This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “Market reaction to temporary liquidity crises and the permanent market impact”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
This paper analyzes market reactions and liquidity crises after sudden large variations in spreads, corresponding to temporary crisis situations. The researchers study bid-ask spread dynamics, order placement rates, distribution, and decay of the spread. They also measure permanent impacts both for generic events altering spreads and single transactions. Their findings reveal an approximately linear relation between immediate impact and permanent impact in these cases.
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
- **Data Set** [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Composed set of stocks used to perform empirical analyses (Tick Symbol, Stock Name) - **Decentralized Market** [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Bilateral exchange market mechanism involving private agreements among traders; characterized by trading without relying on a centralized market system or clearinghouse. - **Centralized Limit Order Book** [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
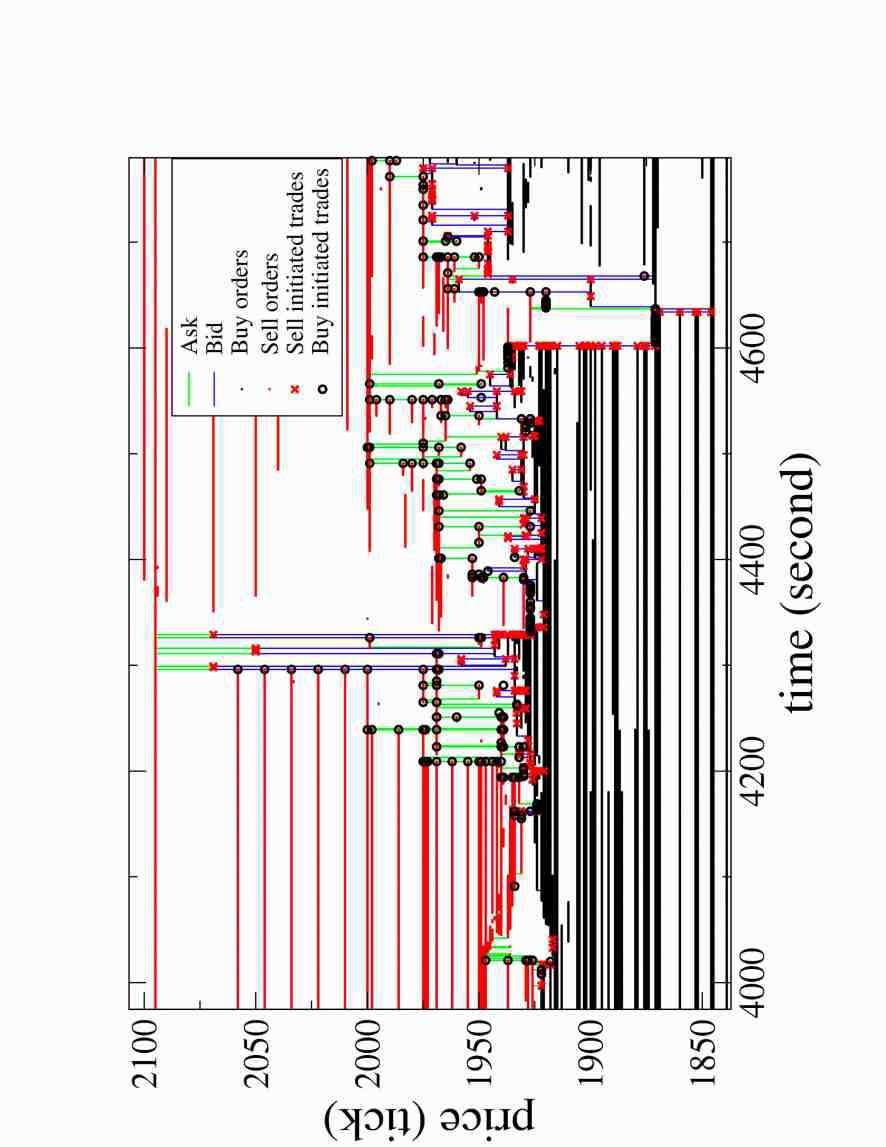
Explanation: Mechanism of double auction markets where agents can place market orders and limit orders, corresponding to the worst available price for transactions (Tick Symbol) - **Visualizing Dynamics** [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Representing dynamics in the order book using graphical representations like Figures 1-20. - **Order Submission Strategy** [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Optimal way traders decide how to read quotes; strategy involving market order placement, limit order placement, and analysis of orders placed during trading periods (Tick Symbol)
View Original Excerpt (English)
Market reaction to temporary liquidity crises and the permanent market impact Adam Ponzi,1, ∗Fabrizio Lillo,1, 2, 3, † and Rosario N. Mantegna1, 2, ‡ 1INFM-CNR, Unit`a di Palermo, Palermo, Italy 2Dipartimento di Fisica e Tecnologie Relative, University of Palermo, Viale delle Scienze, Edificio 18, I-90128 Palermo, Italy 3Santa Fe Institute, 1399 Hyde Park Road, Santa Fe, NM 87501 (Dated: July 13, 2021) We study the relaxation dynamics of the bid-ask spread and of the midprice after a sudden, large variation of the spread, corresponding to a temporary crisis of liquidity in a double auction financial market. We find that the spread decays very slowly to its normal value as a consequence2006 of the strategic limit order placement of liquidity providers. We consider several quantities, such as order placement rates and distribution, that affect the decay of the spread. We measure the permanent impact both of a generic event altering the spread and of a single transaction and weAug find an approximately linear relation between immediate and permanent impact in both cases. 3 I. INTRODUCTION in the order book, corresponding to a block of adjacent price levels containing no quotes. When such a gap exists next to the best price, a new order can remove the best Many theoretical and empirical studies have exam- quote, triggering a large midpoint price change. Thus, ined microstructure properties of double auction finan- the distribution of large price changes merely reflects the cial markets. Limit order book data provide the max- distribution of gaps in the limit order book. The market imum amount of information at the lowest aggregation order triggering the trade must have a size at least equal level. Early examples of investigations of order book to the opposite best and can therefore be of small size. A data can be found in…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
이 논문은 임시 위기 상황에 해당하는 스프레드의 갑작스런 큰 변화 후 시장 반응 및 유동성 위기를 분석합니다. 연구원들은 입찰 스프레드 역학, 주문 배치율, 분포 및 스프레드의 붕괴를 연구합니다. 또한 스프레드 변경 및 단일 거래에 대한 일반적인 이벤트에 대한 영구적 인 영향을 측정합니다. 그들의 연구 결과는이 경우 즉각적인 영향과 영구적 인 영향 사이의 대략 선형 관계를 보여줍니다.
