Summary (English)
The Very Small Array (VSA) has been used to observe cosmic microwave background (CMB) anisotropies between angular multipoles ℓ=160-1400.
The measurements at high ℓare vital for breaking degeneracies in parameter estimation from the CMB power spectrum and other cosmo-logical data.
The VSA comprises a conical horn feeding a section of paraboloidal mirror, with longer baselines allowing observations on smaller angular scales.
Both Cas A and Tau A are suf-iciently similar in structure at 1.4 GHz for this process to work well; tests show that the contamination is negligible for the 1-second sampled data over all 91 baselines during a 16-second hour angles cycle time of 3 OBSERVATIONS, with three overlapping fields observed in each region.
The measurements at high ℓare vital for breaking degeneracies in parameter estimation from the CMB power spectrum and other cosmo-logical data.
The VSA comprises a conical horn feeding a section of paraboloidal mirror, with longer baselines allowing observations on smaller angular scales.
Both Cas A and Tau A are suf-iciently similar in structure at 1.4 GHz for this process to work well; tests show that the contamination is negligible for the 1-second sampled data over all 91 baselines during a 16-second hour angles cycle time of 3 OBSERVATIONS, with three overlapping fields observed in each region.
요약 (Korean)
매우 작은 어레이 (VSA)는 각도 다중 공간 ℓ = 160-1400 사이의 우주 전자 레인지 배경 (CMB) 이방성을 관찰하는 데 사용되었습니다.
높은 측정은 CMB 전력 스펙트럼 및 기타 코스모 로그 데이터로부터 파라미터 추정에서 퇴행성을 깨뜨리는 데 필수적이다.
VSA는 포물선형 거울의 한 부분을 공급하는 원추형 혼을 포함하며, 더 긴 기준선은 더 작은 각도 비늘에서 관찰 할 수 있습니다.
Cas A와 Tau A는이 프로세스가 잘 작동하기 위해 1.4GHz에서 구조에서 유사하게 유사합니다.
테스트에 따르면 오염은 16 초의 시간 각도 사이의 모든 91 기준선에 대한 1 초 샘플링 된 데이터에 대해 무시할 수 있으며 3 개의 관측치 사이클 시간주기 시간이 있으며, 각 영역에서 3 개의 중첩 필드가 관찰됩니다.
높은 측정은 CMB 전력 스펙트럼 및 기타 코스모 로그 데이터로부터 파라미터 추정에서 퇴행성을 깨뜨리는 데 필수적이다.
VSA는 포물선형 거울의 한 부분을 공급하는 원추형 혼을 포함하며, 더 긴 기준선은 더 작은 각도 비늘에서 관찰 할 수 있습니다.
Cas A와 Tau A는이 프로세스가 잘 작동하기 위해 1.4GHz에서 구조에서 유사하게 유사합니다.
테스트에 따르면 오염은 16 초의 시간 각도 사이의 모든 91 기준선에 대한 1 초 샘플링 된 데이터에 대해 무시할 수 있으며 3 개의 관측치 사이클 시간주기 시간이 있으며, 각 영역에서 3 개의 중첩 필드가 관찰됩니다.
기술적 용어 설명 (Technical Terms)
- Cosmic microwave background (CMB): 전자기 방사선은 우주의 원시 단계에서 방출되어 과거와 현재 상태에 대한 정보를 제공합니다. 우주 진화 모델을 이해하는 데 필수적입니다. (Original English Explanation: The electromagnetic radiation emitted from the universe’s primordial phase, providing information about its past and present state. It is essential for understanding cosmic evolutionary models.)
- Angular multipoles ℓ: 다양한 척도에서 CMB 이방성 패턴을 설명하는 양자 역학에서 각 운동량의 수학적 표현. 더 높은 값은 더 작은 규모 관측에 해당합니다. (Original English Explanation: A mathematical representation of angular momentum in quantum mechanics that describes CMB anisotropy patterns on various scales. Higher values correspond to smaller scale observations.)
