This post, leveraging AI, summarizes and analyzes the key aspects of the research paper “Antiferroelectric liquid crystal model with ions diffusion.”. For in-depth information, please refer to the original PDF.
📄 Original PDF: Download / View Fullscreen
English Summary
This paper focuses on antiferroelectric liquid crystals (AFLCs), which are crucial components in display applications. The study models ion behavior and molecular switching under the application of certain combinations of voltage pulses, considering simultaneously ion delocalization from alignment layers. Key technical terms include diffusion coefficient, electrostatic interaction, Gauss equation, Nernst-Planck mechanism, and ion concentration.
Key Technical Terms
Below are key technical terms and their explanations to help understand the core concepts of this paper. You can explore related external resources via the links next to each term.
- Diffusion coefficient [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Describes the movement of ions within liquid crystal cells under an external electric field through diffusion processes. - Electrostatic interaction [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Mixes ionic behavior with antiferroelectric liquid crystals by means of Gauss equation, affecting molecular switching in display applications. - Gauss equation [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Used to obtain equations governing electrostatic interactions between ions and molecules within alignment layers under the influence of an external electric field. - Nernst-Planck mechanism [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Describes ion concentration evolution with respect to diffusion processes when voltage pulses are applied, enhancing molecular switching in liquid crystal cells. - Ion concentration [Wikipedia (Ko)] [Wikipedia (En)] [나무위키] [Google Scholar] [Nature] [ScienceDirect] [PubMed]
Explanation: Represents ion mobility within antiferroelectric liquid crystals under the influence of an external electric field through equations like Gauss equation and Nernst-Planck mechanism.
View Original Excerpt (English)
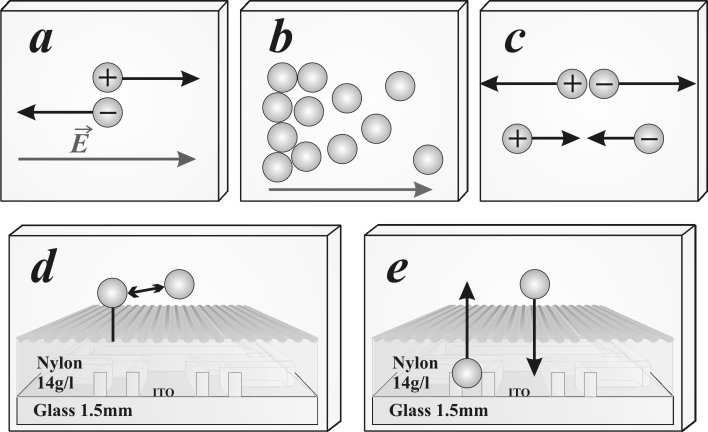
2006 Antiferroelectric liquid crystal model with ions Dec diffusion. 27 P.L. del Castillo,1 P.L. Lucas,2 N. Bennis,3 A. Spadlo4 and D. Rodriguez-Perez,5 September 25, 2018 1 Department of Mathematics, CEIPS. El Molar n◦2, C/San Isidro 2, El Molar, E-28710 Madrid, Spain. E-mail: antiferroelectrica@yahoo.es 2 Department of Mathematics, IES. Fco. G´ıner de los R´ıos, Carretera Alcobendas-Barajas s/n, Alcobendas, Madrid, Spain. E-mail: selairi@bluebottle.com 3 Dpt. Tecnolog´ıa Fot´onica, ETSI Telecomunicaci´on, Universidad Polit´ecnica[cond-mat.soft] de Madrid, Ciudad Universitaria, E-28040 Madrid, Spain 4 Institute of Chemistry, Military University of Technology, ul. Kaliskiego 2, 00-908 Warsaw, Poland 5 Dpto. de F´ısica y Matem´atica de Fluidos, Facultad de Ciencias, UNED, Senda del Rey s/n, 28040 Madrid, Spain Abstract Antiferroelectric liquid crystals can be considered as a promising al- ternative to nematic mixtures in the area of microdisplays. Switching behaviour of the molecules has been modelled as two adjacent smectic layers. However, some studies made so far reveal that electrooptical response can be seriously affected by ion content of the test cells, spe- cially in the area of asymmetric cells. Regarding such influence, both molecules and ions have been studied in the present work under the influence of an external electric field. The mechanisms governing ionic behaviour considered so far in the simulations have been diffusion, which was dealt through the Nerst-Planck equation, and electrostatic interaction, which mixes ionic and antiferroelectric liquid crystal ef-arXiv:cond-mat/0612631v1 fects by means of Gauss equation. In addition, voltage pulses applied to the simulated antiferroelectric liquid crystal cell, have been consid- ered under different waveforms for possible driving schemes in display applications. Results show time evolution of ions within the cell, under different external applied electric fields and their delocalization from alignment 1 layers when high frequency AC pulses are included in the structure of the switching waveform. 1 Introduction. Liquid crystals are becoming crucial…
🇰🇷 한국어 보기 (View in Korean)
한글 요약 (Korean Summary)
이 논문은 디스플레이 응용 분야에서 중요한 구성 요소 인 항 색소 전기 액정 (AFLC)에 중점을 둡니다. 이 연구는 정렬 층으로부터의 이온 비편성을 동시에 고려하여 전압 펄스의 특정 조합을 적용하던 이온 거동 및 분자 스위칭을 모델링한다. 주요 기술 용어에는 확산 계수, 정전기 상호 작용, 가우스 방정식, Nernst-Planck 메커니즘 및 이온 농도가 포함됩니다.