주요 기술 용어 (한글 설명)
- **Data Set**
설명 (Korean): 경험적 분석을 수행하는 데 사용되는 재고 세트 (진드기 기호, 주식 이름)
(Original English: Composed set of stocks used to perform empirical analyses (Tick Symbol, Stock Name)) - **Decentralized Market**
설명 (Korean): 거래자들 사이의 민간 계약과 관련된 양자 교환 시장 메커니즘; 중앙 집중식 시장 시스템이나 Clearinghouse에 의존하지 않고 거래가 특징입니다.
(Original English: Bilateral exchange market mechanism involving private agreements among traders; characterized by trading without relying on a centralized market system or clearinghouse.) - **Centralized Limit Order Book**
설명 (Korean): 에이전트가 시장 주문 및 제한 주문을 할 수있는 이중 경매 시장의 메커니즘 (Tick 기호)
(Original English: Mechanism of double auction markets where agents can place market orders and limit orders, corresponding to the worst available price for transactions (Tick Symbol)) - **Visualizing Dynamics**
설명 (Korean): 그림 1-20과 같은 그래픽 표현을 사용하여 주문서에서 역학을 나타냅니다.
(Original English: Representing dynamics in the order book using graphical representations like Figures 1-20.) - **Order Submission Strategy**
설명 (Korean): 최적의 방법 거래자는 인용문을 읽는 방법을 결정합니다. 시장 주문 배치, 제한 주문 배치 및 거래 기간 동안 배치 된 주문 분석 (진드기 기호)
(Original English: Optimal way traders decide how to read quotes; strategy involving market order placement, limit order placement, and analysis of orders placed during trading periods (Tick Symbol))
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
임시 유동성 위기 및 영구 시장 영향 Adam Ponzi, 1, * Fabrizio Lillo, 1, 2, 3, † 및 Rosario N. Mantegna1, 2, ‡ 1infm-CNR, Unit`a Di Palermo, Palermo, 이탈리아 2 디지파 멘토 디 Fisica E Tecnologie, University, University, Univers. Edificio 18, I-90128 Palermo, Italy 3santa Fe Institute, 1399 Hyde Park Road, Santa Fe, NM 87501 (Dated : 7 월 13 일) 우리는 이중 공정 시장에서 유동성에 대항하여 Spredy의 큰 위기에 대항하여 갑작스런 스프레드와 대규모 변형 후 입찰 스프레드와 중간 분류의 이완 역학을 연구합니다. 우리는 유동성 제공 업체의 전략적 한계 주문 배치의 결과 2006으로 스프레드가 정상 가치로 매우 느리게 붕괴된다고 생각합니다. 우리는 스프레드의 붕괴에 영향을 미치는 주문 배치율 및 분포와 같은 여러 수량을 고려합니다. 우리는 스프레드와 단일 트랜잭션을 변경하는 일반적인 이벤트의 영구적 인 영향을 측정하고 두 경우 모두에서 즉각적인 영향과 영구적 인 영향 사이의 대략 선형 관계를 유지합니다. 3 I. 소개 주문서에서 인용문이 포함 된 인접 가격 수준 블록에 해당합니다. 이러한 차이가 최고의 가격 옆에 존재할 때, 새로운 주문은 최고의 이론 및 경험적 연구가 시험 견적을 제공하여 큰 중간 점 가격 변동을 일으키는 것을 제거 할 수 있습니다. 따라서, 이중 경매 자료의 ined 미세 구조 특성- 대규모 가격 변화의 분포는 단지 cial 시장을 반영 할 뿐이다. 제한 주문서 데이터는 한계 주문서에서 갭의 최대 분포를 제공합니다. 거래를 유발하는 가장 낮은 집계 명령의 시장의 금액은 적어도 동일한 수준을 가져야합니다. 주문서에 대한 초기 사례는 반대쪽으로 최고가되므로 크기가 작을 수 있습니다. 데이터를 찾을 수 있습니다 …
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기