Summary (English)
This scientific paper presents the development and validation of SuperSalt, a machine learning interatomic potential (MLIP) designed for modeling multicomponent molten salt systems, specifically focusing on 11-cation chloride melts.
The authors propose an intermediate approach between universal MLIPs and system-specific ones to achieve near-DFT accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency.
SuperSalt exhibits excellent transferability across diverse chemical compositions and accurately predicts key properties such as density, bulk modulus, thermal expansion, and heat capacity.
By combining SuperSalt with Bayesian optimization, the discovery of optimal salt compositions with desired properties can be accelerated.
This work provides a foundation for future studies on molten salts for advanced energy applications.
The authors propose an intermediate approach between universal MLIPs and system-specific ones to achieve near-DFT accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency.
SuperSalt exhibits excellent transferability across diverse chemical compositions and accurately predicts key properties such as density, bulk modulus, thermal expansion, and heat capacity.
By combining SuperSalt with Bayesian optimization, the discovery of optimal salt compositions with desired properties can be accelerated.
This work provides a foundation for future studies on molten salts for advanced energy applications.
요약 (Korean)
이 과학 논문은 다중 성분 용융 소금 시스템을 모델링하기 위해 설계된 기계 학습 간 전위 (MLIP) 인 Supersalt의 개발 및 검증을 제시합니다.
저자는 범용 MLIP와 시스템 별 접근 방식 사이의 중간 접근법을 제안하여 계산 효율을 유지하면서 거의 DFT 정확도를 달성합니다.
Supersalt는 다양한 화학 조성물에 걸쳐 우수한 전달성을 나타내며 밀도, 벌크 모듈러스, 열 팽창 및 열 용량과 같은 주요 특성을 정확하게 예측합니다.
수퍼 살트를 베이지안 최적화와 결합함으로써, 최적의 소금 조성물을 원하는 특성과 발견하는 것을 가속화 할 수있다.
이 연구는 고급 에너지 응용을위한 용융 염에 대한 향후 연구를위한 토대를 제공합니다.
저자는 범용 MLIP와 시스템 별 접근 방식 사이의 중간 접근법을 제안하여 계산 효율을 유지하면서 거의 DFT 정확도를 달성합니다.
Supersalt는 다양한 화학 조성물에 걸쳐 우수한 전달성을 나타내며 밀도, 벌크 모듈러스, 열 팽창 및 열 용량과 같은 주요 특성을 정확하게 예측합니다.
수퍼 살트를 베이지안 최적화와 결합함으로써, 최적의 소금 조성물을 원하는 특성과 발견하는 것을 가속화 할 수있다.
이 연구는 고급 에너지 응용을위한 용융 염에 대한 향후 연구를위한 토대를 제공합니다.
기술적 용어 설명 (Technical Terms)
추출된 기술 용어가 없습니다.
Excerpt (English Original)
SuperSalt: Equivariant Neural Network Force Fields for Multicomponent Molten Salts System Chen Shen1*†, Siamak Attarian1†, Yixuan Zhang2, Hongbin Zhang2, Mark Asta3, Izabela Szlufarska1, Dane Morgan1* 1Materials Science and Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, 53706, Wisconsin, United States.2024 2Materials Science, Technical University of Darmstadt, Darmstadt, 64287, Hessen, Germany.
3Materials Science and Engineering, University of California, Berkeley,Dec 94720, California, United States.
26 *Corresponding author(s).
E-mail(s): cshen89@wisc.edu; ddmorgan@wisc.edu; Contributing authors: sattarian@wisc.edu; yixuan.zhang@tu-darmstadt.de; hzhang@tmm.tu-darmstadt.de; mdasta@berkeley.edu; szlufarska@wisc.edu; †These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract Molten salts are crucial for clean energy applications, yet exploring their ther- mophysical properties across diverse chemical space remains challenging.
