How to Set Up a Mac Mini Cluster for DeepSeek Execution
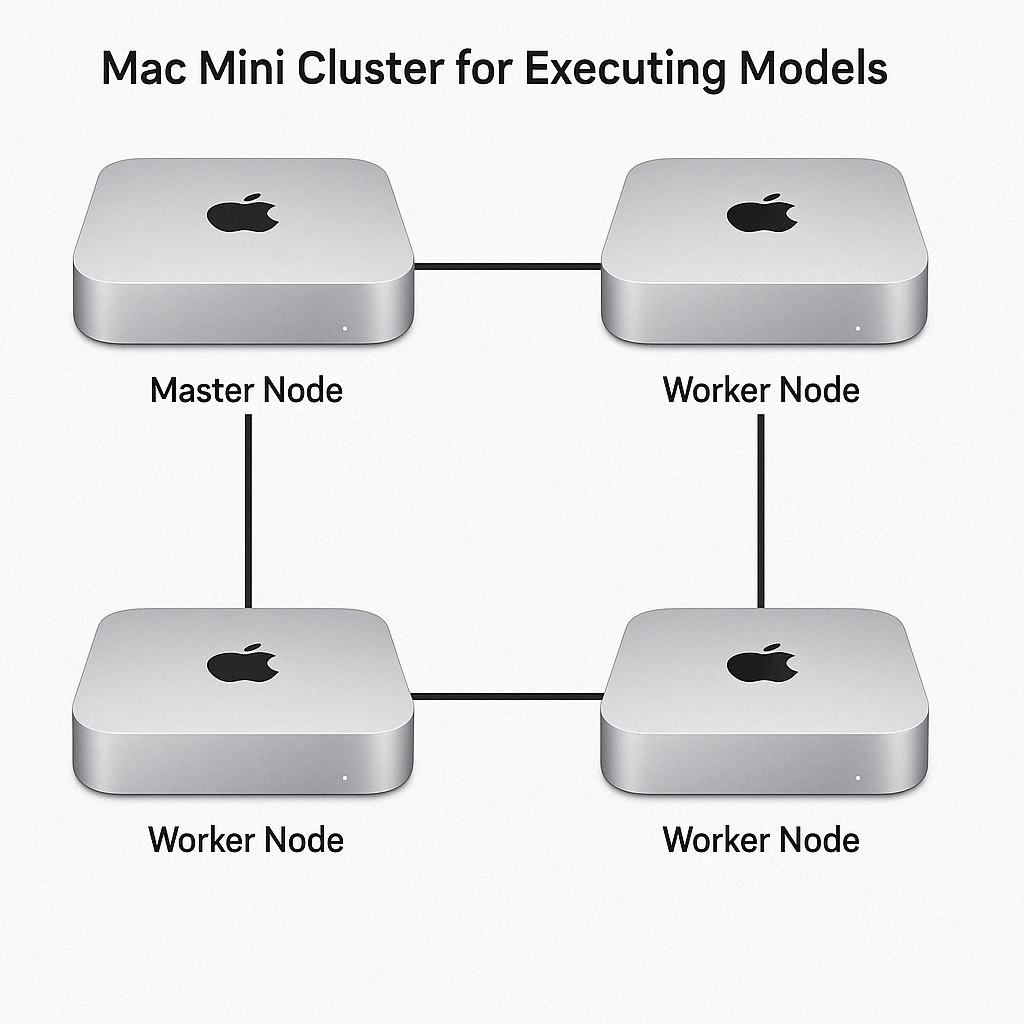
To create a cluster using multiple Mac Minis for executing models like DeepSeek, you can follow these steps:

1. Hardware Setup:
• Use multiple M1 Mac Minis with at least 16GB of unified memory.
• Connect the Mac Minis using Thunderbolt cables or via a high-speed Ethernet switch to ensure low-latency communication between nodes.
2. Cluster Management Software:
• Install a cluster orchestration tool like Kubernetes, Ray, or Open MPI on each Mac Mini. These tools will help distribute tasks across the cluster.
• Configure one Mac Mini as the master node and the others as worker nodes.
3. Model Deployment:
• Use a distributed ML framework like TensorFlow or PyTorch with Horovod for model parallelism.
• Split the model across nodes using Tensor Parallelism or Pipeline Parallelism, depending on the size of the DeepSeek model.
4. Resource Sharing:
• Leverage shared memory through Thunderbolt or network-based file systems like NFS or GlusterFS to allow seamless data sharing.
5. Optimization:
• Optimize the cluster setup using load balancing and fault tolerance mechanisms to ensure efficient task allocation.
• Enable mixed precision or quantization for large models to reduce memory and computational overhead.
6. Monitoring:
• Use tools like Prometheus and Grafana to monitor resource usage (CPU, GPU, memory, and network) across the cluster.
Considerations:
• M1 Mac Minis have limited GPU performance. For very large models like DeepSeek-70B, this cluster might struggle, as such models require high VRAM and compute power.
• If performance is critical, consider GPUs with NVLink or cloud-based solutions for large-scale LLMs.
This setup provides an affordable and scalable way to experiment with distributed computing on Mac Minis, but it is best suited for smaller models or parallel tasks.


