본 게시물은 AI를 활용하여 논문 “First stars XIV. Sulfur abundances in extremely metal-poor stars ⋆”에 대한 주요 내용을 요약하고 분석한 결과입니다. 심층적인 정보는 원문 PDF를 직접 참고해 주시기 바랍니다.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
영문 요약 (English Summary)
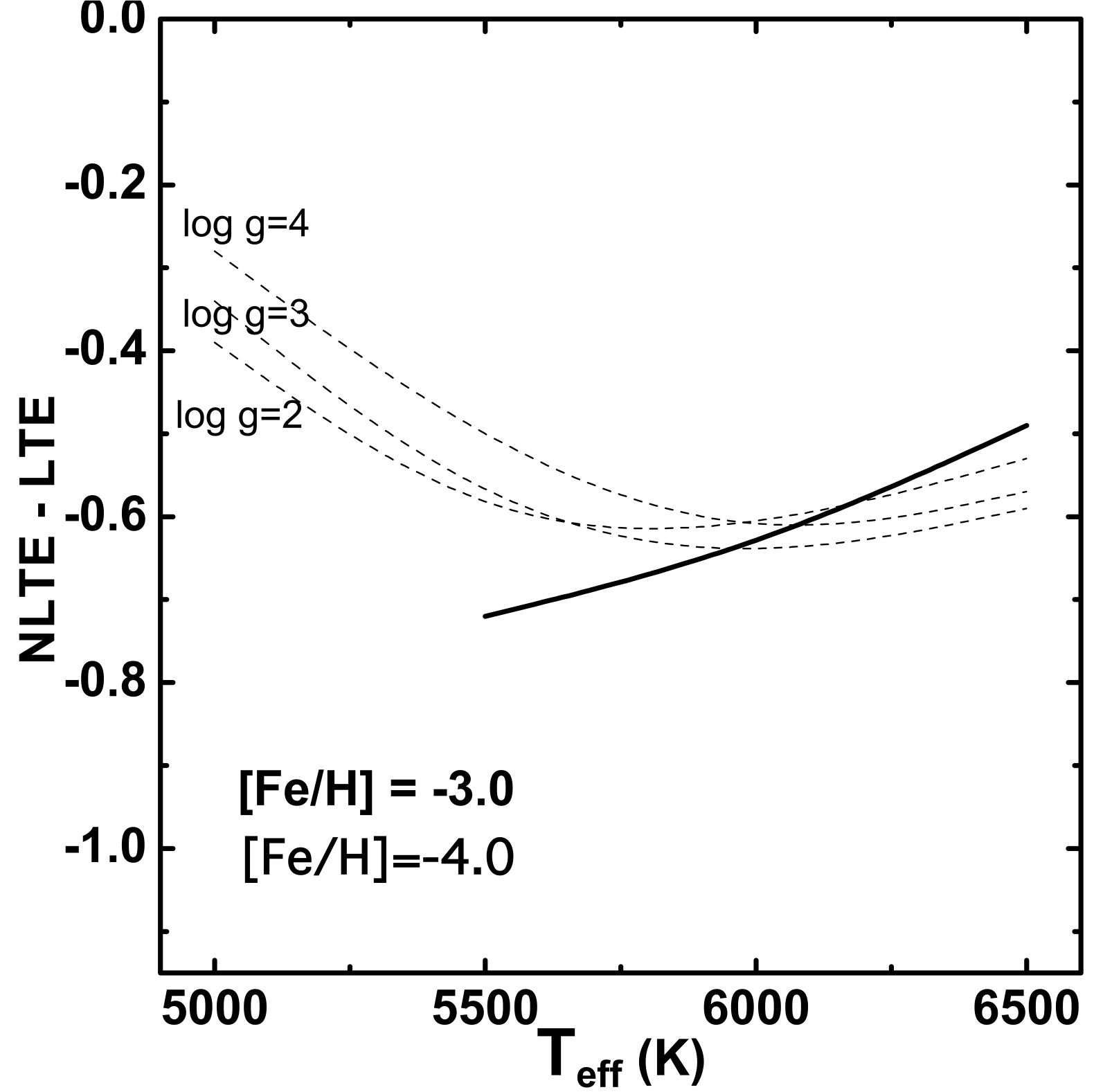
The paper focuses on the sulfur abundance in extremely metal-poor stars and aims to precisely measure this abundance using NLTE analysis of lines belonging to multiplet 1 of S I at wavelengths ranging from 921.29 nm to 923.75 nm. The study includes 33 very metal-poor stars, with a particular focus on extremely metal-poor (EMP) stars having [Fe/H] < −2.9. By analyzing the lines of multiplet 1 in these stars, researchers hope to better understand sulfur behavior compared to other elements such as magnesium and calcium. The paper suggests that S abundances behave like other alpha-elements with [S/Fe] remaining approximately constant below [Fe/H] = −3 but observes a slight decrease in [S/Fe] versus [Mg/H]. Researchers also derive an upper limit for sulfur abundance [S/Zn] ratio in extremely metal-poor stars, finding it to be solar.