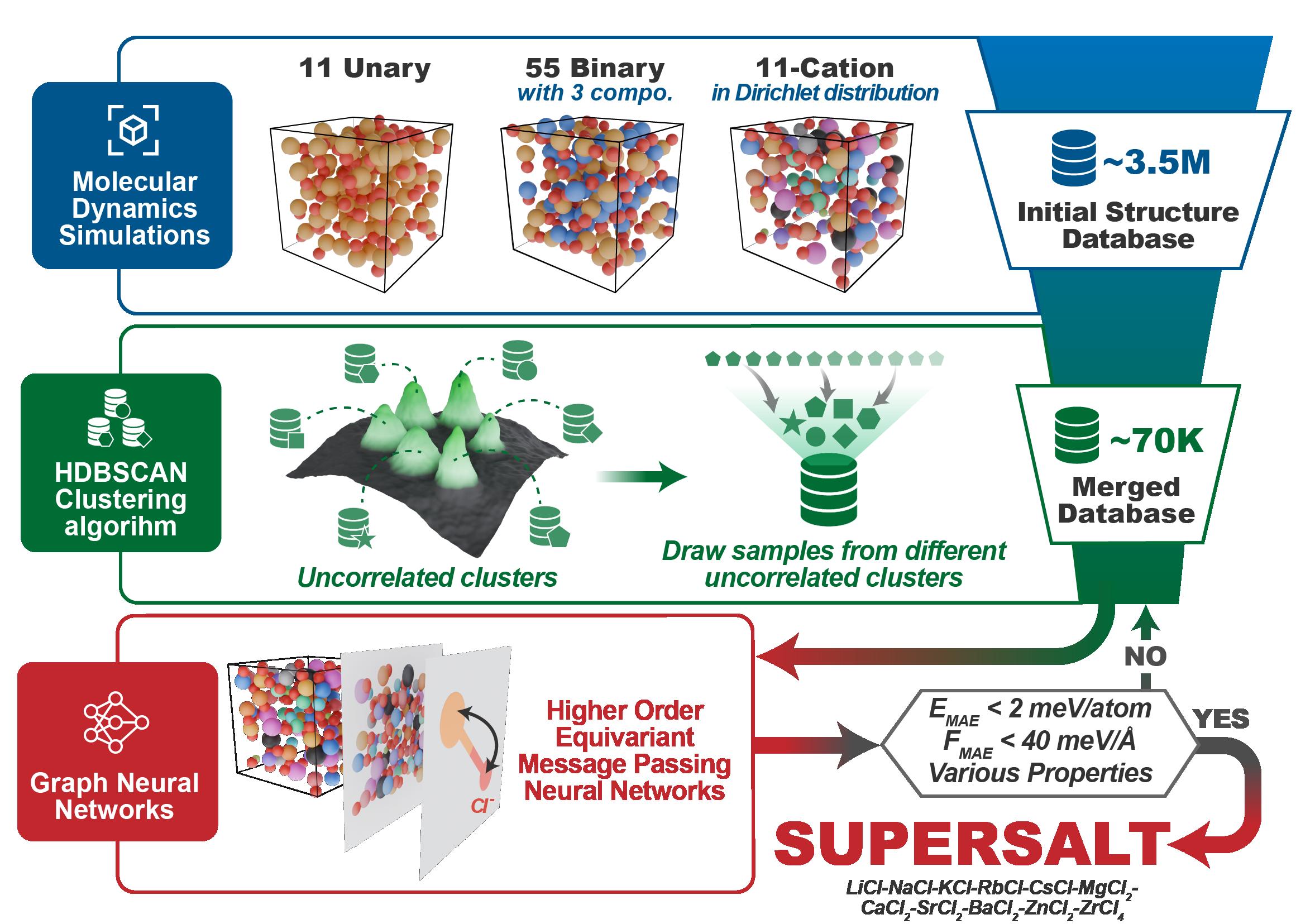
We present the development of a machine learning interatomic potential (MLIP)[cond-mat.mtrl-sci] called SuperSalt, which targets 11-cation chloride melts and captures the essen- tial physics of molten salts with near-DFT accuracy.
Using an efficient workflow that integrates systems of one, two, and 11 components, the SuperSalt potential can accurately predict thermophysical properties such as density, bulk modulus, thermal expansion, and heat capacity.
Our model is validated across a broad chemical space, demonstrating excellent transferability.
We further illustrate how Bayesian optimization combined with SuperSalt can accelerate the discovery of optimal salt compositions with desired properties.
