This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “Computational modeling of collective human behavior: Example of financial markets”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
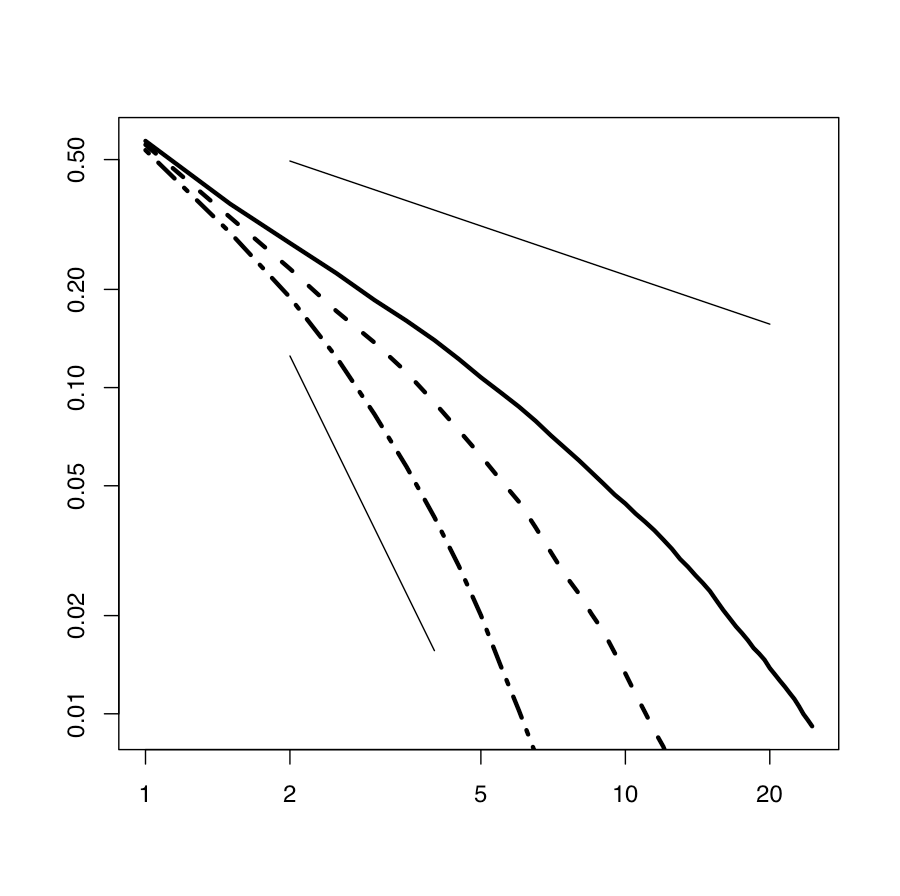
Computational modeling of collective human behavior: Example of financial markets Andy Kirou1, B la˙zej Ruszczycki1, Markus Walser2 and Neil F. Johnson1,∗ 1Department of Physics, University of Miami, P.O. Box 248046, Coral Gables, FL 33124 USA 2Landesbank Baden-W¨urttemberg, Am Hauptbahnhof 2, 70173 Stuttgart, Germany Draft of keynote lecture at International Conference on Computational Science (June, 2008). Final version published in LNCS M. Bubak et al. (Eds.) p. 33 (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2008) We discuss how minimal financial market models can be constructed by bridging the gap between two existing, but incomplete, market models: a model in which a population of virtual traders make decisions based on common global information but lack local information from their social network, and a model in which the traders form a dynamically evolving social network but lack any decision-making based on global information. We show that a suitable combination of these two models2008 – in particular, a population of virtual traders with access to both global and local information – produces results for the price return distribution which are closer to the reported stylized facts. We believe that this type of model can be applied across a wide range of systems in which collectiveDec human activity is observed. 14 INTRODUCTION known that such many-body problems are in general intractable. Given the additional feature that the objects themselves may be semi-autonomous (i.e., they each have As a result of the increased availability of higher pre- some form of independent decision-making ability such spatiotemporal datasets, coupled with the real- that a given external input may yield various possible
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
Key technical terms were not identified or extracted by the LLM.