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
이 논문은 극도로 금속성 별의 황 풍부도에 중점을두고 921.29 nm 내지 923.75 nm 범위의 파장에서 S I의 다중 줄 1에 속하는 라인의 NLTE 분석을 사용 하여이 풍부도를 정확하게 측정하는 것을 목표로한다. 이 연구에는 33 개의 매우 금속이 부족한 별이 포함되어 있으며, [Fe/h] <-2.9를 가진 매우 금속이 부족한 (EMP) 별에 특히 중점을 둡니다. 이 별에서 멀티 플 레 1 라인을 분석함으로써 연구자들은 마그네슘 및 칼슘과 같은 다른 요소에 비해 황수방을 더 잘 이해하기를 희망합니다. 이 논문은 [s/fe]가 [Fe/h] = -3 아래에 남아있는 다른 알파 요소와 같이 S 풍부도가 행동하지만 [s/fe] 대 [mg/h]의 약간의 감소를 관찰한다는 것을 시사한다. 연구원들은 또한 매우 금속이 빈약 한 별에서 황 풍부 [S/Zn] 비율의 상한을 도출하여 태양이라는 것을 발견했습니다.
주요 기술 용어 설명 (Key Technical Terms)
이 논문의 핵심 개념을 이해하는 데 도움이 될 수 있는 주요 기술 용어와 그 설명을 제공합니다. 각 용어 옆의 링크를 통해 관련 외부 자료를 검색해 보실 수 있습니다.
- Sulfur abundances [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 921.29 nm 내지 923.75 nm 범위의 파장에서 S I의 다중 줄 1에 속하는 라인의 NLTE 분석을 사용하여 매우 금속이 부족한 별에서 황 풍부의 정확한 측정. 연구원들은 마그네슘과 칼슘과 같은 다른 요소들에 비해 황수방을 더 잘 이해하는 것을 목표로합니다.
(Original: Precise measurement of sulfur abundance in extremely metal-poor stars using NLTE analysis of lines belonging to multiplet 1 of S I at wavelengths ranging from 921.29 nm to 923.75 nm. Researchers aim to better understand sulfur behavior compared to other elements such as magnesium and calcium.) - Alpha-elements [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 1 세대의 별을 포함하여 대규모 타입 II 초신성에서 우선적으로 형성되었다. 여기에는 황, 마그네슘, 칼슘 등이 포함되며, 일반적으로 Heger & Woosley의 SN 모델 수율과 같은 캡처 요소 소스로 간주됩니다.
(Original: Elements formed preferentially in massive type II supernovae, including those of the first generations of stars. These include Sulfur, Magnesium, Calcium, etc., which are generally considered as capture element sources such as SN models yields by Heger & Woosley.) - NLTE analysis [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 제 2의 황 1에 속하는 라인에 대한 비선형 효과 나는 921.29 nm 내지 923.75 nm 범위의 파장에서 S I의 멀티 플렛 1에 속하는 라인의 NLTE 분석을 사용하여 매우 금속성 불완전한 별에서 황가 풍부한 별의 정확한 측정에 사용했다. 연구원들은 마그네슘과 칼슘과 같은 다른 요소들에 비해 황수방을 더 잘 이해하는 것을 목표로합니다.
