< Summary (English) >
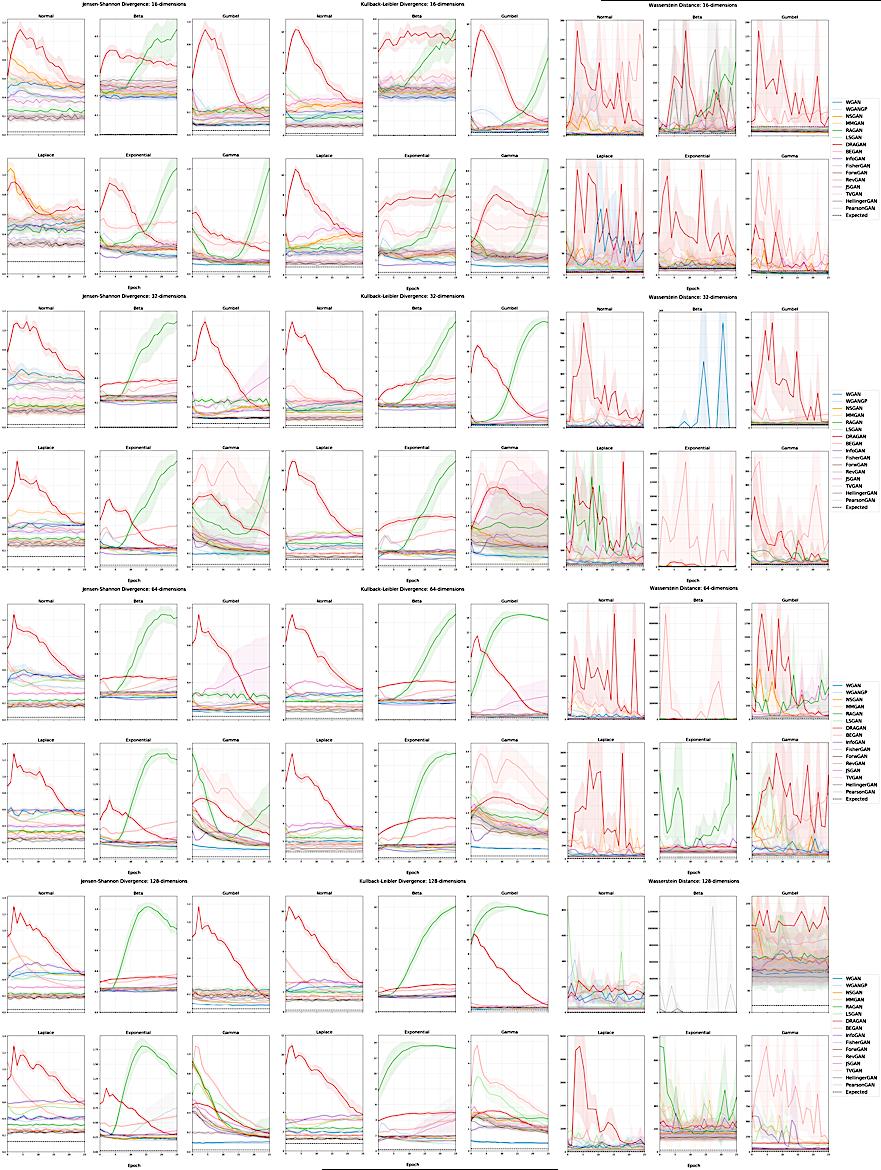
This paper investigates the performance of sixteen GAN variants on six explicitly parameterized multivariate distributions of varying dimensionalities and training set sizes.
The authors observe that GANs exhibit similar performance trends across dimensionalities, learning depends on the underlying distribution and its complexity, the number of training samples can have a large impact on performance, evaluation and relative comparisons are metric-dependent, diverse sets of hyperparameters can produce a “best” result, and some GANs are more robust to hyperparameter changes than others.
The authors observe that GANs exhibit similar performance trends across dimensionalities, learning depends on the underlying distribution and its complexity, the number of training samples can have a large impact on performance, evaluation and relative comparisons are metric-dependent, diverse sets of hyperparameters can produce a “best” result, and some GANs are more robust to hyperparameter changes than others.
