Summary (English)
A scientific paper presents a new method for implementing quantum computation in a 3D lattice, which involves introducing a lattice defect and using the Rudolph-Grover rebit encoding.
The paper also discusses circuit compaction and algorithmic circuit verification for magic state distillation.
The performance analysis shows improvements over previous methods.
The paper also discusses circuit compaction and algorithmic circuit verification for magic state distillation.
The performance analysis shows improvements over previous methods.
요약 (Korean)
과학 논문은 3D 격자에서 양자 계산을 구현하는 새로운 방법을 제시하며, 여기에는 격자 결함을 도입하고 Rudolph-Grover Rebit Encoding을 사용하는 것이 포함됩니다.
이 논문은 또한 마법 상태 증류에 대한 회로 압축 및 알고리즘 회로 검증에 대해 논의합니다.
성능 분석은 이전 방법에 비해 개선을 보여줍니다.
이 논문은 또한 마법 상태 증류에 대한 회로 압축 및 알고리즘 회로 검증에 대해 논의합니다.
성능 분석은 이전 방법에 비해 개선을 보여줍니다.
기술적 용어 설명 (Technical Terms)
- Lattice defect: 이원성을 깨뜨리는 규칙적인 격자의 국소 적 탈구로 하다마르 게이트의 본질적으로 결함이없는 구현이 가능합니다. (Original English Explanation: A local dislocation in a regular lattice that breaks its duality, allowing for an intrinsically fault-tolerant implementation of the Hadamard gate.)
- Rudolph-Grover rebit encoding: Rebits를 사용하여 양자 게이트를 구현하는 방법 (두 개의 가능한 상태를 가진 양자 비트). (Original English Explanation: A method for implementing quantum gates using rebits (quantum bits with two possible states).)
- Circuit compaction: 양자 회로의 크기와 복잡성을 줄이는 기술. (Original English Explanation: Techniques for reducing the size and complexity of quantum circuits.)
- Algorithmic circuit verification: 주어진 양자 회로가 실행될 때 올바른 출력을 생성 할 것인지 확인하는 방법. (Original English Explanation: Methods for checking whether a given quantum circuit will produce the correct output when executed.)
Excerpt (English Original)
A 3D lattice defect and efficient computations in topological MBQC Gabrielle Tournaire1,2, Marvin Schwiering3, Robert Raussendorf2,3, and Sven Bachmann1,4 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z1, Canada 2Stewart Blusson Quantum Matter Institute, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada 3Institut f¨ur Theoretische Physik, Leibniz Universit¨at Hannover, Appelstraße 2, 30167 Hannover, Germany2024 4Department of Mathematics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z2, Canada Dec December 13, 2024 13 Abstract We describe an efficient, fully fault-tolerant implementation of Measurement-Based Quantum Computation (MBQC) in the 3D cluster state.