(Original: Non-linear effect on lines belonging to multiplet 1 of sulfur I used for precise measurement of sulfur abundance in extremely metal-poor stars using NLTE analysis of lines belonging to multiplet 1 of S I at wavelengths ranging from 921.29 nm to 923.75 nm. Researchers aim to better understand sulfur behavior compared to other elements such as magnesium and calcium.) - Multiplets [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 특정 요소에 속하는 스펙트럼 라인의 수집,이 경우 황. 이 논문은 921.29 nm 내지 923.75 nm의 파장 1에 속하는 라인 1에 속하는 라인 1의 NLTE 분석을 사용하여 극도로 금속이 부족한 별에서 921.29 nm 내지 923.75 nm 범위의 파장 1에 중점을 둔다. 연구원들은 마그네슘과 칼슘과 같은 다른 요소들에 비해 황수방을 더 잘 이해하는 것을 목표로합니다.
(Original: Collections of spectral lines belonging to a particular element, in this case Sulfur. The paper focuses on multiplet 1 at wavelengths ranging from 921.29 nm to 923.75 nm for precise measurement of sulfur abundance in extremely metal-poor stars using NLTE analysis of lines belonging to multiplet 1 of S I at wavelengths ranging from 921.29 nm to 923.75 nm. Researchers aim to better understand sulfur behavior compared to other elements such as magnesium and calcium.) - ISM [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
설명: 은하 내의 행성 시스템 사이의 문제를 언급하는 성간 매체. 연구원들은 S I의 다중 줄 1에 속하는 라인의 NLTE 분석을 사용하여 921.29 nm에서 923.75 nm 범위의 파장에서 921.29 NM에서 921.75 NM에 비해 SELENGTER의 2 개의 멀티 플리트 1에 속하는 라인의 NLTE 분석을 사용하여 매우 금속 팝 오루 별의 황색 풍부도의 정확한 측정을 위해 923.75 NM에서 더 잘 이해합니다. ISM 맥락에서 마그네슘 및 칼슘과 같은 요소.
(Original: Interstellar medium, referring to the matter between planetary systems within galaxies. Researchers use NLTE analysis of lines belonging to multiplet 1 of S I at wavelengths ranging from 921.29 nm to 923.75 nm for precise measurement of sulfur abundance in extremely metal-popoor stars using NLTE analysis of lines belonging to multiplet 1 of S I at wavelengths ranging from 921.29 nm to 923.75 nm, aiming to better understand sulfur behavior compared to other elements such as magnesium and calcium in ISM context.)
원문 발췌 및 번역 보기 (Excerpt & Translation)
원문 발췌 (English Original)
1 Astronomy (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) & c⃝ESO 2022 Astrophysics First stars XIV. Sulfur abundances in extremely metal-poor stars ⋆ M. Spite1, E. Caffau2,1, S.M. Andrievsky1,3, S.A. Korotin3, E. Depagne4, F. Spite1, P. Bonifacio1, H.-G. Ludwig2, R. Cayrel1, P. Franc¸ois1, V. Hill5, B. Plez6, J. Andersen7,8, B. Barbuy9, T. C. Beers10, P. Molaro11, B. Nordstr¨om7, and F. Primas12 1 GEPI Observatoire de Paris, CNRS, Universit´e Paris Diderot, F-92195 Meudon Cedex France e-mail : monique.spite@obspm.fr 2 Zentrum f¨ur Astronomie der Universit¨at Heidelberg, Landessternwarte, K¨onigstuhl 12, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany2011 3 Department of Astronomy and Astronomical Observatory, Odessa National University, and Isaac Newton Institute of Chile, Odessa branch, Shevchenko Park, 65014, Odessa, Ukraine 4Jan Las Cumbres Observatory, Goleta, CA 93117, USA 5 Observatoire de la Cˆote d’Azur, CNRS UMR6202, BP4229, 06304 Nice Cedex 4, France8 6 GRAAL, Universit´e de Montpellier II, F-34095 Montpellier Cedex 05, France 7 The Niels Bohr Institute, Astronomy, Juliane Maries Vej 30, DK-2100 Copenhagen, Denmark 8 Nordic Optical Telescope, Apartado 474, E-38700 Santa Cruz de La Palma, Spain 9 Universidade de S˜ao Paulo, Departamento de Astronomia, Rua do Mat˜ao 1226, 05508-900 S˜ao Paulo, Brazil 10 Department of Physics & Astronomy and JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA 11 Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste, Via Tiepolo 11, I-34143 Trieste, Italy 12 European Southern Observatory (ESO), Karl-Schwarschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching b. M¨unchen, Germany[astro-ph.SR] ABSTRACT Context. Precise S abundances are important in the study of the early chemical evolution of the Galaxy. In particular the site of the formation remains uncertain because, at low metallicity, the trend of this α-element versus [Fe/H] remains unclear. Moreover, although sulfur is not bound significantly in dust grains in the ISM, it seems to behave differently in DLAs and old metal-poor stars….
