본 게시물은 AI를 활용하여 논문 “A wide-field H i mosaic of Messier 31”에 대한 주요 내용을 요약하고 분석한 결과입니다. 심층적인 정보는 원문 PDF를 직접 참고해 주시기 바랍니다.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
영문 요약 (English Summary)
—
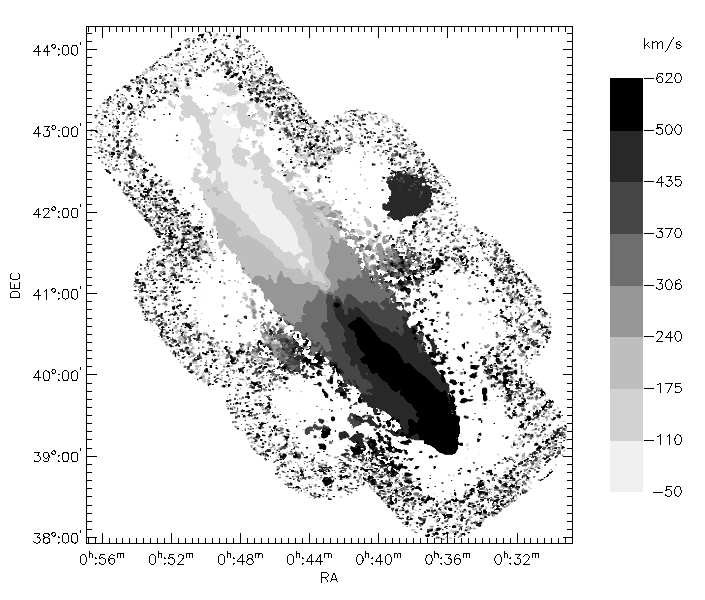
The paper investigates the rotation curve of Messier 31 (M31), a nearby galaxy, using deep HI imaging surveys. By fitting tilted ring models and analyzing rotational curves, they establish conclusively the presence of dark matter halos in M31 galaxies. Newtonian dynamics without accounting for dark matter provide poor fits to rotation curves, while modified Newtonian dynamic (MOND) provides a good fit by tracing gravitational potentials with baryonic matter density alone. The paper also explores the inclusion of dark matter halos with predicted density profiles based on hierarchical clustering and structure formation in ΛCDM cosmology, making mass models compatible with rotation curve data. Dark halo concentration parameters for best fits are C = 12, while total masses range from 1.2 to 1.3×10^12 M_sun. Core radius must be larger than 20 kpc in order to provide a good fit considering dark matter halos with constant density cores. The paper extrapolates best-fit mass models to very large galactocentric radii, confirming validity through comparisons of predicted masses using other dynamical tracers.
—
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
—
이 논문은 깊은 HI 이미징 조사를 사용하여 인근 은하 인 Messier 31 (M31)의 회전 곡선을 조사합니다. 기울어 진 링 모델을 장착하고 회전 곡선을 분석함으로써, 그들은 M31 은하에서 암흑 물질 후광의 존재를 결정적으로 확립합니다. 암흑 물질을 설명하지 않고 뉴턴 역학은 회전 곡선에 적합하지 않은 반면, 수정 된 뉴턴의 역학 (mond)은 바라 니닉 물질 밀도만으로 중력 전위를 추적함으로써 적합합니다. 이 논문은 또한 λCDM 우주론에서 계층 적 클러스터링 및 구조 형성에 기초하여 예측 된 밀도 프로파일로 암흑 물질 후광의 포함을 탐구하여 대량 모델을 회전 곡선 데이터와 양립 할 수있게한다. 최상의 적합에 대한 어두운 후광 농도 매개 변수는 C = 12이고, 총 질량은 1.2 ~ 1.3 × 10^12 m_sun입니다. 일정한 밀도 코어를 갖는 암흑 물질 후광을 고려하여 적합을 제공하려면 코어 반경이 20kpc보다 커야합니다. 이 논문은 가장 큰 질량 모델을 매우 큰 은하 중심 반경에 추정하여 다른 동적 추적기를 사용한 예측 된 질량의 비교를 통해 유효성을 확인합니다.
—
주요 기술 용어 설명 (Key Technical Terms)
이 논문의 핵심 개념을 이해하는 데 도움이 될 수 있는 주요 기술 용어와 그 설명을 제공합니다. 각 용어 옆의 링크를 통해 관련 외부 자료를 검색해 보실 수 있습니다.
- Galactic Cosmicobjects (GCO) [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 별과 행성과 다른 은하에서 발견 된 천문학적 물체; 그것들은 은하 자기장의 영향을받는 혈장, 먼지 또는 방사선으로 구성됩니다. GCO에는 우주 광선, 중성자 별, 펄서, 행성 성직자, 별 남은 잔해 등이 포함되지만 블랙홀을 제외합니다 (중력 효과로 인해).
(Original: Astronomical objects found in galaxies that differ from stars and planets; they consist of plasma, dust, or radiation, which are influenced by galactic magnetic fields. GCOs include cosmic rays, neutron stars, pulsars, planetary nebulova, stellar remnants, etc., but exclude black holes (due to their gravitational effects)) - Galactic Cosmosob [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 은하에서 발견 된 천문학적 물체; 이들은 은하의 중심을 중심으로 궤도를 돌리는 천상의 몸입니다. 여기에는 행성과 달, 별, 소행성, 유동기, 혜성, 난쟁이 행성 등이 포함되지만 검은 전기를 제외합니다 (중력 효과로 인해).