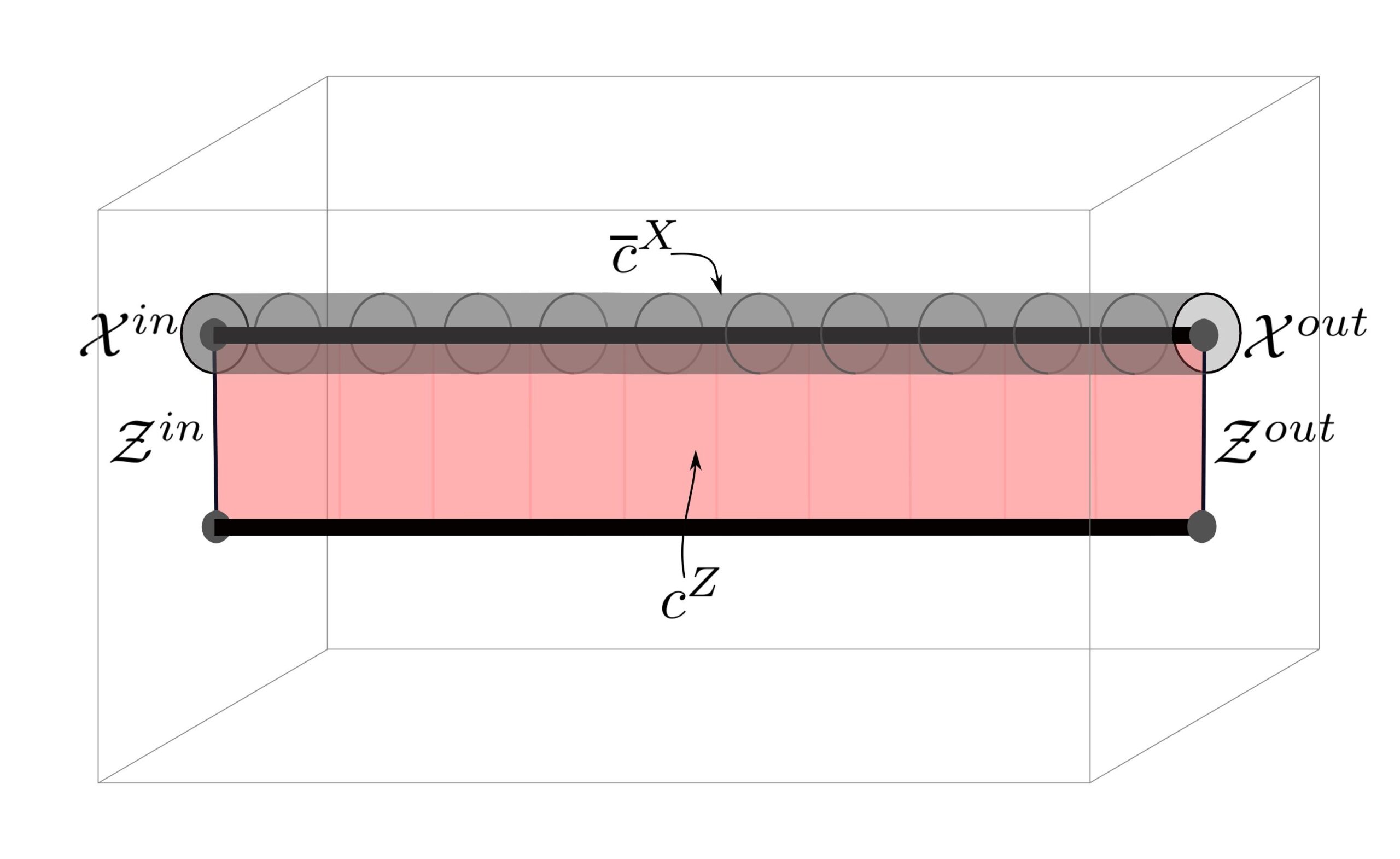
The two key novelties are (i) the introduction of a lattice defect in the underlying cluster state and (ii) the use of the Rudolph-Grover rebit encoding.
Concretely, (i) allows for a topological implementation of the Hadamard gate, while (ii) does the same for the phase gate.
Furthermore, we develop general ideas towards circuit compaction and algorithmic circuit verification, which we implement for the Reed-Muller code used for magic state[quant-ph] distillation.
Our performance analysis highlights the overall improvements provided by the new methods.
1 Introduction Decoherence is an obstacle to scaling up quantum computers.
It was once thought fundamental [1], but was later shown to be surmountable by the techniques of fault-tolerant quantum computation [2–4].
The central result in this regard is the Threshold Theorem [5, 6], which says that arbitrarily long and accurate quantum computation is possible if the amount of decoherence per elementary quantum gate is below a certain value—the error threshold.
Furthermore, the operational and spatial costs of fault-tolerance are benign in the sense of scaling, albeit large in absolute terms.
After the threshold theorem was established, work on fault-tolerant quantum computation has focused on (i) relaxing the preconditions under which the theorem can be applied [7,8], (ii) improving the value of the…
The two key novelties are (i) the introduction of a lattice defect in the underlying cluster state and (ii) the use of the Rudolph-Grover rebit encoding.
Concretely, (i) allows for a topological implementation of the Hadamard gate, while (ii) does the same for the phase gate.
Furthermore, we develop general ideas towards circuit compaction and algorithmic circuit verification, which we implement for the Reed-Muller code used for magic state[quant-ph] distillation.
Our performance analysis highlights the overall improvements provided by the new methods.
1 Introduction Decoherence is an obstacle to scaling up quantum computers.
It was once thought fundamental [1], but was later shown to be surmountable by the techniques of fault-tolerant quantum computation [2–4].
The central result in this regard is the Threshold Theorem [5, 6], which says that arbitrarily long and accurate quantum computation is possible if the amount of decoherence per elementary quantum gate is below a certain value—the error threshold.
