< Summary (English) >
English Summary:
This paper presents a study of ground vibrational state SiO emission in the VLA BAaDE survey.
The researchers explore the prevalence and characteristics of 28SiO J = 1 −0, v = 0 emission using a subsample of the Bulge Asymmetries and Dynamical Evolution (BAaDE) survey of stellar SiO masers.
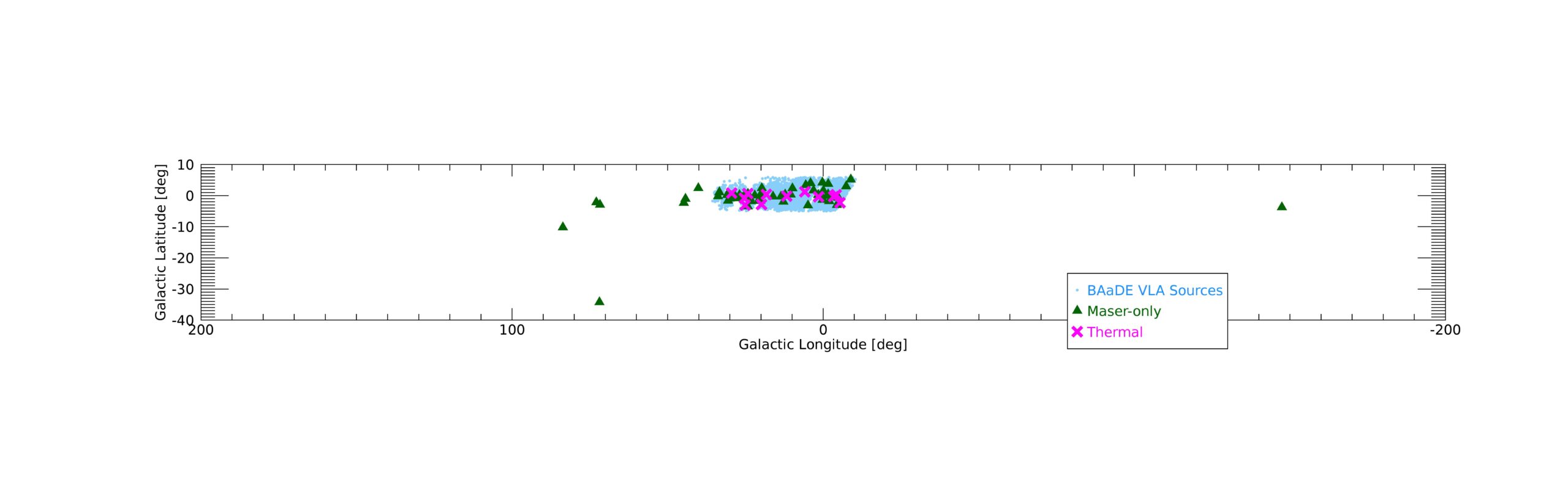
They identify 90 detections of maser, thermal, or composite 28SiO J = 1 −0, v = 0 emission out of approximately 13,000 candidate spectra from the NSF’s Karl G.
Jansky Very Large Array (VLA).
The detected sources are likely asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars belonging to a bright, foreground Milky Way stellar disk population.
This study is the largest survey of stellar ground-vibrational-state SiO masers to date and will be expanded to include the entire VLA BAaDE dataset when data reduction for the 18,988 target sources is completed.
This paper presents a study of ground vibrational state SiO emission in the VLA BAaDE survey.
The researchers explore the prevalence and characteristics of 28SiO J = 1 −0, v = 0 emission using a subsample of the Bulge Asymmetries and Dynamical Evolution (BAaDE) survey of stellar SiO masers.
They identify 90 detections of maser, thermal, or composite 28SiO J = 1 −0, v = 0 emission out of approximately 13,000 candidate spectra from the NSF’s Karl G.
Jansky Very Large Array (VLA).
The detected sources are likely asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars belonging to a bright, foreground Milky Way stellar disk population.
This study is the largest survey of stellar ground-vibrational-state SiO masers to date and will be expanded to include the entire VLA BAaDE dataset when data reduction for the 18,988 target sources is completed.
< 요약 (Korean) >
이 논문은 천문대의 VLA BAaDE 조사를 활용하여 28SiO J = 1 -0, v = 0 진동 원자 잠재 감소에 대한 발견 및 특성을 연구합니다.