This work provides a foun- dation for future studies that allows easy extensions to more complex systems, such as those containing additional elements.
SuperSalt represents a shift towards a more universal, efficient, and accurate modeling of molten salts for advanced energy applications.
1arXiv:2412.19353v1 Keywords: Molten Salts, Machine Learning Interatomic Potential, Foundation models, Bayesian optimization 1 Introduction Over the past several decades, atomic-scale simulation has emerged as an indispensable tool for predicting and providing microscopic insights into experimentally observed phenomena in molten salt materials.
Numerous scientifically important thermophysical and transport properties of molten salts can be accurately evaluated using molecu- lar dynamics (MD) simulations, in which atomic motion…
3Materials Science and Engineering, University of California, Berkeley,Dec 94720, California, United States.
26 *Corresponding author(s).
E-mail(s): cshen89@wisc.edu; ddmorgan@wisc.edu; Contributing authors: sattarian@wisc.edu; yixuan.zhang@tu-darmstadt.de; hzhang@tmm.tu-darmstadt.de; mdasta@berkeley.edu; szlufarska@wisc.edu; †These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract Molten salts are crucial for clean energy applications, yet exploring their ther- mophysical properties across diverse chemical space remains challenging.
We present the development of a machine learning interatomic potential (MLIP)[cond-mat.mtrl-sci] called SuperSalt, which targets 11-cation chloride melts and captures the essen- tial physics of molten salts with near-DFT accuracy.
Using an efficient workflow that integrates systems of one, two, and 11 components, the SuperSalt potential can accurately predict thermophysical properties such as density, bulk modulus, thermal expansion, and heat capacity.
Our model is validated across a broad chemical space, demonstrating excellent transferability.
We further illustrate how Bayesian optimization combined with SuperSalt can accelerate the discovery of optimal salt compositions with desired properties.
This work provides a foun- dation for future studies that allows easy extensions to more complex systems, such as those containing additional elements.
SuperSalt represents a shift towards a more universal, efficient, and accurate modeling of molten salts for advanced energy applications.
1arXiv:2412.19353v1 Keywords: Molten Salts, Machine Learning Interatomic Potential, Foundation models, Bayesian optimization 1 Introduction Over the past several decades, atomic-scale simulation has emerged as an indispensable tool for predicting and providing microscopic insights into experimentally observed phenomena in molten salt materials.
Numerous scientifically important thermophysical and transport properties of molten salts can be accurately evaluated using molecu- lar dynamics (MD) simulations, in which atomic motion…
발췌문 (Korean Translation)
SUPERSALT : 다 성분 용융 소금 시스템 Chen Shen1* †, Siamak Attarian1 †, Yixuan Zhang2, Hongbin Zhang2, Mark Asta3, Izabela Szlufarska1, Dane Morgan1* 1Materials Science 및 Engineering, Madon, Madon, Madon, Madon, Madon, 5370 년, Izabela Szlufarska1, Dane Morgan1* 1Materials Science 및 Engineering의 동료 신경 네트워크 힘 필드.
위스콘신, 미국 .2024 2MATERIALS DARMSTADT 기술 대학교, Darmstadt, 64287, Hessen, Germany.
3 MATERIALS 과학 및 공학, 캘리포니아 대학교, 버클리, 12 월 94720, 캘리포니아, 미국.
26 *해당 저자.
이메일 : cshen89@wisc.edu; ddmorgan@wisc.edu; 기고자 : sattarian@wisc.edu; yixuan.zhang@tu-darmstadt.de; hzhang@tmm.tu-darmstadt.de; mdasta@berkeley.edu; szlufarska@wisc.edu; †이 저자들은이 작업에 똑같이 기여했습니다.
초록 용융 염은 청정 에너지 응용에 중요하지만 다양한 화학 공간에 걸쳐 생리적 특성을 탐색하는 것은 여전히 어려운 일입니다.
우리는 SuperSalt라고 불리는 기계 학습 간 전위 (MLIP) [cond-mat.mtrl-sci]의 개발을 제시하며, 이는 11 상자의 염화물 용융물을 대상으로하고 접근에 거의 정확성을 갖는 용융 염의 에세트 물리학을 포착합니다.