< 요약 (Korean) >
이 논문은 16종의 GAN 변형을 6개의 명시적으로 매개변수화된 다차원 분포에서의 성능을 조사합니다.
각각의 차원과 훈련 데이터 집합의 크기에 따른 성능 트렌드를 확인하며, 학습은 데이터 분포와 그 복잡성에 따라 달라진다는 것을 발견했습니다.
또한 성능 평가와 상대적인 비교는 지표에 따라 다르며, 하이퍼파라미터의 다양한 조합으로는 “최고”의 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
일부 GAN은 하이퍼파라미터 변경에 비교적 강력해질 때 발견되었습니다.
각각의 차원과 훈련 데이터 집합의 크기에 따른 성능 트렌드를 확인하며, 학습은 데이터 분포와 그 복잡성에 따라 달라진다는 것을 발견했습니다.
또한 성능 평가와 상대적인 비교는 지표에 따라 다르며, 하이퍼파라미터의 다양한 조합으로는 “최고”의 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
일부 GAN은 하이퍼파라미터 변경에 비교적 강력해질 때 발견되었습니다.
< 기술적 용어 설명 >
* 명시적으로 매개변수화된 분포(Explicitly Parameterized Distributions): 데이터 집합의 전체 분포에 대한 완전한 접근 권한이 있는 특별한 형태의 분포입니다. * GAN(Generative Adversarial Networks): 생성적 대응 네트워크로, 데이터 공간에 대한 전체 분포를 학습하기 위해 사용되는 딥러닝 모델입니다. * 하이퍼파라미터(Hyperparameters): 모델의 성능을 결정짓는 매개변수로, 학습 속도, 데이터 집합 크기 등과 같은 것들입니다.
< 참고 논문 또는 관련 자료 >
* [1] Shayne O’Brien, Matt Groh, Abhimanyu Dubey. “Evaluating Generative Adversarial Networks on Explicitly Parameterized Distributions. ” arXiv:1812. 10782v1 [cs. LG], 27 Dec 2018. * [2] Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, Aaron Courville. “Generative Adversarial Networks. ” In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-15), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9276. Springer, Cham, pp. 48-56, 2016. différences entre les deux
< Excerpt (English) >
Evaluating Generative Adversarial Networks on Explicitly Parameterized Distributions Shayne O’Brien, Matt Groh, Abhimanyu Dubey {shayneob, groh, dubeya}@mit.edu Massachusetts Institute of Technology Abstract The true distribution parameterizations of commonly used image datasets are inaccessible. Rather than designing metrics for feature spaces with unknown characteristics, we propose to measure GAN performance by evaluating on explicitly parameterized, synthetic data distributions. As a case study, we examine the performance of 16 GAN variants on six multivariate distributions of varying dimensionalities and training set sizes. In this learning environment, we observe that: GANs exhibit similar performance trends across dimensionalities; learning depends on the underlying distribution and its complexity; the number of training samples can have a large impact on performance; evaluation and relative comparisons are metric-dependent; diverse sets of hyperparameters can produce a “best” result; and some GANs are more robust to hyperparam- eter changes than others. These observations both corroborate findings of previous GAN evaluation studies and make novel contributions regarding the relationship between size, complexity, and GAN performance. 1 Introduction Generative adversarial network (GAN) optimization stability and convergence properties remain poorly understood despite the introduction of hundreds of GAN variants since their conception [8, 11]. While GAN learning and performance behavior has been studied [10, 19, 23], most existing work examining this relationship focuses on image datasets for which the underlying distribution parameterization is inaccessible [1, 2, 4, 18, 25]. This is problematic since claims of behavior that are made by modeling an unknown target distribution require a strong assumption for generalizability. The goal of generative modeling is to approximate a distribution pd by learning a parameterized distribution pg, where both pd and pg are defined over samples. If we do not have full access to pd, generalizability requires us to assume that the modeled dataset is a reasonable proxy for the family of distributions from which it was sampled. Without this assumption that is often only implicitly made, using images to understand GAN behavior limits conclusions to the data context being modeled. We seek to address a gap in the literature by investigating GAN variant performance on datasets for which we have full access to the distribution parameterization. This allows us to study empirical performance on data where we can make claims of model behavior that generalize to the full distribution, as opposed to on image datasets for which this is not necessarily true. To this end, we examine the performance of 16 GAN variants on six explicitly parameterized multivariate distributions of four different dimensionalities and three different training set sizes. Across 20 grid search trials, we observe that: (1) GANs exhibit similar performance trends across di- mensionalities, (2) learning depends on the underlying distribution and its complexity, (3) the number of training samples can have a large impact on performance, (4) evaluation and relative comparisons 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2018), Montréal, Canada. arXiv:1812.10782v1 [cs.LG] 27 Dec 2018 are metric-dependent, (5) diverse sets of hyperparameters can produce a “best” result, and (6) some GANs are more robust to…
< 번역 (Korean) >
명시 적으로 매개 변수화 된 분포에 대한 생성 적대적 네트워크 평가 Shayne O’Brien, Matt Groh, Abhimanyu Dubey {Shayneob, Groh, dubeya}@massachusetts Institute of Technology Institute of Technology의 일반적으로 사용되는 이미지 데이터 세트의 실제 분포 매개 변수화는 발생할 수 없습니다.