연구자들은 천문대 SiO 마서의 부분 조사인 불균형 대칭 및 동적 진화(BAaDE) 조사의 28SiO J = 1 -0, v = 0 감소에 대한 90 발견을 확인하였습니다.
이들은 약 13,000 대상 중 대략 13,000 대의 NSF의 칼 G.
대규모 배경 어레이 조사(VLA) 데이터를 사용하여 수행했습니다.
발견된 소스는 우주 천체 진화 중간 단계인 비상성 거대 별의 밝고, 우리 가лакти크 앞부분에 속한 많은 팔레트를 갖고 있습니다.
이 연구는 지금까지 가장 큰 연구 중 하나인 천문대 원자 잠재 감소의 스타 진동 원자 마서 조사입니다.
이 연구에서는 VLA BAaDE 데이터셋의 전체를 포함하여 18,988 대상의 데이터 처리가 완료될 때까지 진행됩니다.
Einsatzzustand SiO-Emission in der VLA BAaDE-Studie V.
Dike, M.
R.
Morris, R.
M.
Rich, M.
O.
Lewis, L.
H.
Quiroga-Nu˜nez, M.
C.
Stroh, A.
Trapp und M.
J.
Claussen
* [1] 제목: “Bulge Asymmetries and Dynamical Evolution (BAaDE) Survey”; 저자/출처: Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California Los Angeles, Department of Physics and
연구자들은 천문대 SiO 마서의 부분 조사인 불균형 대칭 및 동적 진화(BAaDE) 조사의 28SiO J = 1 -0, v = 0 감소에 대한 90 발견을 확인하였습니다.
이들은 약 13,000 대상 중 대략 13,000 대의 NSF의 칼 G.
대규모 배경 어레이 조사(VLA) 데이터를 사용하여 수행했습니다.
발견된 소스는 우주 천체 진화 중간 단계인 비상성 거대 별의 밝고, 우리 가лакти크 앞부분에 속한 많은 팔레트를 갖고 있습니다.
이 연구는 지금까지 가장 큰 연구 중 하나인 천문대 원자 잠재 감소의 스타 진동 원자 마서 조사입니다.
이 연구에서는 VLA BAaDE 데이터셋의 전체를 포함하여 18,988 대상의 데이터 처리가 완료될 때까지 진행됩니다.
Einsatzzustand SiO-Emission in der VLA BAaDE-Studie V.
Dike, M.
R.
Morris, R.
M.
Rich, M.
O.
Lewis, L.
H.
Quiroga-Nu˜nez, M.
C.
Stroh, A.
Trapp und M.
J.
Claussen
* [1] 제목: “Bulge Asymmetries and Dynamical Evolution (BAaDE) Survey”; 저자/출처: Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California Los Angeles, Department of Physics and
< 기술적 용어 설명 >
< 참고 논문 또는 관련 자료 >
< Excerpt (English) >
Draft version September 14, 2022 Typeset using LATEX modern style in AASTeX63 Ground Vibrational State SiO Emission in the VLA BAaDE Survey V. Dike,1 M. R. Morris,1 R. M. Rich,1 M. O. Lewis,2, 3 L. H. Quiroga-Nu˜nez,3, 2, ∗M. C. Stroh,4 A. C. Trapp,1 and M. J. Claussen3 1Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California Los Angeles 2Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of New Mexico 3National Radio Astronomy Observatory 4Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Northwestern University ABSTRACT Using a subsample of the Bulge Asymmetries and Dynamical Evolution (BAaDE) survey of stellar SiO masers, we explore the prevalence and characteristics of 28SiO J = 1 −0, v = 0 emission. We identify 90 detections of maser, thermal, or composite 28SiO J = 1 −0, v = 0 emission out of approximately 13,000 candidate spectra from the NSF’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA). We find that the detected sources are likely asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars belonging to a bright, foreground Milky Way stellar disk population. For the 32 sources showing thermal components, we extract values for outflow velocity by fitting thermal line profiles. We find a range of circumstellar envelope expansion velocities, and compare to previously recorded OH and CO expansion velocities. This preliminary survey is already the largest study of stellar ground-vibrational-state SiO masers to date, and will be expanded to include the entire VLA BAaDE dataset when data reduction for the 18,988 target sources is completed. 1. INTRODUCTION SiO emission, thought to be produced above the atmospheres of AGB stars in material that has been levitated by stellar pulsations, is a powerful tool for probing the conditions of the AGB circumstellar environment. SiO masers have long been observed in the excited vibrational states (v ≥1) since their discovery in the Orion nebula by Snyder & Buhl (1974), but, with a few exceptions, they have been found in the circumstellar envelopes of evolved, mass-losing stars. Originally, the emission found in the ground vibrational state was observed to be thermal (in this paper, “thermal” means unaffected by maser amplification, rather than “thermalized”). The first surveys of stellar SiO emission focused on the J = 2 −1, v = 0 thermal line (Dickinson et al. 1978, Morris et al. 1979). Thermal lines ∗L. H. Quiroga-Nu˜nez is a Jansky Fellow of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory. arXiv:2012.09348v2 [astro-ph.GA] 13 Sep 2022 2 are useful because their line width gives a measure of the local velocity of the stellar outflow, and their line intensity provides a measure of how much of the gas-phase SiO in the extended envelope has survived grain formation (Morris & Alcock 1977). Circumstellar masing from the J = 1−0, v = 0 state was predicted by the radiative pumping model of Kwan & Scoville (1974). A tentative detection of maser emission from the ground vibrational state (v = 0) of 28SiO in NML Cyg was reported by Dickinson et al. (1978). Chandler & de Pree (1995) observed…
< 번역 (Korean) >
2022 년 9 월 14 일 드래프트 버전 Aastex63에서 라텍스 현대 스타일을 사용한 조판체 VLA Baade Survey V.