- Paraboloidal mirror: 망원경 및 기타 천문학기구에 사용되는 광학 장치로, 수신광이 탐지기 어레이에 초점을 맞 춥니 다. 이를 통해 천상의 대상의 위치와 속성을 정확하게 측정 할 수 있습니다. (Original English Explanation: An optical device used in telescopes and other astronomical instruments, which focuses incoming light onto a detector array. This allows for precise measurements of celestial objects’ positions and properties.)
- Cas A/Tau A: 1.4GHz에서 구조의 유사성으로 인한 VSA 관찰을위한 캘리브레이터 역할을하는 무선 소스. 그들은 싱크로트론의 VSA 필드, 자유로운 먼지 배출 및 기타 천문 현상의 오염 수준을 추정하는 데 도움이됩니다. (Original English Explanation: Radio sources that serve as calibrators for VSA observations due to their similarity in structure at 1.4 GHz. They help estimate the level of contamination in the VSA fields from synchrotron, free-free dust emissions, and other astronomical phenomena.)
- Baselines: 하늘 대상의 위치를 정확하게 측정하기 위해 간섭 간 관측에 사용되는 망원경 스테이션 사이의 거리. 더 긴 기준선은 우주 모델에서 매개 변수 추정에 필수적인 작은 각도 스케일 측정을 허용합니다. (Original English Explanation: Distances between telescope stations used for interferometric observations to measure celestial objects’ positions accurately. Longer baselines allow smaller angular scale measurements essential for parameter estimation in cosmological models.)
Excerpt (English Original)
Mon.
Not.
R.
Astron.
Soc.
000, 1–5 (2002) Printed 2 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The CMB power spectrum out to ℓ= 1400 measured by the VSA Keith Grainge1, Pedro Carreira2, Kieran Cleary2, Rod D.
Davies2, Richard J.
Davis2, Clive Dickinson2, Ricardo Genova-Santos3, Carlos M.
Guti´errez3, Yaser A.
Hafez2, Michael P.
Hobson1, Michael E.
Jones1, R¨udiger Kneissl1, Katy Lancaster1, Anthony Lasenby1, J.
P.
Leahy2, Klaus Maisinger1, Guy G.
Pooley1, Rafael Rebolo3,4,2003 Jos´e Alberto Rubi˜no-Martin3,‡, Pedro Sosa Molina3, Carolina ¨Odman1, Ben Rusholme1,⋆, Richard D.E.
Saunders1, Richard Savage1, Paul F.
Scott1, Anˇze Slosar1, Angela C.
Taylor1,Mar David Titterington1, Elizabeth Waldram1, Robert A.
Watson2,†, Althea Wilkinson2 5 1 Astrophysics Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK 2 Jodrell Bank Observatory, Macclesfield, Cheshire, SK11 9DL, UK 3 Instituto de Astrof´isica de Canarias, 38200 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain.
4Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cient´ıficas, Spain ⋆Present address: Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA †Present address: Instituto de Astrof´ısica de Canarias.
‡Present address: Max-Planck Institut f¨ur Astrophysik, Garching, Germany 2 October 2018 ABSTRACT We have observed the cosmic microwave background (CMB) in three regions of sky us- ing the Very Small Array (VSA) in an extended configuration with antennas of beamwidth 2◦ at 34 GHz.
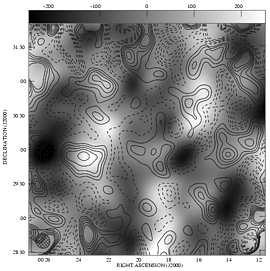
Combined with data from previous VSA observations using a more compact array with larger beamwidth, we measure the power spectrum of the primordial CMB anisotropies between angular multipoles ℓ= 160 – 1400.
Such measurements at high ℓare vital for break- ing degeneracies in parameter estimation from the CMB power spectrum and other cosmo- logical data.