View Original Excerpt (English)
Computational modeling of collective human behavior: Example of financial markets Andy Kirou1, B la˙zej Ruszczycki1, Markus Walser2 and Neil F. Johnson1,∗ 1Department of Physics, University of Miami, P.O. Box 248046, Coral Gables, FL 33124 USA 2Landesbank Baden-W¨urttemberg, Am Hauptbahnhof 2, 70173 Stuttgart, Germany Draft of keynote lecture at International Conference on Computational Science (June, 2008). Final version published in LNCS M. Bubak et al. (Eds.) p. 33 (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2008) We discuss how minimal financial market models can be constructed by bridging the gap between two existing, but incomplete, market models: a model in which a population of virtual traders make decisions based on common global information but lack local information from their social network, and a model in which the traders form a dynamically evolving social network but lack any decision- making based on global information. We show that a suitable combination of these two models2008 – in particular, a population of virtual traders with access to both global and local information – produces results for the price return distribution which are closer to the reported stylized facts. We believe that this type of model can be applied across a wide range of systems in which collectiveDec human activity is observed. 14 INTRODUCTION known that such many-body problems are in general in- tractable. Given the additional feature that the objects themselves may be semi-autonomous (i.e. they each have As a result of the increased availability of higher pre- some form of independent decision-making ability such cision spatiotemporal datasets, coupled with the real- that a given external input may yield various possible ization that most real-world human systems are com- outputs depending on some internal state of the object plex, a new field of computational modeling has emerged itself) the most realistic route toward advancing our un- in which the…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
집단적 인간 행동의 계산 모델링 : 금융 시장의 예 Andy Kirou1, B La˙zej Ruszczycki1, Markus Walser2 및 Neil F. Johnson1, * 1 Miami 대학교 물리학, P.O. Box 248046, Coral Gables, FL 33124 USA 2landesbank Baden-W¨urttemberg, AM Hauptbahnhof 2, 70173 슈투트가르트, 독일 국제 전산 과학 회의에서 기조 연설 초안 (2008 년 6 월). LNCS M. Bubak et al.에 게시 된 최종 버전. (eds.) p. 33 (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2008) 우리는 기존의 두 가지, 불완전한 시장 모델 사이의 격차를 해소함으로써 최소의 금융 시장 모델을 구성 할 수있는 방법에 대해 논의합니다. 가상 트레이더 인구가 공통된 글로벌 정보를 기반으로 결정을 내리지 만 소셜 네트워크의 로컬 정보가 부족한 모델이 부족하지만 소셜 네트워크를 기반으로 한 모든 정보가 부족한 모델. 우리는이 두 모델의 조합 2008, 특히 글로벌 및 로컬 정보에 액세스 할 수있는 가상 거래자 집단이보고 된 양식화 된 사실에 더 가까운 가격 수익 분포에 대한 결과를 생성 함을 보여줍니다. 우리는 이러한 유형의 모델이 수집 된 인간 활동이 관찰되는 광범위한 시스템에 적용될 수 있다고 생각합니다. 14 소개 그러한 많은 신체 문제는 일반적으로 다루기 힘들다는 것을 알고 있습니다. 객체 자체가 반 자율적 일 수 있다는 추가적인 기능을 감안할 때 (즉, 각각의 외부 입력이 다양한 가능성을 산출 할 수있는 실수와 결합 된 시공간 데이터 세트와 같은 일부 형태의 독립적 인 의사 결정 능력이 높아짐에 따라
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
집단 인간 행동의 계산 모델링 : 금융 시장의 예 Andy Kirou1, B la˙zej ruszczycki1, Markus Walser2 및 Neil F. Johnson1, * 1 Miami, P.O. Box 248046, Coral Gables, FL 33124 USA 2landesbank Baden-W¨urttemberg, AM Hauptbahnhof 2, 70173 슈투트가르트, 독일 국제 전산 과학 회의에서 기조 연설 초안 (2008 년 6 월). LNCS M. Bubak et al.에 게시 된 최종 버전. (eds.) p. 33 (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2008) 우리는 기존의 두 가지이지만 불완전한 시장 모델 사이의 격차를 해소함으로써 최소한의 재무 시장 모델을 구성 할 수있는 방법에 대해 논의합니다. 가상 트레이더 인구가 공통된 글로벌 정보를 기반으로 결정하지만 소셜 네트워크의 로컬 정보가 부족한 모델을 형성하는 모델을 형성하지만 소셜 네트워크를 기반으로 한 결정을 내리는 모델입니다. 우리는이 두 모델의 조합 2008, 특히 글로벌 및 로컬 정보에 액세스 할 수있는 가상 거래자 집단이보고 된 양식화 된 사실에 더 가까운 가격 수익 분포에 대한 결과를 생성 함을 보여줍니다. 우리는 이러한 유형의 모델이 수집 된 인간 활동이 관찰되는 광범위한 시스템에 적용될 수 있다고 생각합니다. 14 소개 그러한 많은 신체 문제는 일반적으로 관련이 없다는 것을 알고있다. 객체 자체가 반 자율적 일 수 있다는 추가적인 기능을 감안할 때 (즉, 각각의 외부 입력이 대부분의 실제 인간 시스템이 일부 내부적 상태에 따라 COM- 출력이라는 다양한 가능한 IZATION을 생성 할 수있는 실수와 결합 된 실수와 결합 된 Cision 시공간 데이터 세트의 일부 독립적 인 의사 결정 능력이 증가함에 따라 증가한 결과로서 각각이 가용성이 증가함에 따라 각각이 새로운 형태의 독립적 인 의사 결정 능력의 결과를 얻었습니다. 그 자체로))
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기