This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “The Physics of turbulent and dynamically unstable Herbig-Haro jets”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
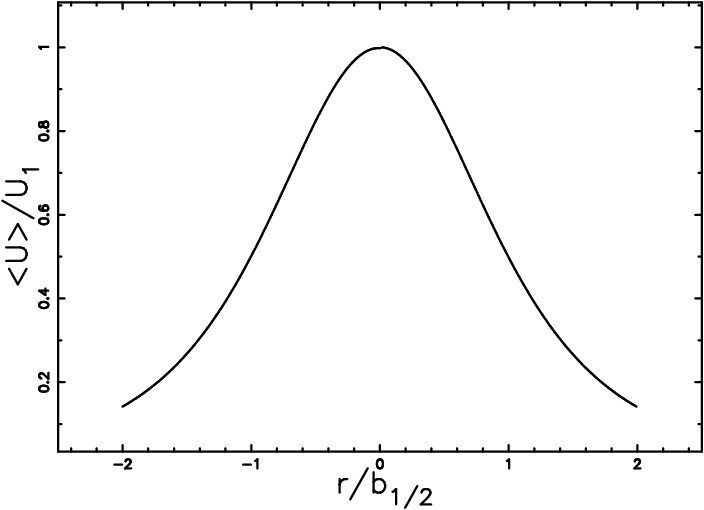
The paper explains the main objectives, methods, key findings, and conclusions related to Herbig-Haro objects (HH), which are emission objects associated with young stars. The authors explore geometrical arguments, turbulent jet models, and bipolar flows in deepening their understanding of HHs. They also present known and new formulas on turbulent round jets from chapter V in Pope et al., highlighting the self-similar solution for velocity along the main direction.
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
- Pre-main sequence objects, young stellar [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Objects associated with young stars that are studied through emission lines such as [OIII], [NeIII], etc.; includes HH objects and Bok globules. - Jet’s bending, knots [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Complex phenomena arising from turbulent jets; these features are explained in astrophysical equations adopting the combination of di�erent kinematic effects such as velocity behavior along the main direction and flow rate of kinetic energy. - Intensity or brightness behavior [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: The intensity or brightness enhancement observed through emission lines such as [FeII], Hα, etc., is explained using linear models with turbulent power.
View Original Excerpt (English)
Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/s•••••-•••-••••-• The Physics of turbulent and dynamically unstable Herbig-Haro jets L. Zaninetti 1 2009 c⃝Springer-Verlag ••••Dec Abstract The overall properties of the Herbig-Haro Curiel et al. (1989); Anglada et al. (1992); Curiel et al. 24 objects such as centerline velocity , transversal pro- (1993); Rodriguez and Reipurth (1994) ; in the infrared file of velocity , flow of mass and energy are explained see Reipurth and Aspin (1997); Reipurth, Devine, and adopting two models for the turbulent jet. The com- Bally (1998); Chrysostomou et al. (2000); Davis, Smith, plex shapes of the Herbig-Haro objects , such as the arc and Eisl¨offel (2000); Davis et al. (2002); Takami et al. in HH34 can be explained introducing the combination (2005, 2006); in the optical see Schwartz et al. (1988); of different kinematic effects such as velocity behavior Rolph, Scarrott, and Wolstencroft (1990); Scarrott along the main direction of the jet and the velocity of et al. (1990); Bohm, Raga, and Binette (1991); Uchida the star in the interstellar medium. The behavior of the et al. (1992); G´omez, Whitney, and Wood (1998); intensity or brightness of the line of emission is explored Masciadri and Raga (2001); in the ultraviolet Dopita, in three different cases : transversal 1D cut , longitu- Binette, and Schwartz (1982); Cameron and Liseau[astro-ph.GA] dinal 1D cut and 2D map. An analytical explanation (1990); Bohm, Raga, and Binette (1991); Boehm, Scott, for the enhancement in intensity or brightness such as and Solf (1991); Boehm, Noriega-Crespo, and Solf usually modeled by the bow shock is given by a careful (1993) ; in the X-ray see Pravdo and Angelini (1993); analysis of the geometrical properties of the torus. Raga, Noriega-Crespo, and Vel´azquez (2002). The HH’s are also observed through emission-line spectra Keywords Pre-main sequence objects, young stellar…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
이 논문은 젊은 별과 관련된 배출 물체 인 Herbig-Haro Objects (HH)와 관련된 주요 목표, 방법, 주요 결과 및 결론을 설명합니다. 저자는 HHS에 대한 이해를 심화시키는 데있어 기하학적 인수, 난류 제트 모델 및 양극 흐름을 탐구합니다. 또한 Pope et al.의 V 장에서 난류 라운드 제트기에 알려진 새로운 공식을 제시하며, 주요 방향을 따라 속도에 대한 자체 유사 솔루션을 강조합니다.
