This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “Measuring and calibrating Galactic synchrotron emission”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
Cosmic Magnetic Fields paper focuses on the calibration and adjustment of Galactic total intensity surveys, essential for understanding polarization surveys. The paper discusses techniques such as sky horn measurements, TT-plots, and absolute measurements to accurately measure large-scale sky emission. All-sky surveys aim to include emission structures exceeding their angular resolution, including isotropic components like synchrotron radiation up to specific frequencies.
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
- Polarimetric [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Techniques used for polarization surveys, enabling the measurement of polarized diffuse emission structures with no relation to total intensity emission resulting from Faraday rotation effects in interstellar medium. - Surveys [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: All-sky measurements required to reveal large-scale properties of galaxies and provide absolute levels for sky maps constructed from corrected scans, addressing challenges faced by technical measurement methods. - Radio continuum [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Emission processes dominating synchrotron radiation up to certain frequencies in surveys, enabling the interpretation of polarization structures critical to setting zero-level calibration accurately.
View Original Excerpt (English)
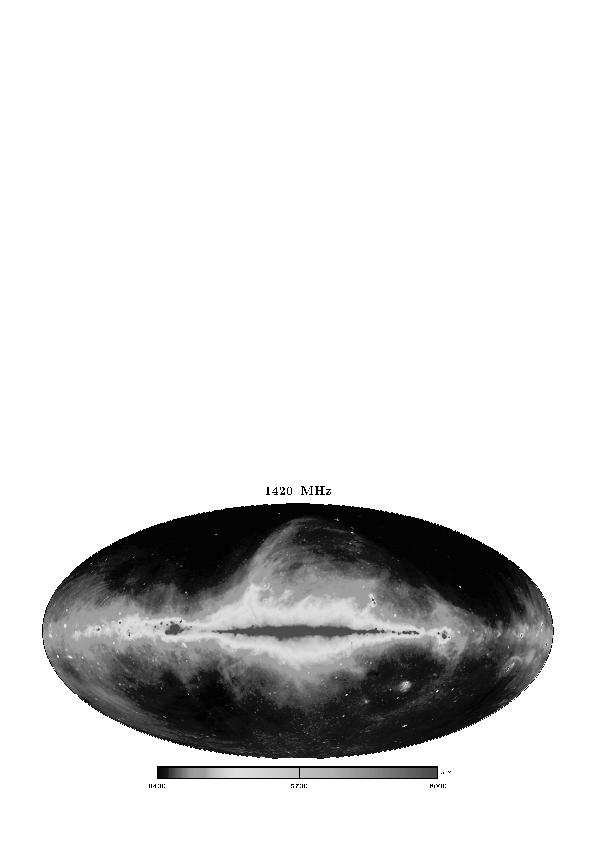
Cosmic Magnetic Fields: From Planets, ¿ to Stars and Galaxies Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 259, 2009 c⃝2009 International Astronomical Union K.G. Strassmeier, A.G. Kosovichev & ¿ J.E. Beckman, eds. DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Measuring and calibrating Galactic synchrotron emission Wolfgang Reich and Patricia Reich Max-Planck-Institut f¨ur Radioastronomie, Auf dem H¨ugel 69, 52121 Bonn, Germany email: wreich, preich@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de Abstract. Our position inside the Galaxy requires all-sky surveys to reveal its large-scale prop- erties. The zero-level calibration of all-sky surveys differs from standard ’relative’ measurements, where a source is measured in respect to its surroundings. All-sky surveys aim to include emission structures of all angular scales exceeding their angular resolution including isotropic emission components. Synchrotron radiation is the dominating emission process in the Galaxy up to fre-2008 quencies of a few GHz, where numerous ground based surveys of the total intensity up to 1.4 GHz exist. Its polarization properties were just recently mapped for the entire sky at 1.4 GHz. All-sky total intensity and linear polarization maps from WMAP for frequencies of 23 GHz and higherDec became available and complement existing sky maps. Galactic plane surveys have higher an- gular resolution using large single-dish or synthesis telescopes. Polarized diffuse emission shows structures with no relation to total intensity emission resulting from Faraday rotation effects in22 the interstellar medium. The interpretation of these polarization structures critically depends on a correct setting of the absolute zero-level in Stokes U and Q. Keywords. techniques: polarimetric, surveys, radio continuum: ISM 1. Introduction[astro-ph] All-sky radio continuum surveys provide basic information on our local environment and the large-scale properties of the Galaxy. They are required to model the Galactic emission components in 3-D (Sun et al. (2008)) and guide more sensitive higher-angular resolution observations of the Galactic plane or other regions or objects of interest. All-sky surveys are quite time…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
Cosmic Magnetic Fields 용지는 편광 측량 조사를 이해하는 데 필수적인 은하계 총 강도 측량의 교정 및 조정에 중점을 둡니다. 이 논문은 스카이 혼 측정, TT- 플롯 및 대규모 하늘 배출량을 정확하게 측정하기위한 절대 측정과 같은 기술에 대해 설명합니다. All-Sy Surveys는 특정 주파수까지의 Synchrotron 방사선과 같은 등방성 성분을 포함하여 각도 분해능을 초과하는 배출 구조를 포함하는 것을 목표로합니다.