Dike, 1 M.
R.
Morris, 1 M.
O.
Lewis, 2, 3 L.
H.
Quiroga-Nu ~ Nez, 3, 2, * m.
C.
Stroh, 4 A.
C.
Trapp, 1 및 M.
J.
Claussen3 1 캘리포니아 로스 앤젤레스 대학교 물리학 및 천문학, 뉴 멕시코 대학교 3National Radio Astronomy Observomy 4Center, Astrophysics and Astronomy and Astronomy and Astronomy and Astronom Memetres의 초기 연구를위한 학제 간 탐사 및 연구를위한 물리학 및 천문학의 물리학 및 천문학 물리학 및 천문학 2 부.
(Baade) Stellar Sio Masers의 조사에서, 우리는 28SIO J = 1 −0, v = 0 방출의 유병률과 특성을 탐구합니다.
우리는 NSF의 Karl G.
Jansky 매우 큰 배열 (VLA)에서 약 13,000 개의 후보 스펙트럼 중에서 MASER, THERMAL 또는 COMPOSITE 28SIO J = 1 −0, V = 0 방출의 90 개의 검출을 식별합니다.
우리는 감지 된 소스가 밝고 전경하는 은하수의 디스크 개체군에 속하는 AGB (Astymptotic Giant Branch) 스타 일 가능성이 높습니다.
열 구성 요소를 보여주는 32 개의 소스의 경우 열선 프로파일을 뽑아 아웃 흐름 속도에 대한 값을 추출합니다.
우리는 다양한 환경 봉투 확장 속도를 찾았으며 이전에 기록 된 OH 및 CO 확장 속도와 비교합니다.
이 예비 조사는 이미 현재까지 현명한 지상 진동 상태 SIO Masers에 대한 가장 큰 연구이며 18,988 개의 대상 소스에 대한 데이터 감소가 완료 될 때 전체 VLA Baade 데이터 세트를 포함하도록 확장 될 것입니다.
1.
소개 SIO 방출은 별 맥박에 의해 침입 된 재료에서 AGB 별의 대기 위에서 생산되는 것으로 생각되며 AGB 상황 환경의 조건을 조사하기위한 강력한 도구입니다.
Sio Masers는 Snyder & Buhl (1974)에 의해 Orion Nebula에서 발견 된 이래로 흥분된 진동 상태 (v ≥1)에서 오랫동안 관찰되어 왔지만, 몇 가지 예외를 제외하고는 진화 된 대량의 별들의 상황에 따라 발견되었습니다.
원래, 지상 진동 상태에서 발견되는 방출은 열이 관찰되었다 (이 논문에서,“열”은“열 화”이 아니라 Maser 증폭에 영향을받지 않는 것을 의미한다).
STELLAR SIO 방출의 첫 번째 조사는 J = 2 −1, v = 0 열선에 중점을 두었습니다 (Dickinson et al.
1978, Morris et al.
1979).
열선 * l.
H.
Quiroga-Nu ~ Nez는 National Radio Astronomy Observatory의 Jansky 동료입니다.