(Original: Astronomical objects found in galaxies; these are celestial bodies that orbit around the center of galaxies. They include planets and moons, stars, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, dwarf planets etc., but exclude black holes (due to their gravitational effects)) - Galactic Cosmology [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 은하에서 발견 된 천문학적 물체; 이들은 은하의 중심을 중심으로 궤도를 돌리는 천상의 몸입니다. 여기에는 행성과 달, 별, 소행성, 유성, 혜성 등이 포함되지만 중력 효과로 인해 블랙홀을 제외합니다.
(Original: Astronomical objects found in galaxies; these are celestial bodies that orbit around the center of galaxies. They include planets and moons, stars, asteroids, meteoroids, comets etc., but exclude black holes (due to their gravitational effects))
원문 발췌 및 번역 보기 (Excerpt & Translation)
원문 발췌 (English Original)
Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. ec˙m31 c⃝ESO 2018 October 23, 2018 A wide-field H i mosaic of Messier 31 II. The disk warp, rotation and the dark matter halo Edvige Corbelli1, Silvio Lorenzoni1, Rene Walterbos2, Robert Braun3, and David Thilker4 1 INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi, 5 – 50125 Firenze – Italy2009 e-mail: [edvige, silvio]@arcetri.astro.it 2 Department of Astronomy, New Mexico State University, P.O. Box 30001, MSC 4500, Las Cruces, NM 88003, USA e-mail: rwalterb@nmsu.edu 3 CSIRO-ATNF, PO Box 76, Epping, NSW 2121, AustraliaDec e-mail: Robert.Braun@csiro.au 4 Center for Astrophysical Sciences, Johns Hopkins University, 3400 North Charles Street, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA e-mail: dthilker@pha.jhu.edu21 Received; accepted ABSTRACT Aims. We test cosmological models of structure formation using the rotation curve of the nearest spiral galaxy, M31, determined using a recent deep, full-disk 21-cm imaging survey smoothed to 466 pc resolution. Methods. We fit a tilted ring model to the HI data from 8 to 37 kpc and establish conclusively the presence of a dark halo and its density distribution via dynamical analysis of the rotation curve. Results. The disk of M31 warps from 25 kpc outwards and becomes more inclined with respect to our line of sight. Newtonian dynamics without a dark matter halo provide a very poor fit to the rotation curve. In the framework of modified Newtonian dynamic (MOND) however the 21-cm rotation curve is well fitted by the gravitational potential traced by the baryonic matter density alone.[astro-ph.CO] The inclusion of a dark matter halo with a density profile as predicted by hierarchical clustering and structure formation in a ΛCDM cosmology makes the mass model in newtonian dynamic compatible with the rotation curve data. The dark halo concentration param- eter for the best fit is C = 12 and its total mass is 1.2 1012 M⊙. If a…
발췌문 번역 (Korean Translation)
천문학 및 천체 물리학 원고 번호. EC˙M31 CATESO 2018 2018 년 10 월 23 일 Messier 31 II의 광범위한 H I 모자이크. 디스크 워프, 회전 및 암흑 물질 Halo Edvige Corbelli1, Silvio Lorenzoni1, Rene Walterbos2, Robert Braun3 및 David Thilker4 1 Inaf -Sosservatorio Astro Friesico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi, 5-50125 Firenze- 이탈리아. Silvio]@arcetri.astro.it 2 뉴 멕시코 주립 대학, P.O. Box 30001, MSC 4500, LAS Cruces, NM 88003, USA 이메일 : rwalterb@nmsu.edu 3 Csiro-ATNF, PO Box 76, Epping, NSW 2121, AustraliaDec 이메일 : Robert.braun@csiro.au 4 개의 천체 학적 스키; 21218, 미국 이메일 : dthilker@pha.jhu.edu21 수신; 허용 된 추상 목표. 우리는 466 개의 PC 해상도로 평활화 된 최근의 깊은 풀 디스크 21-cm 이미징 조사를 사용하여 가장 가까운 나선 은하 M31의 회전 곡선을 사용하여 구조 형성의 우주적 모델을 테스트합니다. 행동 양식. 우리는 기울어 진 링 모델을 8 ~ 37 kpc의 HI 데이터로 구성하고 회전 곡선의 동적 분석을 통해 어두운 후광의 존재와 밀도 분포를 결정적으로 확립합니다. 결과. M31의 디스크는 25kpc 바깥쪽으로 뒤틀리고 우리 시야에 더욱 기울어집니다. 암흑 물질의 후광이없는 뉴턴 역학은 회전 곡선에 매우 열악한 것을 제공합니다. 수정 된 Newtonian Dynamic (mond)의 프레임 워크에서 21cm 회전 곡선은 바라 닉 물질 밀도만으로 추적 된 중력 전위에 의해 잘 어울립니다. [Astro-Ph.co] Hierarchical Clsing에 의해 예측 된 밀도의 고밀도와 어두운 물질 후광을 포함시키고 AR Massmom의 Mass Modic에서 구조적으로 구성된 구조적 형성에 의해 예측 된 밀도 프로파일을 포함시킵니다. 회전 곡선 데이터. 최상의 획득의 어두운 후광 농도 매개 변수는 C = 12이고 총 질량은 1.2 1012m입니다. 만약 …
출처(Source): arXiv.org (또는 해당 논문의 원 출처)
답글 남기기