주요 기술 용어 (한글 설명)
- Polarimetric
설명 (Korean): 분극 측량에 사용되는 기술, 성간 매체에서 패러데이 회전 효과로 인한 총 강도 방출과 관련이없는 편광 Di ff 방출 구조의 측정을 가능하게합니다.
(Original English: Techniques used for polarization surveys, enabling the measurement of polarized diffuse emission structures with no relation to total intensity emission resulting from Faraday rotation effects in interstellar medium.) - Surveys
설명 (Korean): 은하의 대규모 특성을 드러내고 수정 된 스캔으로 구성된 하늘 맵에 대한 절대 레벨을 제공하는 데 필요한 모든 스키 측정은 기술 측정 방법에 직면 한 문제를 해결하는 데 절대 레벨을 제공합니다.
(Original English: All-sky measurements required to reveal large-scale properties of galaxies and provide absolute levels for sky maps constructed from corrected scans, addressing challenges faced by technical measurement methods.) - Radio continuum
설명 (Korean): 배출 공정은 조사에서 특정 주파수까지 싱크로트론 방사선을 지배하는데, 이는 제로 레벨 교정을 정확하게 설정하는 데 중요한 편광 구조의 해석을 가능하게합니다.
(Original English: Emission processes dominating synchrotron radiation up to certain frequencies in surveys, enabling the interpretation of polarization structures critical to setting zero-level calibration accurately.)
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
우주 자기 분야 : 행성에서 ¿ 별과 은하 절차에 이르기까지 IAU 심포지엄 No. 259, 2009 C⃝2009 International Astronomical Union K.G. Strassmeier, A.G. Kosovichev & ¿ J.E. Beckman, eds. doi : 00.0000/x0000000000000000x 은하 싱크로트론 방출 Wolfgang Reich 및 Patricia Reich Max-Planck-Institut f¨ur Radioastronomie, auf dem h¨ugel 69, 52121 Bonn, Germany 이메일 : wreich, preich@mpifr-bonn.de. 은하 내부의 우리의 위치는 대규모 설문 조사를 요구합니다. All-Sky Survey의 제로 수준 교정은 표준 ‘상대적’측정과 다릅니다. 여기서 소스는 주변 환경과 관련하여 소스를 측정합니다. 모든 스키 설문 조사는 등방성 방출 성분을 포함하여 각도 해상도를 초과하는 모든 각도 스케일의 배출 구조를 포함하는 것을 목표로합니다. Synchrotron 방사선은 Galaxy에서 FRE-2008 Quencies의 Galaxy에서 지배적 인 배출 공정으로, 최대 1.4GHz의 총 강도에 대한 수많은 지상 조사가 존재합니다. 그것의 분극 특성은 최근 1.4GHz에서 하늘 전체에 매핑되었습니다. 23GHz 및 HigherDEC 주파수에 대한 WMAP의 모든 스카이 총 강도 및 선형 편광 맵을 사용할 수있게되었으며 기존의 스카이 맵을 보완합니다. 은하 평면 측량은 큰 단일 또는 합성 망원경을 사용하여 더 높은 angular 해상도를 가지고 있습니다. 분극화 된 차이 사용 방출은 22 성간 매체에서 패러데이 회전 효과로 인한 총 강도 방출과 관련이없는 구조를 보여준다. 이러한 분극 구조의 해석은 Stokes U 및 Q. 키워드에서 절대 제로 레벨의 올바른 설정에 크게 의존합니다. 기술 : 편광 메트릭, 설문 조사, 라디오 연속체 : ISM 1. 소개 [Astro-PH] All-Sky Radio Continuum Survey는 지역 환경과 은하의 대규모 특성에 대한 기본 정보를 제공합니다. 그것들은 3-D (Sun et al. (2008))에서 은하 방출 성분을 모델링하고 은하계 또는 다른 영역 또는 관심있는 물체의보다 민감한 고해상 해상도 관찰을 안내해야합니다. 모든 스키 설문 조사는 꽤 시간입니다 …
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기