Furthermore, the operational and spatial costs of fault-tolerance are benign in the sense of scaling, albeit large in absolute terms.
After the threshold theorem was established, work on fault-tolerant quantum computation has focused on (i) relaxing the preconditions under which the theorem can be applied [7,8], (ii) improving the value of the…
발췌문 (Korean Translation)
토폴로지 MBQC Gabrielle Tournaire1,2, Marvin Schwiering3, Robert Raussendorf2,3 및 Sven Bachmann1,4 1 물리학과 천문학, 영국 컬럼비아 대학교, BC V6T 1Z1, 캐나다 2stewart Quantum institute institute institute institute institute institute institute institute institute instit BC v6t 1z4, 캐나다 3institut f¨ur theoretische physik, Leibniz Universitathat Hannover, Appelstraße 2, 30167 Hannover, Germany2024 Department of Mathematics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC V6t 1Z2, Canada 12 월 13, 2024 13 13 우리는 효율적이며, 완전히 묘사하고 있습니다.
3D 클러스터 상태의 측정 기반 양자 계산 (MBQC).
두 가지 주요 참신은 (i) 기본 클러스터 상태에서 격자 결함의 도입 및 (ii) 루돌프 그로버 리비브 인코딩의 사용입니다.
구체적으로, (i) Hadamard 게이트의 토폴로지 구현을 허용하는 반면 (ii) 위상 게이트에 대해 동일하게 수행합니다.
또한, 우리는 회로 압축 및 알고리즘 회로 검증에 대한 일반적인 아이디어를 개발하는데, 이는 Magic State [Quant-PH] 증류에 사용되는 Reed-Muller 코드를 위해 구현합니다.
우리의 성과 분석은 새로운 방법으로 제공되는 전반적인 개선 사항을 강조합니다.
1 소개 디코 언어는 양자 컴퓨터를 확장하는 데 장애물입니다.
그것은 한때 기본적으로 생각되었지만 [1], 나중에 결함에 관개 양자 계산의 기술에 의해 극복 할 수있는 것으로 나타났습니다 [2-4].
이와 관련하여 중심 결과는 임계 값 정리 [5, 6]이며, 이는 기본 양자 게이트 당 디코 언가 특정 값, 즉 오차 임계 값 미만이면 임의로 길고 정확한 양자 계산이 가능하다고 말합니다.
또한, 결함-장애의 운영 및 공간 비용은 절대적인 용어에도 불구하고 스케일링의 의미에서 양성이다.
임계 값 정리가 확립 된 후, 결함 내성 양자 계산에 대한 연구는 (i) 정리가 적용될 수있는 전제 조건을 완화하는 데 중점을 두었다 [7,8], (ii) …의 가치를 향상시킨다.
3D 클러스터 상태의 측정 기반 양자 계산 (MBQC).
두 가지 주요 참신은 (i) 기본 클러스터 상태에서 격자 결함의 도입 및 (ii) 루돌프 그로버 리비브 인코딩의 사용입니다.
구체적으로, (i) Hadamard 게이트의 토폴로지 구현을 허용하는 반면 (ii) 위상 게이트에 대해 동일하게 수행합니다.
또한, 우리는 회로 압축 및 알고리즘 회로 검증에 대한 일반적인 아이디어를 개발하는데, 이는 Magic State [Quant-PH] 증류에 사용되는 Reed-Muller 코드를 위해 구현합니다.
우리의 성과 분석은 새로운 방법으로 제공되는 전반적인 개선 사항을 강조합니다.
1 소개 디코 언어는 양자 컴퓨터를 확장하는 데 장애물입니다.
그것은 한때 기본적으로 생각되었지만 [1], 나중에 결함에 관개 양자 계산의 기술에 의해 극복 할 수있는 것으로 나타났습니다 [2-4].
이와 관련하여 중심 결과는 임계 값 정리 [5, 6]이며, 이는 기본 양자 게이트 당 디코 언가 특정 값, 즉 오차 임계 값 미만이면 임의로 길고 정확한 양자 계산이 가능하다고 말합니다.
또한, 결함-장애의 운영 및 공간 비용은 절대적인 용어에도 불구하고 스케일링의 의미에서 양성이다.
임계 값 정리가 확립 된 후, 결함 내성 양자 계산에 대한 연구는 (i) 정리가 적용될 수있는 전제 조건을 완화하는 데 중점을 두었다 [7,8], (ii) …의 가치를 향상시킨다.
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기