The power spectrum clearly resolves the first three acoustic peaks, shows thearXiv:astro-ph/0212495v2 expected fall off in power at high ℓand starts to constrain the position and height of a fourth peak.
Key words: cosmology:observations – cosmic microwave background 1 INTRODUCTION (hereafter Paper I) is an…
Not.
R.
Astron.
Soc.
000, 1–5 (2002) Printed 2 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The CMB power spectrum out to ℓ= 1400 measured by the VSA Keith Grainge1, Pedro Carreira2, Kieran Cleary2, Rod D.
Davies2, Richard J.
Davis2, Clive Dickinson2, Ricardo Genova-Santos3, Carlos M.
Guti´errez3, Yaser A.
Hafez2, Michael P.
Hobson1, Michael E.
Jones1, R¨udiger Kneissl1, Katy Lancaster1, Anthony Lasenby1, J.
P.
Leahy2, Klaus Maisinger1, Guy G.
Pooley1, Rafael Rebolo3,4,2003 Jos´e Alberto Rubi˜no-Martin3,‡, Pedro Sosa Molina3, Carolina ¨Odman1, Ben Rusholme1,⋆, Richard D.E.
Saunders1, Richard Savage1, Paul F.
Scott1, Anˇze Slosar1, Angela C.
Taylor1,Mar David Titterington1, Elizabeth Waldram1, Robert A.
Watson2,†, Althea Wilkinson2 5 1 Astrophysics Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK 2 Jodrell Bank Observatory, Macclesfield, Cheshire, SK11 9DL, UK 3 Instituto de Astrof´isica de Canarias, 38200 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain.
4Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cient´ıficas, Spain ⋆Present address: Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA †Present address: Instituto de Astrof´ısica de Canarias.
‡Present address: Max-Planck Institut f¨ur Astrophysik, Garching, Germany 2 October 2018 ABSTRACT We have observed the cosmic microwave background (CMB) in three regions of sky us- ing the Very Small Array (VSA) in an extended configuration with antennas of beamwidth 2◦ at 34 GHz.
Combined with data from previous VSA observations using a more compact array with larger beamwidth, we measure the power spectrum of the primordial CMB anisotropies between angular multipoles ℓ= 160 – 1400.
Such measurements at high ℓare vital for break- ing degeneracies in parameter estimation from the CMB power spectrum and other cosmo- logical data.
The power spectrum clearly resolves the first three acoustic peaks, shows thearXiv:astro-ph/0212495v2 expected fall off in power at high ℓand starts to constrain the position and height of a fourth peak.
Key words: cosmology:observations – cosmic microwave background 1 INTRODUCTION (hereafter Paper I) is an…
발췌문 (Korean Translation)
몬.
아니다.
R.
Astron.
사회 000, 1–5 (2002) 2018 년 10 월 2 일 인쇄 (MN 라텍스 스타일 파일 v2.2) CMB 전력 스펙트럼은 VSA Keith Grainge1, Pedro Carreira2, Kieran Cleary2, Rod D.
Davies2, Richard J.
Davis2, Clive Dickinson2, Ricardo Genova genova-soSTI3, Carlos-SONTO3 Yaser A.
Hafez2, Michael P.
Hobson1, Michael E.
Jones1, R¨udiger Kneissl1, Katy Lancaster1, Anthony Lasenby1, J.
P.
Leahy2, Klaus Maisinger1, Guy G.
Pooley1, Rafael Rebolo3,4,2003 Jos´e Alberto rubi ~ rafael rebolo3,4,2003 Jos’e Alberto rubi ~ rafael ¨odman1, Ben Rusholme1, ⋆, Richard D.E.
Saunders1, Richard Savage1, Paul F.
Scott1, Anˇze Slosar1, Angela C.
Taylor1, Mar David Titterington1, Elizabeth Waldram1, Robert A.
Watson2, †, Althea Wilkinson2 5 1 천체 물리 그룹, Camendish Laboratory, Cambride University, UK 2 Jodrell Bank Observatory, MacCles eld, charhire, charse, sk eld.