1, 2 및 11 개의 구성 요소의 시스템을 통합하는 효율적인 워크 플로우를 사용하여 SuperSalt 전위는 밀도, 벌크 모듈러스, 열 팽창 및 열 용량과 같은 열 물리학 적 특성을 정확하게 예측할 수 있습니다.
우리의 모델은 넓은 화학 공간에서 검증되어 우수한 전달성을 보여줍니다.
우리는 베이지안 최적화가 SuperSalt와 결합하여 원하는 특성으로 최적의 염 구성의 발견을 가속화 할 수있는 방법을 설명합니다.
이 작업은 추가 요소가 포함 된 것과 같은보다 복잡한 시스템으로 쉽게 확장 할 수있는 향후 연구를위한 유도를 제공합니다.
SuperSalt는 고급 에너지 응용을위한 용융 염의보다 보편적이고 효율적이며 정확한 모델링으로 이동하는 것을 나타냅니다.
1ARXIV : 2412.19353V1 키워드 : 녹은 소금, 기계 학습 간 잠재력, 기초 모델, 베이지안 최적화 1 지난 수십 년 동안 원자 규모의 시뮬레이션은 미세한 통찰력을 실험적으로 관찰 된 페일트 재료에서 미세한 통찰력을 제공하기위한 필수적인 도구로 등장했습니다.
용융 염의 수많은 과학적으로 중요한 열 물리학 및 수송 특성은 분자 역학 (MD) 시뮬레이션을 사용하여 정확하게 평가할 수 있습니다.
위스콘신, 미국 .2024 2MATERIALS DARMSTADT 기술 대학교, Darmstadt, 64287, Hessen, Germany.
3 MATERIALS 과학 및 공학, 캘리포니아 대학교, 버클리, 12 월 94720, 캘리포니아, 미국.
26 *해당 저자.
이메일 : cshen89@wisc.edu; ddmorgan@wisc.edu; 기고자 : sattarian@wisc.edu; yixuan.zhang@tu-darmstadt.de; hzhang@tmm.tu-darmstadt.de; mdasta@berkeley.edu; szlufarska@wisc.edu; †이 저자들은이 작업에 똑같이 기여했습니다.
초록 용융 염은 청정 에너지 응용에 중요하지만 다양한 화학 공간에 걸쳐 생리적 특성을 탐색하는 것은 여전히 어려운 일입니다.
우리는 SuperSalt라고 불리는 기계 학습 간 전위 (MLIP) [cond-mat.mtrl-sci]의 개발을 제시하며, 이는 11 상자의 염화물 용융물을 대상으로하고 접근에 거의 정확성을 갖는 용융 염의 에세트 물리학을 포착합니다.
1, 2 및 11 개의 구성 요소의 시스템을 통합하는 효율적인 워크 플로우를 사용하여 SuperSalt 전위는 밀도, 벌크 모듈러스, 열 팽창 및 열 용량과 같은 열 물리학 적 특성을 정확하게 예측할 수 있습니다.
우리의 모델은 넓은 화학 공간에서 검증되어 우수한 전달성을 보여줍니다.
우리는 베이지안 최적화가 SuperSalt와 결합하여 원하는 특성으로 최적의 염 구성의 발견을 가속화 할 수있는 방법을 설명합니다.
이 작업은 추가 요소가 포함 된 것과 같은보다 복잡한 시스템으로 쉽게 확장 할 수있는 향후 연구를위한 유도를 제공합니다.
SuperSalt는 고급 에너지 응용을위한 용융 염의보다 보편적이고 효율적이며 정확한 모델링으로 이동하는 것을 나타냅니다.
1ARXIV : 2412.19353V1 키워드 : 녹은 소금, 기계 학습 간 잠재력, 기초 모델, 베이지안 최적화 1 지난 수십 년 동안 원자 규모의 시뮬레이션은 미세한 통찰력을 실험적으로 관찰 된 페일트 재료에서 미세한 통찰력을 제공하기위한 필수적인 도구로 등장했습니다.
용융 염의 수많은 과학적으로 중요한 열 물리학 및 수송 특성은 분자 역학 (MD) 시뮬레이션을 사용하여 정확하게 평가할 수 있습니다.
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기