, Harvard- Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, MS-51, Cambridge, MA 02138 USA 5 Department of Physics, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138 USA 6 Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, K¨onigstuhl 17, D- 69117 Heidelberg, Germany 7 Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Zentrum f¨ur Astronomie der Universit¨at Heidelberg, M¨ochhofstrasse 12-14, D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany 8 Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA 9 Department of Physics, Durham University, South Road, Durham DH1 3LE, UK 10 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street,…
< 번역 (Korean) >
초안 버전 2019 년 1 월 29 일 라텍스 스타일 Emulateapj v.
12/16/11 Pan-Starrs 광도 및 천체 교정 Eugene을 사용한 프리 인쇄 조판.
A.
Magnier, 1 Edward.
F.
Schlafly, 2,3 Douglas P.
Finkbeiner, 4,5 J.
L.
Tonry, 1 B.
Goldman, 6 S.
R¨oser, 7 E.
Schilbach, 7 K.
C.
Chambers, 1 H.
A.
Flewelling, 1 M.
E.
Huber, 1 P.
A.
Price, 8 W.
E.
Sweeney, 1 C.
Z.
Waters, 1 L.
Denneau, 1 P.
Draper, 9 K.
W.
W.
W.
W.
W.
N.
Kaiser, 1 R.-P.
Kudritzki, 1 N.
Metcalfe, 9 C.
W.
Stubbs, 10 R.
J.
Wainscoat1 드래프트 버전 2019 년 1 월 29 일 초록 우리는 Pan-Starrs 1 3π 조사의 광도계 및 천체 교정에 대한 세부 사항을 제시합니다.
광도 목표는 카메라와 탐지기에 의해 도입 된 체계적인 효과를 줄이고, 조사 된 전체 영역에 걸쳐 일관된 영역에 걸쳐 모든 관측치를 δ = -30 ℃의 북쪽으로 30,000 평방 ℃로 배치하는 것이었다.
천체 교정은 위치, 적절한 동작 및 시차도 신뢰할 수 있도록 유사한 체계적인 효과를 보상합니다.
Pan-Starrs Data Release 2 (DR2) 천체는 GAIA DR1 릴리스에 묶여 있습니다.
키워드 : 설문 조사 : Pan-Starrs 1 1.
2010 년 5 월부터 2014 년 3 월까지 Pan-Starrs Science Consortium은 1.8m Pan-Starrs 1 망원경을 사용하여 광범위한 과학 설문 조사를 수행했습니다.
이 설문 조사는 위험한 소행성에 대한 검색, 은하계 은하의 형성 및 건축에 대한 연구, 우주의 확장의 역사를 측정하기위한 IA 유형의 검색을 포함하여 다양한 과학 목표를 다루기 위해 고안되었습니다.
대부분의 시간 (56%)은 소위 3π 수술에서 gp1, rp1, ip1, zp1, yp1 필터로 -30 편각의 하늘 3 개를 조사하는 데 소비되었습니다.
시간의 또 다른 ~ 25%는 중간 깊이 조사에서 10 개의 특정 필드의 반복 된 깊은 관찰에 집중되었다.
나머지 시간은 태양계에서 잠재적으로 위험한 소행성에 대한 검색을 포함하여 다른 여러 조사에 사용되었습니다.
망원경, 설문 조사 및 결과 과학 간행물의 세부 사항은 Chambers et al.
(2017).
와이드 파이어 팬-스타 1 망원경은 0.9m 2 차의 1.8 미터 직경 F/4.4 1 차 미러로 구성되어 3.3 도의 시야를 생성합니다 (Hodapp et al.
2004).
광학 디자인은 조명 된 1 천문학 연구소, 하와이 대학교, 2680 Wood-Lawn Drive, Honolulu HI 96822 2 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, One Cyclotron Road, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA 3 ASTROPINS, 60 ASTROPINS, 60 ASTROTION, HANDORD-SMITHBLE Fellow 4 Institution of Astrotic, 60 Astrophy Institution of Astrophys 4, 1 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Honolulu Hi 96822 2 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory의 광학 디자인을 생성합니다.
Garden Street, MS-51, MA 02138 USA 5 물리학과, 하버드 대학교, 케임브리지, MA 02138 USA 6 Max Planck Institute, K¨onigstuhl 17, D-69117 Heidelberg, Germany 7 Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Zentrum fromat heidelberg, Zentrum fromat heidelberg, michophit.
