< Summary (English) >
This study investigates the distribution of the C statistic for modeling low-count Poisson data in astronomy.
The C statistic is an alternative to the commonly used χ² statistic and has advantages when dealing with small or null counts in each resolution element.
However, its probability distribution under the null hypothesis is not known exactly.
This paper presents an effort towards improving our understanding of the C statistic by studying the distribution of C statistic for a fully specified model, the distribution of Cmin resulting from maximum-likelihood fitting to a simple one-parameter constant model (representing the sample mean of N Poisson measurements), and the distribution of.
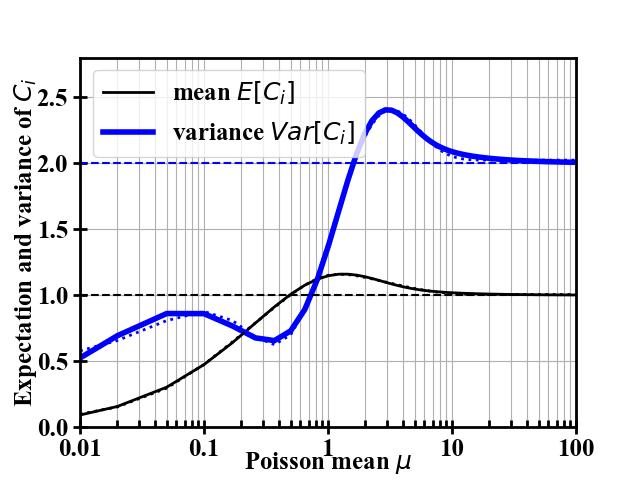
The results confirm that in the high-count limit, both C statistic and Cmin have the same mean and variance as a χ² statistic with the same number of degrees of freedom.
However, in the low-count regime, the expectation of the C statistic and Cmin can be substantially lower than for a χ² distribution.
The study uses recent X-ray observations of the astronomical source PG 1116+215 to illustrate the application of the C statistic to Poisson data and identifies biases in the use of the χ² statistic for Poisson data, especially in.
The C statistic is an alternative to the commonly used χ² statistic and has advantages when dealing with small or null counts in each resolution element.
However, its probability distribution under the null hypothesis is not known exactly.
This paper presents an effort towards improving our understanding of the C statistic by studying the distribution of C statistic for a fully specified model, the distribution of Cmin resulting from maximum-likelihood fitting to a simple one-parameter constant model (representing the sample mean of N Poisson measurements), and the distribution of.
The results confirm that in the high-count limit, both C statistic and Cmin have the same mean and variance as a χ² statistic with the same number of degrees of freedom.
However, in the low-count regime, the expectation of the C statistic and Cmin can be substantially lower than for a χ² distribution.
The study uses recent X-ray observations of the astronomical source PG 1116+215 to illustrate the application of the C statistic to Poisson data and identifies biases in the use of the χ² statistic for Poisson data, especially in.
< 요약 (Korean) >
이 연구는 천문학에서 작은 카운트를 가진 포이슨 데이터를 모델링하기 위해 C 통계량의 분포를 조사합니다.
C 통계량은 각각의 분석 요소에서 작은 또는 무수한 카운트가 있을 때 유용한 대안으로 널리 사용되는 χ² 통계량보다 장점이 있습니다.
그러나 이 통계량의 확률 분포는 Null 가설에서 정확하게 알려져 있지 않습니다.
이 연구에서는 C 통계량의 분포를 더욱 이해하기 위해 완전히 정의된 모델에 대한 C 통계량의 분포, 최대가능성 적합을 통해 단일 매개변수 상수 모델(N 포이슨 측정값의 표본 평균을 나타내는)에 대한 Cmin 분포, 및 매개 변수 추정을 위해 사용되는 연관된 ∆C 통계량의 분포를 연구합니다.
결과는 높은 카운트 한도에서 C 통계량과 Cmin이 동일한 의미와 분산을 χ² 통계량과 같은 동일한 수의 자유 차수를 가진 것을 확인합니다.
그러나 작은 카운트 영역에서는 χ² 분포보다 기대치가 크게 낮을 수 있습니다.