발췌문 번역 (Korean Translation)
1 천문학 (DOI : 나중에 손으로 삽입 될 것입니다) & C⃝eso 2022 천체 물리학 첫 번째 별 XIV. 극도로 금속성 별의 유황 풍부함 ⋆ M. stite1, E. ca ff au2,1, S.M. Andrievsky1,3, S.A. Korotin3, E. Depagne4, F. Spite1, P. Bonifacio1, H.-G. Ludwig2, R. Cayrel1, P. Franc¸ois1, V. Hill5, B. Plez6, J. Andersen7,8, B. Barbuy9, T.C. Beers10, P. Molaro11, B. Nordstr¨om7 및 F. Primas12 1 Gepi Observatoire de Paris, Cnrs, CNR, Universit’e Paris Diderot, f-92195 Meudon e e Paris Diderot : monique.spite@obspm.fr 2 Zentrum f¨ur Astronomie der Universitat at Heidelberg, Landestternwarte, K¨onigstuhl 12, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany2011 3 천문학 및 천문학적 천문학 부서, Odessa National University 및 Isaac Newton Institute of Chile, Odcho Park, 65014, Odcho Park, Isaac Newton Institute. 우크라이나 4jan las cumbres 전망대, 골레타, 캘리포니아 93117, USA 5 Observatoire de la c; Cnrs UMR6202, BP4229, 06304 NICE CEDEX 4, FRANCE8 6 GRAAL, Universit’e de Montpellier II, F-34095 Montpellier Cedex 05. 연구소, 천문학, Juliane Maries VEJ 30, DK-2100 COPENHAGEN, DENMARK 8 북유럽 광학 망원경, Apartado 474, E-38700 Santa Cruz de La Palma, 스페인 9 Universidade de S ~ Ao Paulo, Departamento de Astronomia, Rua do Mat ~ 1226, 05508-900 S ~ Ooo oo oo, and aoo aoo and aoo Paulo의 부서. 천문학 및 Jina : 미시간 주립 대학교, 이스트 랜싱, MI 48824, USA 11 Istituto Nazionale Di AstrofiCica, Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste, Tiepolo 11, I-34143 TRIESTE, 12 유럽 남부 관측소 (ESO), Karl-Shard. 2, D-85748 Garching b. M¨unchen, 독일 [Astro-ph.sr] 초록 상황. 은하의 초기 화학 진화에 대한 연구에서 정확한 S 풍부도가 중요합니다. 특히, 낮은 금속성 에서이 α- 요소 대 [Fe/h]의 경향이 불분명하기 때문에 형성 부위는 불확실한 상태로 남아있다. 더욱이, 황은 ISM의 먼지 곡물에서 유황이 크게 결합되지는 않지만, DLA와 오래된 금속 별에서 다른 별에서는 다른 것처럼 보인다 ….
출처(Source): arXiv.org (또는 해당 논문의 원 출처)
답글 남기기