주요 기술 용어 (한글 설명)
- Diffusion coefficient
설명 (Korean): 차이 공정을 통해 외부 전기장 하의 액정 세포 내 이온의 이동을 설명합니다.
(Original English: Describes the movement of ions within liquid crystal cells under an external electric field through diffusion processes.) - Electrostatic interaction
설명 (Korean): 가우스 방정식을 통해 이온 성 거동을 항진계 전기 액정과 혼합하여 디스플레이 응용 분자의 분자 스위칭에 영향을 미칩니다.
(Original English: Mixes ionic behavior with antiferroelectric liquid crystals by means of Gauss equation, affecting molecular switching in display applications.) - Gauss equation
설명 (Korean): 외부 전기장의 영향 하에서 정렬 층 내에서 이온과 분자 사이의 정전기 상호 작용을 제어하는 방정식을 얻는 데 사용됩니다.
(Original English: Used to obtain equations governing electrostatic interactions between ions and molecules within alignment layers under the influence of an external electric field.) - Nernst-Planck mechanism
설명 (Korean): 전압 펄스가 적용될 때의 차이 과정에 대한 이온 농도 진화를 설명하여 액정 세포에서 분자 스위칭을 향상시킨다.
(Original English: Describes ion concentration evolution with respect to diffusion processes when voltage pulses are applied, enhancing molecular switching in liquid crystal cells.) - Ion concentration
설명 (Korean): Gauss 방정식 및 Nernst-Planck 메커니즘과 같은 방정식을 통해 외부 전기장의 영향 하에서 항 색소 전기 액정 내의 이온 이동성을 나타냅니다.
(Original English: Represents ion mobility within antiferroelectric liquid crystals under the influence of an external electric field through equations like Gauss equation and Nernst-Planck mechanism.)
발췌문 한글 번역 (Korean Translation of Excerpt)
2006 이온 DEC DIC USION을 사용한 항염병 전기 액정 모델. 27 P.L. 델 카스티요, 1 P.L. Lucas, 2 N. Bennis, 3 A. Spadlo4 및 D. Rodriguez-Perez, 2018 년 9 월 25 일 1 CEIPS 수학과. El Molar N◦2, C/San Isidro 2, El Molar, E-28710 마드리드, 스페인. 이메일 : antiferroelectrica@yahoo.es 2 수학과, IES. FCO. G´ıner de los R´ıos, Carretera Alcobendas-Barajas S/N, Alcobendas, Madrid, Spain. 이메일 : selairi@bluebottle.com 3 DPT. Tecnolog´ıa fot´onica, Etsi Telecomunicaci´on, Universidad Polit´ecnica [Cond-Mat.soft] De Madrid, Ciudad Universitaria, E-28040 Madrid, Spain 4 화학 연구소, University of Technology, UL. Kaliskiego 2, 00-908 바르샤바, 폴란드 5 DPTO. De f´ısica y matem´atica de fluidos, apultad de ciencias, uned, senda del rey s/n, 28040 마드리드, 스페인 추상 항 안내 전기 액정은 미세 혈증의 영역에서 유망한 아메리카 혼합물로 간주 될 수 있습니다. 분자의 스위칭 거동은 두 개의 인접한 스미스 층으로 모델링되어왔다. 그러나, 일부 연구에 따르면 지금까지 전기성 반응은 특히 비대칭 세포의 영역에서 시험 세포의 이온 함량에 의해 심각하게 영향을받을 수 있음을 보여준다. 이러한 영향과 관련하여, 분자와 이온 모두 외부 전기장의 영향에 따라 현재 연구에서 연구되었다. 지금까지 시뮬레이션에서 고려 된 이온 성 거동을 제어하는 메커니즘은 차이가되었으며, 이는 Nerst-Planck 방정식을 통해 다루어졌으며, 이온 및 항 섬광 액체 결정 EF-Arxiv : Cond-Mat/0612631V1 가용성을 혼합 한 정전기 상호 작용은 GAUSS 방정식을 의미합니다. 또한, 시뮬레이션 된 항 섬광 전기 액정 셀에 적용된 전압 펄스는 디스플레이 응용 분야에서 가능한 구동 체계에 대해 다른 파형 하에서 고려되었다. 결과는 고주파 AC 펄스가 스위칭 파형의 구조에 포함될 때 다른 외부 적용된 전기장 및 정렬 1 층으로부터의 비편 재화 하에서 세포 내 이온의 시간 진화를 보여준다. 1 소개. 액정이 중요 해지고 있습니다 …
Source: arXiv.org (or the original source of the paper)
답글 남기기