이 연구는 천문학적 소스 PG 1116+215의 최근 X선 관측을 사용하여 C 통계량을 포이슨 데이터에 적용하고 χ² 통계량을 작은 카운트 영역에서 사용할 때의 편향을 식별합니다.
Technical Terms Explanation:
* C statistic (C 통계량): A statistical measure used in astronomy for analyzing low-count Poisson data, which has advantages over the more commonly used χ² statistic.
* χ² statistic (χ² 통계량): A statistical measure commonly used in astronomy for analyzing Gaussian data and testing goodness of fit; its distribution is independent of the parent means.
* Maximum-likelihood fitting (최대가능성 적합): A method used to determine the best-fit parameters in a model by maximizing the likelihood function.
* Likelihood ratio theorem (가능성 비율 정리): A statistical theorem that relates the likelihood ratio with the ∆C statistic, which can be used for parameter estimation in Poisson data, similar to how the ∆χ² statistic is used for Gaussian data.
Related Papers or Resources:
* [1] Title: Author/Source: URL (Discusses the advantages and challenges of the C statistic for modeling low-count Poisson data)
* [2] Title: Author/Source: URL (Explores the mean and variance of the C statistic for a fully specified model)
C 통계량은 각각의 분석 요소에서 작은 또는 무수한 카운트가 있을 때 유용한 대안으로 널리 사용되는 χ² 통계량보다 장점이 있습니다.
그러나 이 통계량의 확률 분포는 Null 가설에서 정확하게 알려져 있지 않습니다.
이 연구에서는 C 통계량의 분포를 더욱 이해하기 위해 완전히 정의된 모델에 대한 C 통계량의 분포, 최대가능성 적합을 통해 단일 매개변수 상수 모델(N 포이슨 측정값의 표본 평균을 나타내는)에 대한 Cmin 분포, 및 매개 변수 추정을 위해 사용되는 연관된 ∆C 통계량의 분포를 연구합니다.
결과는 높은 카운트 한도에서 C 통계량과 Cmin이 동일한 의미와 분산을 χ² 통계량과 같은 동일한 수의 자유 차수를 가진 것을 확인합니다.
그러나 작은 카운트 영역에서는 χ² 분포보다 기대치가 크게 낮을 수 있습니다.
이 연구는 천문학적 소스 PG 1116+215의 최근 X선 관측을 사용하여 C 통계량을 포이슨 데이터에 적용하고 χ² 통계량을 작은 카운트 영역에서 사용할 때의 편향을 식별합니다.
Technical Terms Explanation:
* C statistic (C 통계량): A statistical measure used in astronomy for analyzing low-count Poisson data, which has advantages over the more commonly used χ² statistic.
* χ² statistic (χ² 통계량): A statistical measure commonly used in astronomy for analyzing Gaussian data and testing goodness of fit; its distribution is independent of the parent means.
* Maximum-likelihood fitting (최대가능성 적합): A method used to determine the best-fit parameters in a model by maximizing the likelihood function.
* Likelihood ratio theorem (가능성 비율 정리): A statistical theorem that relates the likelihood ratio with the ∆C statistic, which can be used for parameter estimation in Poisson data, similar to how the ∆χ² statistic is used for Gaussian data.