ARXIV : 2012.09348V2 [Astro-PH.Ga] 13 9 월 2022 년 2 월 2 일 선 너비는 스텔라 아웃 흐름의 국소 속도를 측정하고 선 강도는 확장 된 봉투의 가스상 SIO가 곡물 형성을 살아남은 방법을 측정하기 때문에 유용합니다 (Morris & Alcock 1977).
j = 1-0으로부터의 환경 마스터는 v = 0 상태가 Kwan & Scoville (1974)의 복사 펌핑 모델에 의해 예측되었다.
NML CYG에서 28SIO의지면 진동 상태 (V = 0)로부터의 마스 방출의 잠정적 인 검출은 Dickinson et al.
(1978).
Chandler & de Pree (1995) 관찰 …
Dike, 1 M.
R.
Morris, 1 M.
O.
Lewis, 2, 3 L.
H.
Quiroga-Nu ~ Nez, 3, 2, * m.
C.
Stroh, 4 A.
C.
Trapp, 1 및 M.
J.
Claussen3 1 캘리포니아 로스 앤젤레스 대학교 물리학 및 천문학, 뉴 멕시코 대학교 3National Radio Astronomy Observomy 4Center, Astrophysics and Astronomy and Astronomy and Astronomy and Astronom Memetres의 초기 연구를위한 학제 간 탐사 및 연구를위한 물리학 및 천문학의 물리학 및 천문학 물리학 및 천문학 2 부.
(Baade) Stellar Sio Masers의 조사에서, 우리는 28SIO J = 1 −0, v = 0 방출의 유병률과 특성을 탐구합니다.
우리는 NSF의 Karl G.
Jansky 매우 큰 배열 (VLA)에서 약 13,000 개의 후보 스펙트럼 중에서 MASER, THERMAL 또는 COMPOSITE 28SIO J = 1 −0, V = 0 방출의 90 개의 검출을 식별합니다.
우리는 감지 된 소스가 밝고 전경하는 은하수의 디스크 개체군에 속하는 AGB (Astymptotic Giant Branch) 스타 일 가능성이 높습니다.
열 구성 요소를 보여주는 32 개의 소스의 경우 열선 프로파일을 뽑아 아웃 흐름 속도에 대한 값을 추출합니다.
우리는 다양한 환경 봉투 확장 속도를 찾았으며 이전에 기록 된 OH 및 CO 확장 속도와 비교합니다.
이 예비 조사는 이미 현재까지 현명한 지상 진동 상태 SIO Masers에 대한 가장 큰 연구이며 18,988 개의 대상 소스에 대한 데이터 감소가 완료 될 때 전체 VLA Baade 데이터 세트를 포함하도록 확장 될 것입니다.
1.
소개 SIO 방출은 별 맥박에 의해 침입 된 재료에서 AGB 별의 대기 위에서 생산되는 것으로 생각되며 AGB 상황 환경의 조건을 조사하기위한 강력한 도구입니다.
Sio Masers는 Snyder & Buhl (1974)에 의해 Orion Nebula에서 발견 된 이래로 흥분된 진동 상태 (v ≥1)에서 오랫동안 관찰되어 왔지만, 몇 가지 예외를 제외하고는 진화 된 대량의 별들의 상황에 따라 발견되었습니다.
원래, 지상 진동 상태에서 발견되는 방출은 열이 관찰되었다 (이 논문에서,“열”은“열 화”이 아니라 Maser 증폭에 영향을받지 않는 것을 의미한다).
STELLAR SIO 방출의 첫 번째 조사는 J = 2 −1, v = 0 열선에 중점을 두었습니다 (Dickinson et al.
1978, Morris et al.
1979).
열선 * l.
H.
Quiroga-Nu ~ Nez는 National Radio Astronomy Observatory의 Jansky 동료입니다.
ARXIV : 2012.09348V2 [Astro-PH.Ga] 13 9 월 2022 년 2 월 2 일 선 너비는 스텔라 아웃 흐름의 국소 속도를 측정하고 선 강도는 확장 된 봉투의 가스상 SIO가 곡물 형성을 살아남은 방법을 측정하기 때문에 유용합니다 (Morris & Alcock 1977).
j = 1-0으로부터의 환경 마스터는 v = 0 상태가 Kwan & Scoville (1974)의 복사 펌핑 모델에 의해 예측되었다.
NML CYG에서 28SIO의지면 진동 상태 (V = 0)로부터의 마스 방출의 잠정적 인 검출은 Dickinson et al.
(1978).
Chandler & de Pree (1995) 관찰 …
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기