주요 기술 용어 (한글 설명)
- Pre-main sequence objects, young stellar
설명 (Korean): [OIII], [neiii] 등과 같은 방출 라인을 통해 연구되는 젊은 별과 관련된 물체; HH 객체와 Bok globules를 포함합니다.
(Original English: Objects associated with young stars that are studied through emission lines such as [OIII], [NeIII], etc.; includes HH objects and Bok globules.) - Jet’s bending, knots
설명 (Korean): 난류 제트기에서 발생하는 복잡한 현상; 이러한 특징은 주요 방향을 따른 속도 거동과 동역학 에너지의 유량과 같은 다른 운동 학적 효과의 조합을 채택하는 천체 물리학 방정식으로 설명됩니다.
(Original English: Complex phenomena arising from turbulent jets; these features are explained in astrophysical equations adopting the combination of di�erent kinematic effects such as velocity behavior along the main direction and flow rate of kinetic energy.) - Intensity or brightness behavior
설명 (Korean): [FEII], Hα 등과 같은 방출 라인을 통해 관찰 된 강도 또는 밝기 향상은 난류 전력을 갖는 선형 모델을 사용하여 설명됩니다.
(Original English: The intensity or brightness enhancement observed through emission lines such as [FeII], Hα, etc., is explained using linear models with turbulent power.)
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
천체 물리학 및 우주 과학 doi 10.1007/s •••••-•••-••••-• 난류 및 역동적으로 불안정한 허비그-하로 제트 L. Zaninetti 19 2009 c⃝springer-verlag의 물리학. (1989); Anglada et al. (1992); Curiel et al. 중심선 속도, 횡단 프로 (1993)와 같은 24 개의 물체; 로드리게스와 리 푸르트 (1994); 속도의 적외선 파일에서 질량과 에너지의 흐름에 대해 설명되어있다. Reipurth and Aspin (1997); reipurth, devine 및 난류 제트기에 대한 두 가지 모델을 채택합니다. 상담 (1998); Chrysostomou et al. (2000); Davis, Smith, Arc and Eisl¨o ff el (2000)과 같은 허비그-하로 물체의 플렉스 형태; Davis et al. (2002); Takami et al. HH34에서 조합을 도입하는 것으로 설명 될 수있다 (2005, 2006). 광학에서 Schwartz et al. (1988); 속도 동작 Rolph, Scarrott 및 Wolstencroft (1990)와 같은 다른 운동 학적 효과의 영향; 제트의 주요 방향과 et al. (1990); Bohm, Raga 및 Binette (1991); 성간 매체의 스타 Uchida. 등의 행동. (1992); G´omez, Whitney 및 Wood (1998); 방출 라인의 강도 또는 밝기는 Masciadri and Raga (2001); 자외선 도피타에서, 세 가지 다른 경우 : 가로 1D 컷, Longitu-binette 및 Schwartz (1982); Cameron and Liseau [Astro-Ph.ga] Dinal 1D Cut 및 2D 맵. 분석 설명 (1990); Bohm, Raga 및 Binette (1991); Boehm, Scott, 및 Solf (1991)와 같은 강도 또는 밝기 향상; Boehm, Noriega-Crespo 및 SOLF는 일반적으로 활 충격에 의해 모델링됩니다. X- 레이에서는 Pravdo and Angelini (1993)를 참조하십시오. Torus의 기하학적 특성 분석. Raga, Noriega-Crespo 및 Vel´azquez (2002). HH ‘s는 또한 방출 라인 스펙트럼 키워드 프리 메인 시퀀스 객체, Young Stellar를 통해 관찰됩니다.
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기