Related Papers or Resources:
* [1] Title: Author/Source: URL (Discusses the advantages and challenges of the C statistic for modeling low-count Poisson data)
* [2] Title: Author/Source: URL (Explores the mean and variance of the C statistic for a fully specified model)
< 기술적 용어 설명 >
< 참고 논문 또는 관련 자료 >
< Excerpt (English) >
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Distribution of the C statistic with applications to the sample mean of Poisson data Massimiliano Bonamentea a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville AL 35899 (U.S.A) ARTICLE HISTORY Compiled December 12, 2019 ABSTRACT The C statistic, also known as the Cash statistic, is often used in astronomy for the analysis of low–count Poisson data. The main advantage of this statistic, compared to the more commonly used χ2 statistic, is its applicability without the need to combine data points. This feature has made the C statistic a very useful method to analyze Poisson data that have small (or even null) counts in each resolution element. One of the challenges of the C statistic is that its probability distribution, under the null hypothesis that the data follow a parent model, is not known exactly. Such distribution is needed for model testing, namely to determine the acceptability of models and then to determine confidence intervals of model parameters. This is in contrast with the accurate knowledge, for Gaussian data, of the χ2 statistic for any number of free parameters in the parent model. This paper presents an effort towards improving our understanding of the C statistic by studying (a) the distribution of C statistic for a fully specified model, (b) the distribution of Cmin resulting from a maximum–likelihood fit to a simple one–parameter constant model, i.e., a model that represents the sample mean of N Poisson measurements, and (c) the distribution of the associated ∆C statistic that is used for parameter estimation. The results confirm the expectation that, in the high–count limit, both C statistic and Cmin have the same mean and variance as a χ2 statistic with same number of degrees of freedom. It is also found that, in the low–count regime, the expectation of the C statistic and Cmin can be substantially lower than for a χ2 distribution. These result have implications for hypothesis testing in the low–count Poisson regime that are also discussed in the paper. The paper makes use of recent X–ray observations of the astronomical source PG 1116+215 to illustrate the application of the C statistic to Poisson data. These measurements are also used to identify biases in the use of the χ2 statistic for Poisson data, especially in the low–count regime. KEYWORDS Random Effects; Probability; Statistics 1. Introduction: Advantages and challeges of the C statistic for modeling low–count Poisson data Radiation from astronomical sources is often detected by instruments that collect an integer number of photons. This is the case for several X–ray and γ–ray instruments The author gratefully acknowledges support of NASA Chandra grant AR6-17018X. arXiv:1912.05444v1 [astro-ph.HE] 11 Dec 2019 [e.g., 7]. Astronomical observations often feature low photon counts, due to a combi- nation of distance of the source, efficiency of the detectors, and intrinsic luminosity of the source. It is customary to combine the detected counts according to the wave- length of photons, in a number of independent resolution elements or data points. By such method, a…
< 번역 (Korean) >
Poisson Data Massimiliano Bonamentea의 샘플 평균에 대한 응용 프로그램과 함께 C 통계의 원래 연구 기사 분포 앨라배마 앨라배마 대학교의 물리 및 천문학 부, 헌츠빌 AL 35899 (미국) 이력 2019 년 12 월 12 일 CASTISTISTIC는 종종 현금 통계로 알려진 C 통계에 사용됩니다.
보다 일반적으로 사용되는 χ2 통계와 비교 하여이 통계의 주요 장점은 데이터 포인트를 결합 할 필요없이 적용 가능성입니다.
이 기능은 C 통계량을 각 해상도 요소에서 작은 (또는 널) 카운트를 갖는 포아송 데이터를 분석하는 매우 유용한 방법으로 만들었습니다.
C 통계의 과제 중 하나는 데이터가 부모 모델을 따르는 귀무 가설 하에서 확률 분포가 정확히 알려지지 않았다는 것입니다.
이러한 분포는 모델 테스트, 즉 모델의 수용 가능성을 결정한 다음 모델 매개 변수의 구성 간격을 결정하기 위해 필요합니다.
이는 가우스 데이터에 대한 정확한 지식과 대조적으로, 부모 모델의 모든 자유 매개 변수에 대한 χ2 통계량과 대조적입니다.
이 논문은 (a) (a) 완전히 지정된 모델에 대한 C 통계의 분포, (b) CMIN의 분포를 연구함으로써 C 통계에 대한 우리의 이해를 향상시키기위한 효과를 제시한다.
매개 변수 추정에 사용됩니다.
결과는 높은 계수 한계에서 C 통계량과 CMIN이 동일한 수의 자유도를 가진 χ2 통계와 동일한 평균 및 분산을 가질 것으로 기대합니다.
또한 저소득 체제에서 C 통계 및 CMIN의 기대는 χ2 분포보다 실질적으로 낮을 수 있습니다.
이러한 결과는 논문에서 논의 된 저수수 포아송 체제에서 가설 검사에 영향을 미칩니다.