알 수없는 특성을 가진 피처 공간에 대한 메트릭을 설계하는 대신 명시 적으로 매개 변수화 된 합성 데이터 분포를 평가하여 GAN 성능을 측정 할 것을 제안합니다.
사례 연구로서, 우리는 다양한 차원 및 훈련 세트 크기의 6 가지 다변량 분포에서 16 GAN 변형의 성능을 조사합니다.
이 학습 환경에서 우리는 다음을 관찰합니다.
Gans는 차원에서 유사한 성능 추세를 나타냅니다.
학습은 기본 분포와 복잡성에 달려 있습니다.
훈련 샘플의 수는 성능에 큰 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
평가 및 상대 비교는 메트릭에 의존적입니다.
다양한 하이퍼 파라 미터 세트는 “최고의”결과를 생성 할 수 있습니다.
그리고 일부 가스는 다른 가인보다 과다 램프의 변화에 더 강력합니다.
이러한 관찰은 이전 GAN 평가 연구의 발견을 뒷받침하고 크기, 복잡성 및 GAN 성능 사이의 관계에 관한 새로운 기여를합니다.
1 소개 GAN (Generative Adversarial Network) 최적화 안정성 및 수렴 특성은 개념 이후 수백 개의 GAN 변형을 도입 했음에도 불구하고 잘 이해되지 않았다 [8, 11].
GAN 학습 및 성과 행동이 연구되었지만 [10, 19, 23],이 관계를 조사하는 대부분의 기존 작업은 기본 분포 매개 변수화가 접근 할 수없는 이미지 데이터 세트에 중점을 둡니다 [1, 2, 4, 18, 25].
알 수없는 목표 분포를 모델링하여 이루어진 행동에 대한 주장은 일반화에 대한 강력한 가정이 필요하기 때문에 문제가됩니다.
생성 모델링의 목표는 PD와 PG가 샘플을 통해 정의되는 매개 변수 분포 PG를 학습함으로써 분포 PD를 근사화하는 것입니다.
PD에 완전히 액세스 할 수없는 경우 Generalizability를 사용하면 모델링 된 데이터 세트가 샘플링 된 분포 제품군에 대한 합리적인 프록시라고 가정해야합니다.
이 가정이 종종 암시 적으로 만 이루어지면 이미지를 사용하여 GAN 동작을 이해하면 모델링되는 데이터 컨텍스트에 대한 결론을 제한합니다.
우리는 분포 매개 변수화에 완전히 액세스 할 수있는 데이터 세트에서 GAN 변형 성능을 조사함으로써 문헌의 격차를 해결하려고합니다.
이를 통해 우리는 이것이 반드시 사실이 아닌 이미지 데이터 세트와 달리 전체 분포로 일반화하는 모델 동작에 대한 주장을 할 수있는 데이터에 대한 경험적 성능을 연구 할 수 있습니다.
이를 위해, 우리는 4 가지 다른 차원의 6 가지 매개 변수화 된 다변량 분포와 3 개의 서로 다른 훈련 세트 크기에 대한 16 GAN 변형의 성능을 조사합니다.
20 개의 그리드 검색 시험에서 우리는 다음과 같은 것을 관찰합니다.