12-14, D-69120 독일 Heidelberg 8 8 개 성상 물리학과, 프린스턴 대학교, 프린스턴, 뉴저지 08544, 미국 물리학과, Durham University, 남부로드, 더럼 DH1 3L, 영국 10 하버드-스미소니언 센터, 60 Garden Street, 60 Garden Street, …
12/16/11 Pan-Starrs 광도 및 천체 교정 Eugene을 사용한 프리 인쇄 조판.
A.
Magnier, 1 Edward.
F.
Schlafly, 2,3 Douglas P.
Finkbeiner, 4,5 J.
L.
Tonry, 1 B.
Goldman, 6 S.
R¨oser, 7 E.
Schilbach, 7 K.
C.
Chambers, 1 H.
A.
Flewelling, 1 M.
E.
Huber, 1 P.
A.
Price, 8 W.
E.
Sweeney, 1 C.
Z.
Waters, 1 L.
Denneau, 1 P.
Draper, 9 K.
W.
W.
W.
W.
W.
N.
Kaiser, 1 R.-P.
Kudritzki, 1 N.
Metcalfe, 9 C.
W.
Stubbs, 10 R.
J.
Wainscoat1 드래프트 버전 2019 년 1 월 29 일 초록 우리는 Pan-Starrs 1 3π 조사의 광도계 및 천체 교정에 대한 세부 사항을 제시합니다.
광도 목표는 카메라와 탐지기에 의해 도입 된 체계적인 효과를 줄이고, 조사 된 전체 영역에 걸쳐 일관된 영역에 걸쳐 모든 관측치를 δ = -30 ℃의 북쪽으로 30,000 평방 ℃로 배치하는 것이었다.
천체 교정은 위치, 적절한 동작 및 시차도 신뢰할 수 있도록 유사한 체계적인 효과를 보상합니다.
Pan-Starrs Data Release 2 (DR2) 천체는 GAIA DR1 릴리스에 묶여 있습니다.
키워드 : 설문 조사 : Pan-Starrs 1 1.
2010 년 5 월부터 2014 년 3 월까지 Pan-Starrs Science Consortium은 1.8m Pan-Starrs 1 망원경을 사용하여 광범위한 과학 설문 조사를 수행했습니다.
이 설문 조사는 위험한 소행성에 대한 검색, 은하계 은하의 형성 및 건축에 대한 연구, 우주의 확장의 역사를 측정하기위한 IA 유형의 검색을 포함하여 다양한 과학 목표를 다루기 위해 고안되었습니다.
대부분의 시간 (56%)은 소위 3π 수술에서 gp1, rp1, ip1, zp1, yp1 필터로 -30 편각의 하늘 3 개를 조사하는 데 소비되었습니다.
시간의 또 다른 ~ 25%는 중간 깊이 조사에서 10 개의 특정 필드의 반복 된 깊은 관찰에 집중되었다.
나머지 시간은 태양계에서 잠재적으로 위험한 소행성에 대한 검색을 포함하여 다른 여러 조사에 사용되었습니다.
망원경, 설문 조사 및 결과 과학 간행물의 세부 사항은 Chambers et al.
(2017).
와이드 파이어 팬-스타 1 망원경은 0.9m 2 차의 1.8 미터 직경 F/4.4 1 차 미러로 구성되어 3.3 도의 시야를 생성합니다 (Hodapp et al.
2004).
광학 디자인은 조명 된 1 천문학 연구소, 하와이 대학교, 2680 Wood-Lawn Drive, Honolulu HI 96822 2 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, One Cyclotron Road, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA 3 ASTROPINS, 60 ASTROPINS, 60 ASTROTION, HANDORD-SMITHBLE Fellow 4 Institution of Astrotic, 60 Astrophy Institution of Astrophys 4, 1 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Honolulu Hi 96822 2 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory의 광학 디자인을 생성합니다.
Garden Street, MS-51, MA 02138 USA 5 물리학과, 하버드 대학교, 케임브리지, MA 02138 USA 6 Max Planck Institute, K¨onigstuhl 17, D-69117 Heidelberg, Germany 7 Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Zentrum fromat heidelberg, Zentrum fromat heidelberg, michophit.
12-14, D-69120 독일 Heidelberg 8 8 개 성상 물리학과, 프린스턴 대학교, 프린스턴, 뉴저지 08544, 미국 물리학과, Durham University, 남부로드, 더럼 DH1 3L, 영국 10 하버드-스미소니언 센터, 60 Garden Street, 60 Garden Street, …
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기