이 논문은 C 통계량을 Poisson 데이터에 적용하는 것을 설명하기 위해 천문학적 소스 PG 1116+215의 최근 X -Ray 관찰을 사용합니다.
이러한 측정은 또한 Poisson 데이터에 대한 χ2 통계량, 특히 저 카운트 체제에서 편향을 식별하는 데 사용됩니다.
키워드 임의의 효과; 개연성; 통계 1.
소개 : 천문학적 소스의 저음 수 포아송 데이터 방사선 모델링을위한 C 통계의 장점과 challege는 종종 정수 수를 수집하는기구에 의해 감지됩니다.
이것은 여러 x-ray 및 γ-ray 기기의 경우입니다.
저자는 NASA Chandra Grant AR6-17018X의 지원에 감사하게 인정합니다.
ARXIV : 1912.05444V1 [Astro-Ph.he] 2019 년 12 월 11 일 [예 : 7].
천문 관측은 소스의 거리, 탐지기의 효율성 및 소스의 본질적인 광도로 인해 종종 낮은 광자 수를 특징으로합니다.
많은 독립 해상도 요소 또는 데이터 포인트에서 광자의 파도에 따라 감지 카운트를 결합하는 것이 일반적입니다.
그러한 방법으로 …
a …
보다 일반적으로 사용되는 χ2 통계와 비교 하여이 통계의 주요 장점은 데이터 포인트를 결합 할 필요없이 적용 가능성입니다.
이 기능은 C 통계량을 각 해상도 요소에서 작은 (또는 널) 카운트를 갖는 포아송 데이터를 분석하는 매우 유용한 방법으로 만들었습니다.
C 통계의 과제 중 하나는 데이터가 부모 모델을 따르는 귀무 가설 하에서 확률 분포가 정확히 알려지지 않았다는 것입니다.
이러한 분포는 모델 테스트, 즉 모델의 수용 가능성을 결정한 다음 모델 매개 변수의 구성 간격을 결정하기 위해 필요합니다.
이는 가우스 데이터에 대한 정확한 지식과 대조적으로, 부모 모델의 모든 자유 매개 변수에 대한 χ2 통계량과 대조적입니다.
이 논문은 (a) (a) 완전히 지정된 모델에 대한 C 통계의 분포, (b) CMIN의 분포를 연구함으로써 C 통계에 대한 우리의 이해를 향상시키기위한 효과를 제시한다.
매개 변수 추정에 사용됩니다.
결과는 높은 계수 한계에서 C 통계량과 CMIN이 동일한 수의 자유도를 가진 χ2 통계와 동일한 평균 및 분산을 가질 것으로 기대합니다.
또한 저소득 체제에서 C 통계 및 CMIN의 기대는 χ2 분포보다 실질적으로 낮을 수 있습니다.
이러한 결과는 논문에서 논의 된 저수수 포아송 체제에서 가설 검사에 영향을 미칩니다.
이 논문은 C 통계량을 Poisson 데이터에 적용하는 것을 설명하기 위해 천문학적 소스 PG 1116+215의 최근 X -Ray 관찰을 사용합니다.
이러한 측정은 또한 Poisson 데이터에 대한 χ2 통계량, 특히 저 카운트 체제에서 편향을 식별하는 데 사용됩니다.
키워드 임의의 효과; 개연성; 통계 1.
소개 : 천문학적 소스의 저음 수 포아송 데이터 방사선 모델링을위한 C 통계의 장점과 challege는 종종 정수 수를 수집하는기구에 의해 감지됩니다.
이것은 여러 x-ray 및 γ-ray 기기의 경우입니다.
저자는 NASA Chandra Grant AR6-17018X의 지원에 감사하게 인정합니다.
ARXIV : 1912.05444V1 [Astro-Ph.he] 2019 년 12 월 11 일 [예 : 7].
천문 관측은 소스의 거리, 탐지기의 효율성 및 소스의 본질적인 광도로 인해 종종 낮은 광자 수를 특징으로합니다.
많은 독립 해상도 요소 또는 데이터 포인트에서 광자의 파도에 따라 감지 카운트를 결합하는 것이 일반적입니다.
그러한 방법으로 …
a …
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기