(1) GANS는 이차성 전반에 걸쳐 유사한 성능 추세를 나타냅니다.
(2) 학습은 기본 분포와 그 복잡성에 의존합니다.
(3) 교육 샘플의 수는 성능에 큰 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
ARXIV : 1812.10782V1 [CS.LG] 2018 년 12 월 27 일 메트릭에 의존적이며 (5) 다양한 하이퍼 파라미터 세트가 “최상의”결과를 생성 할 수 있으며 (6) 일부 간이는 더 강력합니다 …
알 수없는 특성을 가진 피처 공간에 대한 메트릭을 설계하는 대신 명시 적으로 매개 변수화 된 합성 데이터 분포를 평가하여 GAN 성능을 측정 할 것을 제안합니다.
사례 연구로서, 우리는 다양한 차원 및 훈련 세트 크기의 6 가지 다변량 분포에서 16 GAN 변형의 성능을 조사합니다.
이 학습 환경에서 우리는 다음을 관찰합니다.
Gans는 차원에서 유사한 성능 추세를 나타냅니다.
학습은 기본 분포와 복잡성에 달려 있습니다.
훈련 샘플의 수는 성능에 큰 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
평가 및 상대 비교는 메트릭에 의존적입니다.
다양한 하이퍼 파라 미터 세트는 “최고의”결과를 생성 할 수 있습니다.
그리고 일부 가스는 다른 가인보다 과다 램프의 변화에 더 강력합니다.
이러한 관찰은 이전 GAN 평가 연구의 발견을 뒷받침하고 크기, 복잡성 및 GAN 성능 사이의 관계에 관한 새로운 기여를합니다.
1 소개 GAN (Generative Adversarial Network) 최적화 안정성 및 수렴 특성은 개념 이후 수백 개의 GAN 변형을 도입 했음에도 불구하고 잘 이해되지 않았다 [8, 11].
GAN 학습 및 성과 행동이 연구되었지만 [10, 19, 23],이 관계를 조사하는 대부분의 기존 작업은 기본 분포 매개 변수화가 접근 할 수없는 이미지 데이터 세트에 중점을 둡니다 [1, 2, 4, 18, 25].
알 수없는 목표 분포를 모델링하여 이루어진 행동에 대한 주장은 일반화에 대한 강력한 가정이 필요하기 때문에 문제가됩니다.
생성 모델링의 목표는 PD와 PG가 샘플을 통해 정의되는 매개 변수 분포 PG를 학습함으로써 분포 PD를 근사화하는 것입니다.
PD에 완전히 액세스 할 수없는 경우 Generalizability를 사용하면 모델링 된 데이터 세트가 샘플링 된 분포 제품군에 대한 합리적인 프록시라고 가정해야합니다.
이 가정이 종종 암시 적으로 만 이루어지면 이미지를 사용하여 GAN 동작을 이해하면 모델링되는 데이터 컨텍스트에 대한 결론을 제한합니다.
우리는 분포 매개 변수화에 완전히 액세스 할 수있는 데이터 세트에서 GAN 변형 성능을 조사함으로써 문헌의 격차를 해결하려고합니다.
이를 통해 우리는 이것이 반드시 사실이 아닌 이미지 데이터 세트와 달리 전체 분포로 일반화하는 모델 동작에 대한 주장을 할 수있는 데이터에 대한 경험적 성능을 연구 할 수 있습니다.
이를 위해, 우리는 4 가지 다른 차원의 6 가지 매개 변수화 된 다변량 분포와 3 개의 서로 다른 훈련 세트 크기에 대한 16 GAN 변형의 성능을 조사합니다.
20 개의 그리드 검색 시험에서 우리는 다음과 같은 것을 관찰합니다.
(1) GANS는 이차성 전반에 걸쳐 유사한 성능 추세를 나타냅니다.
(2) 학습은 기본 분포와 그 복잡성에 의존합니다.
(3) 교육 샘플의 수는 성능에 큰 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
ARXIV : 1812.10782V1 [CS.LG] 2018 년 12 월 27 일 메트릭에 의존적이며 (5) 다양한 하이퍼 파라미터 세트가 “최상의”결과를 생성 할 수 있으며 (6) 일부 간이는 더 강력합니다 …
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기