Instituto de Astrof´isica de Canarias, 38200 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain.
4Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cient´ıfas, 스페인 주소 : Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA † 현재 주소 : Instituto de Astrof´ısica de Canarias.
‡ 현재 주소 : 2018 년 10 월 2 일 독일 Garching, Garching, Max-Planck Institut F¨ur Astrophysik, 2018 년 10 월 2 일 초록 우리는 34GHz에서 빔 2 ℃의 안테나와 함께 확장 된 조정에서 매우 작은 배열 (VSA)을 사용하는 하늘의 세 지역에서 우주 전자 레인지 배경 (CMB)을 관찰했습니다.
더 큰 Beamwidth를 갖는보다 컴팩트 한 배열을 사용한 이전 VSA 관측의 데이터와 결합하여, 우리는 각도 다중 공간 사이의 원시 CMB 이방성의 전력 스펙트럼을 측정합니다.
전력 스펙트럼은 첫 번째 3 개의 음향 피크를 명확하게 해결하고, TheArxiv : Astro-PH/0212495V2는 높은 곳에서 전력이 떨어지고 네 번째 피크의 위치와 높이를 제한하기 시작합니다.
키워드 : 우주론 : 관찰 – 우주 전자 레인지 배경 1 소개 (이하 논문 i)는 …
아니다.
R.
Astron.
사회 000, 1–5 (2002) 2018 년 10 월 2 일 인쇄 (MN 라텍스 스타일 파일 v2.2) CMB 전력 스펙트럼은 VSA Keith Grainge1, Pedro Carreira2, Kieran Cleary2, Rod D.
Davies2, Richard J.
Davis2, Clive Dickinson2, Ricardo Genova genova-soSTI3, Carlos-SONTO3 Yaser A.
Hafez2, Michael P.
Hobson1, Michael E.
Jones1, R¨udiger Kneissl1, Katy Lancaster1, Anthony Lasenby1, J.
P.
Leahy2, Klaus Maisinger1, Guy G.
Pooley1, Rafael Rebolo3,4,2003 Jos´e Alberto rubi ~ rafael rebolo3,4,2003 Jos’e Alberto rubi ~ rafael ¨odman1, Ben Rusholme1, ⋆, Richard D.E.
Saunders1, Richard Savage1, Paul F.
Scott1, Anˇze Slosar1, Angela C.
Taylor1, Mar David Titterington1, Elizabeth Waldram1, Robert A.
Watson2, †, Althea Wilkinson2 5 1 천체 물리 그룹, Camendish Laboratory, Cambride University, UK 2 Jodrell Bank Observatory, MacCles eld, charhire, charse, sk eld.
Instituto de Astrof´isica de Canarias, 38200 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain.
4Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cient´ıfas, 스페인 주소 : Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA † 현재 주소 : Instituto de Astrof´ısica de Canarias.
‡ 현재 주소 : 2018 년 10 월 2 일 독일 Garching, Garching, Max-Planck Institut F¨ur Astrophysik, 2018 년 10 월 2 일 초록 우리는 34GHz에서 빔 2 ℃의 안테나와 함께 확장 된 조정에서 매우 작은 배열 (VSA)을 사용하는 하늘의 세 지역에서 우주 전자 레인지 배경 (CMB)을 관찰했습니다.
더 큰 Beamwidth를 갖는보다 컴팩트 한 배열을 사용한 이전 VSA 관측의 데이터와 결합하여, 우리는 각도 다중 공간 사이의 원시 CMB 이방성의 전력 스펙트럼을 측정합니다.
전력 스펙트럼은 첫 번째 3 개의 음향 피크를 명확하게 해결하고, TheArxiv : Astro-PH/0212495V2는 높은 곳에서 전력이 떨어지고 네 번째 피크의 위치와 높이를 제한하기 시작합니다.
키워드 : 우주론 : 관찰 – 우주 전자 레인지 배경 1 소개 (이하 논문 i)는 …
출처: arXiv
답글 남기기